Processing and utilizing method for extracting carbon and iron from blast furnace metallurgy dust and sludge
A technology for metallurgical sludge and blast furnace, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, wet separation, centrifuges with rotating drums, etc. Enhance selectivity, facilitate floc dispersion, and reduce the dosage of chemicals
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
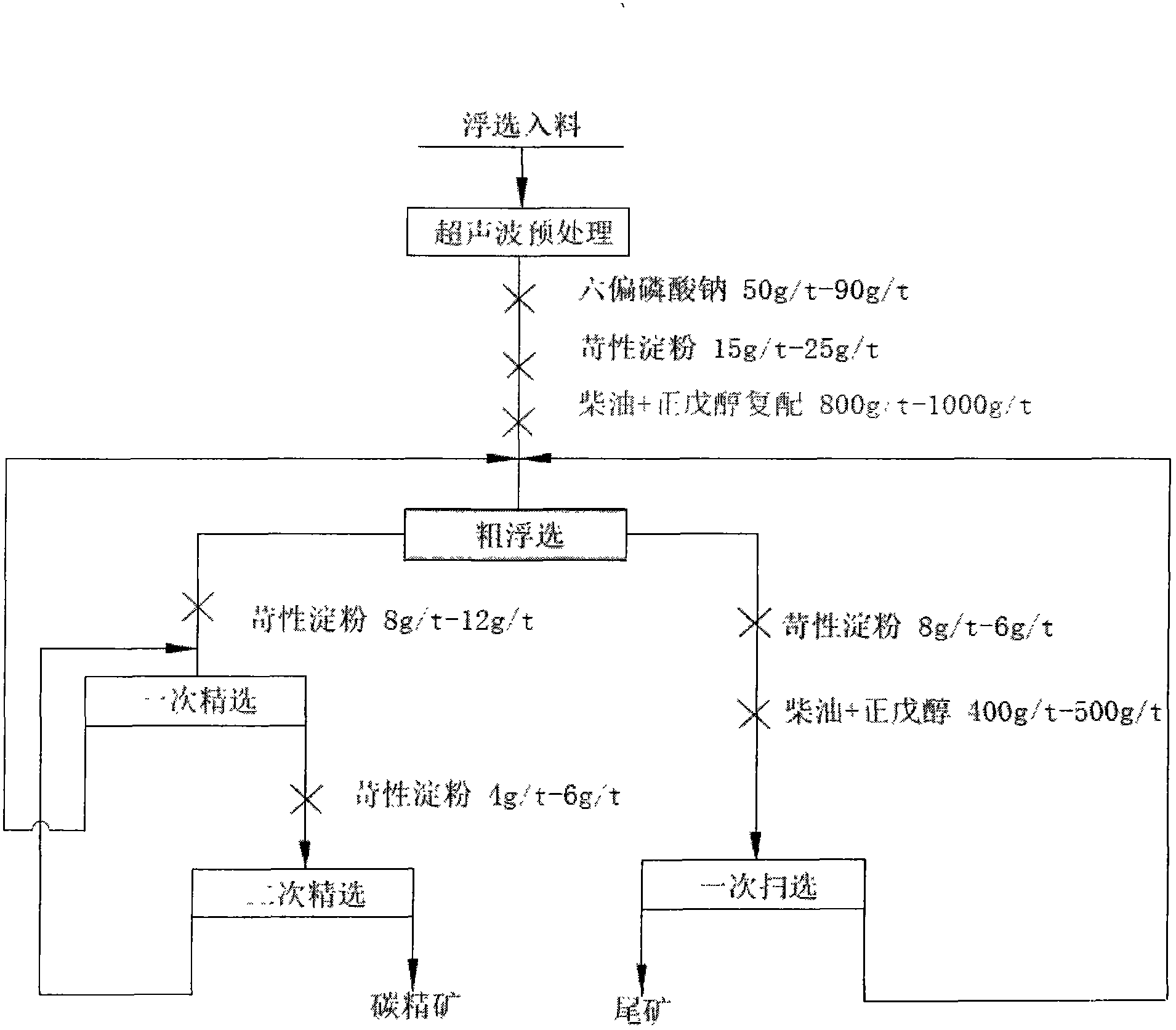
[0018] Main raw materials: metallurgical dust; caustic starch; diesel oil; n-amyl alcohol; sodium hexametaphosphate
[0019] The total iron grade of the metallurgical dust sludge used is 25.00%, SiO 2 14.00%, fixed carbon content is 26.45%, SO 3 is 4.21%, CaO is 5.80%, ZnO is 5.74%, and Cl is 0.78%. Iron minerals mainly exist in the form of hematite, magnetite and elemental iron, and metallurgical dust contains a large amount of polyacrylamide.
