PDMS (polydimethylsiloxane)-based functional polymer patterning method
A functional polymer and patterning technology, which is applied in the photoplate making process, optics, and optomechanical equipment of the patterned surface, can solve the problems of high price, poor mechanical toughness of hard templates, cumbersome acquisition steps, etc., and achieve flatness Low, less disturbance, lower transfer cost effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
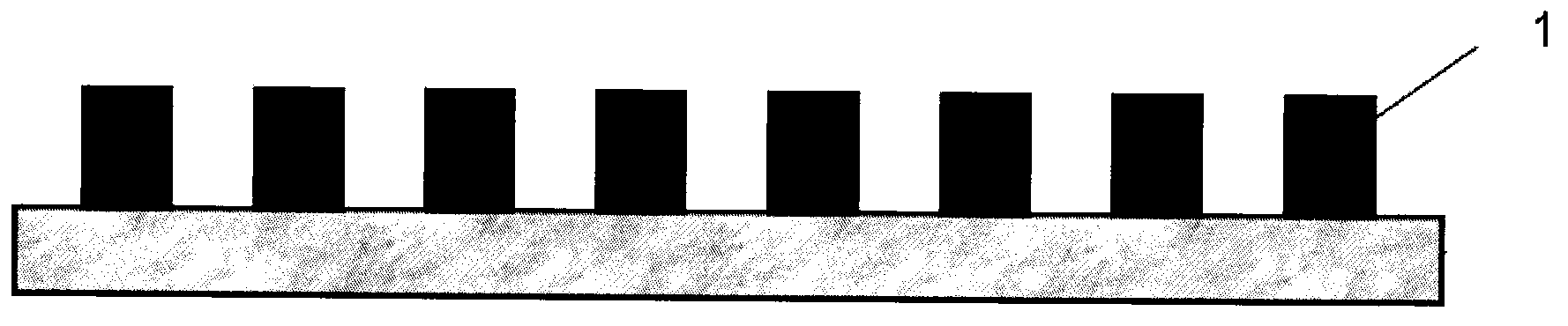
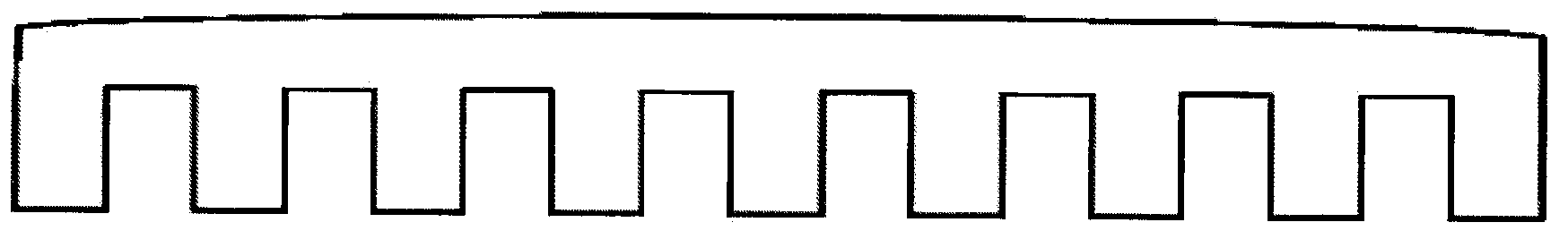
[0020] The PDMS-based functional polymer patterning method is different in that it includes the following steps: step ①, use photolithography to process the required micro-nano structure pattern on the surface of the hard substrate A coated with photoresist, and obtain the band Rigid substrate A with patterned photoresist as original substrate for structure definition during imprint transfer. In step ②, spin-coat or drop-coat the organic material PDMS on the surface of the hard substrate A with the patterned photoresist, and place it in a vacuum drying oven. Specifically, it can be dried at 65° C. for 1 hour. In step ③, after fully cross-linking, the PDMS soft template is peeled off from the above hard substrate A, ready to use. In step ④, select the corresponding hard substrate B to carry the final patterned functional polymer, spin-coat the functional polymer film on the surface of the hard substrate B, and tear off the PDMS soft template from the hard substrate A The stru...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com