Vaccine for prevention and/or treatment of respiratory syncytial virus infection
A technology of syncytial virus and respiratory tract, applied in the field of co-immune vaccines, can solve the problems of limited improvement and low level of neutralizing antibodies, achieve low cost, inhibit inflammation-related reactions, and enhance humoral immune responses
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Embodiment 1, the preparation of DNA vaccine
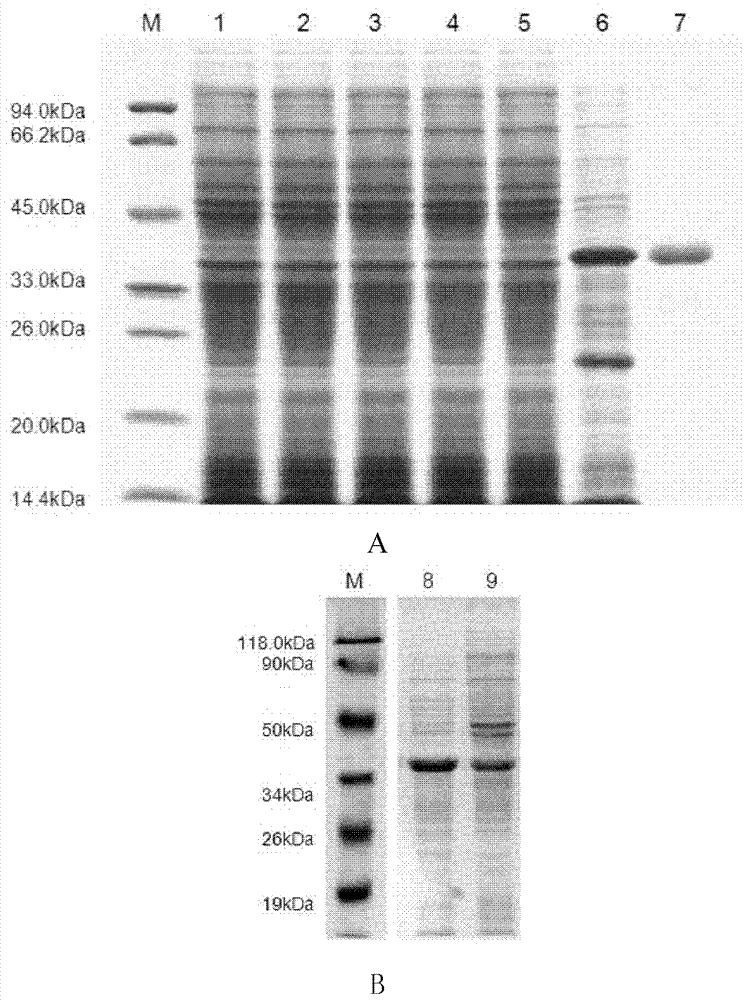
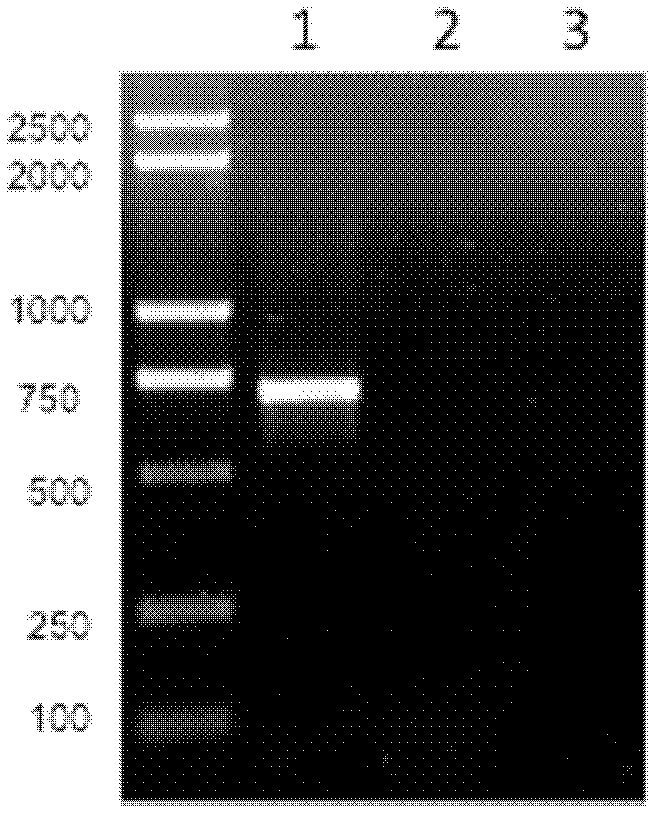
[0044] Respiratory syncytial virus surface glycoprotein G (referred to as G protein) is obtained through the method of whole gene synthesis after codon optimization of eukaryotic cells. The DNA fragment (as shown in sequence 1 in the sequence listing, wherein the 7th-708th is the coding sequence of G protein, the protein shown in sequence 2 in the coding sequence listing) containing the gene encoding the surface glycoprotein G of respiratory syncytial virus The endonucleases EcoR I and Xba I were digested, and connected to the eukaryotic expression vector proVAX (Xiaogang Du, Guoxing Zheng, Huali Jin, Youmin Kang, Junpeng Wang, Chong Xiao, Shuo Zhang, Mingyu Liu, Lin Zhao, Aoshuang Chen and Bin Wang. The adjuvant effects of co-stimulatory molecules on cellular and memory responses to HBsAg DNA vaccination. J. Gene Medicine, 2007; 9: 136-146.), forming recombinant plasmids. After the obtained recombinant plasmid was digeste...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Embodiment 2, the preparation of subunit vaccine
[0049] Respiratory syncytial virus surface glycoprotein G was obtained by total gene synthesis after codon optimization in Escherichia coli cells. The DNA fragment (as shown in sequence 3 in the sequence listing, wherein the 7-708th is the coding sequence of G protein, the protein shown in sequence 2 in the coding sequence listing) containing the gene encoding the surface glycoprotein G of respiratory syncytial virus It was digested with endonucleases EcoR I and Xho I, and connected to the prokaryotic expression vector pET-28a(+) that had been cut with the same restriction enzymes to form a recombinant plasmid. After the obtained recombinant plasmid was digested with restriction endonucleases EcoR I and Xho I, the target fragment with a size of about 708 bp and a vector fragment with a size of about 5400 bp were obtained by agarose gel electrophoresis, which were consistent with the expected results. It was further confi...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Example 3, Detection of Antibody Levels After DNA Vaccine and / or Subunit Vaccine Immunization Model Animals
[0055] 1. Experiments on DNA vaccine and / or subunit vaccine immunization model animals
[0056] Model animals: 6-8 week-old female BALB / c mice, purchased from Beijing Huafukang Biotechnology Co., Ltd., clean grade, divided into 9 groups, 5 mice in each group.
[0057] Vaccines and controls for immunization: PBS, formalin inactivated vaccine FI-RSV (10 7 TCID 50 RSV virus (US ATCC, catalog no. VR-26 TM , after reaction with formaldehyde for 72 hours at 37°C, purified by high-speed centrifugation at 50,000 g for 1 hour), DNA vaccine proVAX / G, subunit vaccine His-G, DNA vaccine empty vector control proVAX and subunit vaccine His-G, etc. Mass mixture, equal mass mixture of DNA vaccine proVAX / G and ovalbumin OVA (product of Sigma Company) of irrelevant protein, equal mass mixture of inventive technology group (common immunization) DNA vaccine proVAX / G and subunit ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com