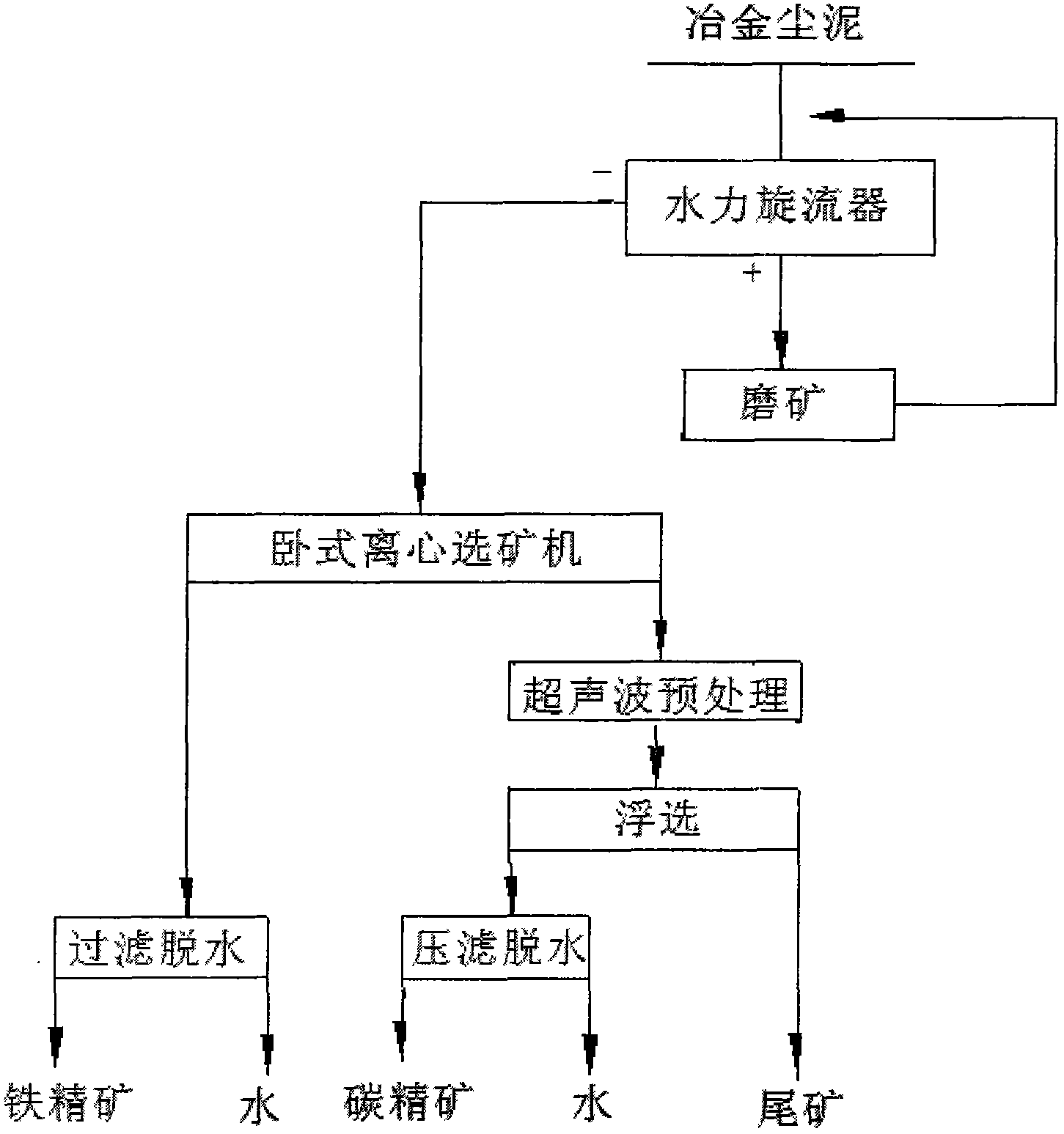
[0020] The metallurgical dust is coarsely and subdivided by the hydrocyclone, and the classification particle size is 0.105mm. The coarse-grained products are ground by a rod mill and then returned to the classification operation. The fineness of the classified products is -200 mesh, accounting for 95%.
[0021] The graded fine-grained products go through a horizontal centrifugal concentrator for one roughing and one beneficiation, and the sorted concentrate products are filtered and dehydrated to obtain iron concentrates for smeltin...
Embodiment 2
[0025] Main raw materials: metallurgical dust; caustic starch; diesel oil; n-amyl alcohol; sodium hexametaphosphate
[0026] The total iron grade of metallurgical dust sludge used is 23.65%, SiO 2 13.59%, fixed carbon content is 27.55%, SO 3 is 3.89%, CaO is 5.62%, ZnO is 4.67%, and Cl is 0.52%. Iron minerals mainly exist in the form of hematite and magnetite, and metallurgical dust contains a large amount of polyacrylamide.
[0027] The metallurgical dust is coarsely and subdivided by the hydrocyclone, and the classification granularity is 0.105mm. The coarse-grained products are ground by a rod mill and then returned to the classification operation. The fineness of the classified products is -200 mesh, accounting for 98%.
[0028] The graded fine-grained products go through a horizontal centrifugal concentrator for one roughing and one beneficiation, and the sorted concentrate products are filtered and dehydrated to obtain iron concentrates for smelting. The operating cond...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com