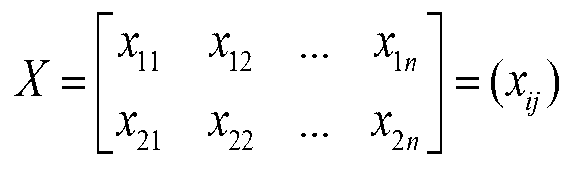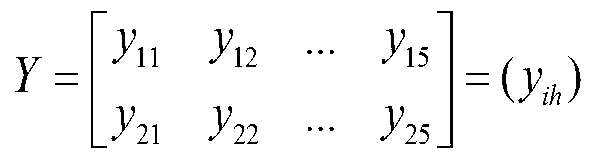Microbial aggregate quantitative microscopic imaging testing and evaluating method
A technology of microbial aggregates and evaluation methods, applied in the field of comprehensive evaluation of the performance of microbial aggregates, can solve the problems of single-factor evaluation of residence and the lack of accurate quantitative comprehensive evaluation methods for microbial aggregates.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Example 1: Research on the performance of microbial aggregates in aquaculture wastewater
[0049] 1. Preparation of microbial aggregates to be tested: Prepare a 1L aerobic batch reactor, inoculate 25mL of sludge, add 1.90g of sucrose, NH 4Cl is 0.0764g simulated aquaculture wastewater to a volume of 755mL. Put the aeration head into the above-mentioned reactor to carry out the aeration experiment, and take a sample at 3 hours after the experiment, as the microbial aggregate to be tested.
[0050] 2. Performance test of microbial aggregates to be tested
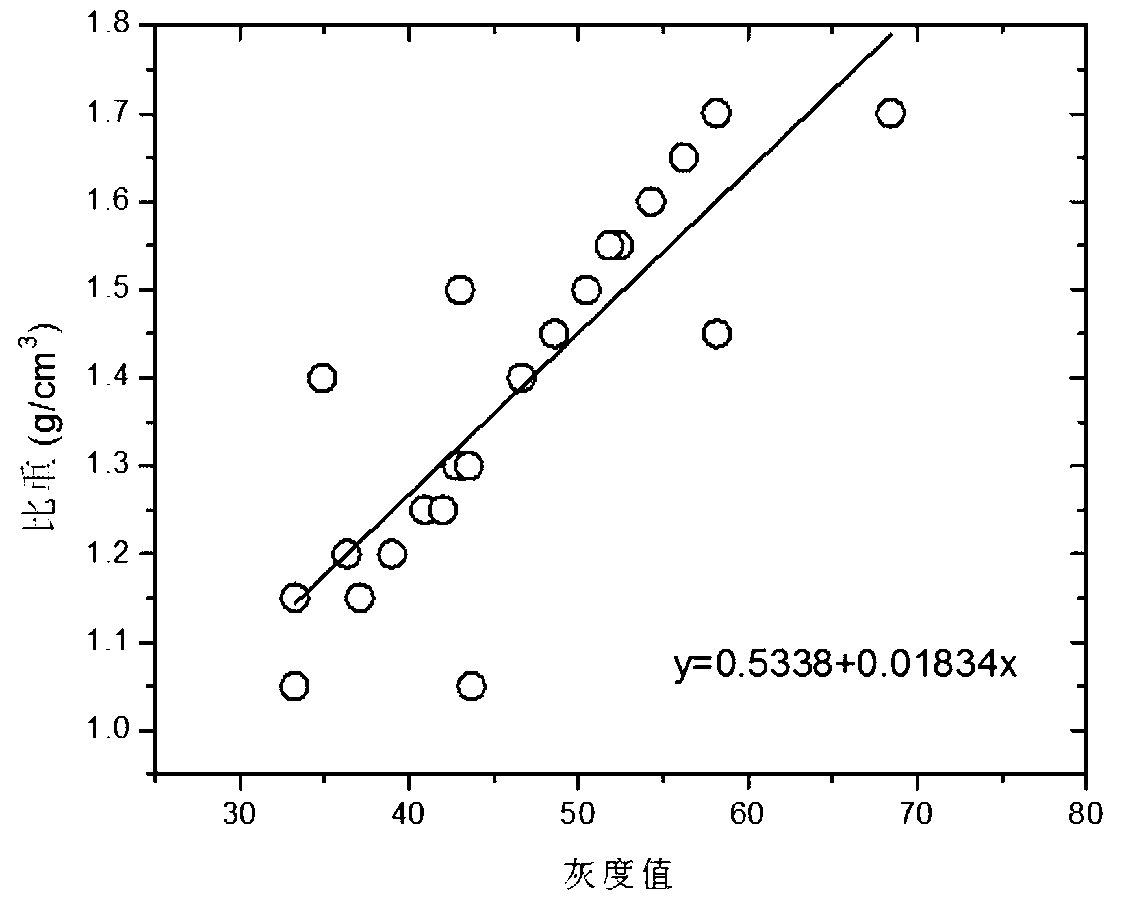
[0051] a. Calibrate the standard relationship curve between the gray value and the specific gravity value of the microbial aggregate sample to be tested. The specific steps are as follows:
[0052] a1. Taking 1.0°Bx as the sugar content gradient, 17 groups of sucrose aqueous solutions with a sugar content ranging from 5.0°Bx to 21.0°Bx were taken, marked as sucrose aqueous solution m, 1≤m≤17;
[0053] a2, take the mi...
Embodiment 2
[0094] Example 2: Test aeration time on performance impact of microbial aggregates in aquaculture wastewater
[0095] 1. Preparation of microbial aggregates to be tested: Prepare a 1L aerobic batch reactor, inoculate 25mL of sludge, add 1.90g of sucrose, NH 4 Cl is 0.0764g simulated aquaculture wastewater to a volume of 755mL. Put the aeration head into the above-mentioned reactor to carry out the aeration experiment, and take samples at the 3h, 6h, 9h, 12h, 24h, 48h, 72h and 96h of the experiment, as 8 groups of microorganisms to be tested body.
[0096] 2. Analyze the sample taken during 3 hours, repeat step 2 a and b of Example 1 to obtain the area and specific gravity values of n microorganism aggregates to be tested, calculate the average value of the area and specific gravity respectively, and record it as x 11 and x 21 . According to the same method, calculate the average area and average specific gravity of the microbial aggregates to be tested in the samples of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com