Method for quickly coating polysaccharide polymer on metal material surface
A polysaccharide polymer and metal material technology, applied in electrolytic organic material coating, etc., can solve the problems of easy peeling off, unfavorable application modification, etc., and achieve the effect of uniform coating, shortening coating time and strong adhesion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
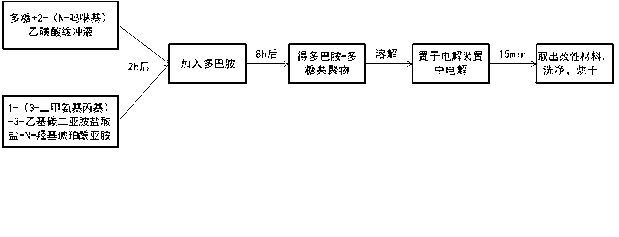
[0023] Such as figure 1 As shown, a method for quickly coating polysaccharide polymers on the surface of metal materials, the water-soluble dopamine derivatives modified polysaccharide polymers are used to electrochemically modify the metal surface in an electrolytic cell. The specific process is:
[0024] 1) Weigh 100mg of sodium hyaluronate at room temperature and dissolve in 10ml of 2-(N-morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid buffer solution with pH=5.5;
[0025] 2) Then add 200mg 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride and 100mg N-hydroxysuccinimide, mix the three and stir at room temperature for 1~2h;
[0026] 3) Add 100mg of dopamine after 1~2h, water is the solvent, dopamine is the modification medium, the concentration is 10mg / ml, and the reaction time is 7h;
[0027] 4) The reaction product was extracted with acetone, and the dopamine-hyaluronic acid polymer was freeze-dried;
[0028] 5) Dissolve an appropriate amount of dopamine-hyaluronic acid polymer ...
Embodiment 2
[0031] 1) Weigh 200mg of sodium hyaluronate at room temperature and dissolve in 20ml of 2-(N-morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid buffer solution with pH=5.5;
[0032] 2) Then add 400mg 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride and 300mg N-hydroxysuccinimide, mix the three and stir at room temperature for 1~2h;
[0033] 3) Add 300mg of dopamine after 1~2h, water is the solvent, dopamine is the modification medium, the concentration is 15mg / ml, and the reaction time is 8h;
[0034] 4) The reaction product was extracted with acetone, and the dopamine-hyaluronic acid polymer was freeze-dried;
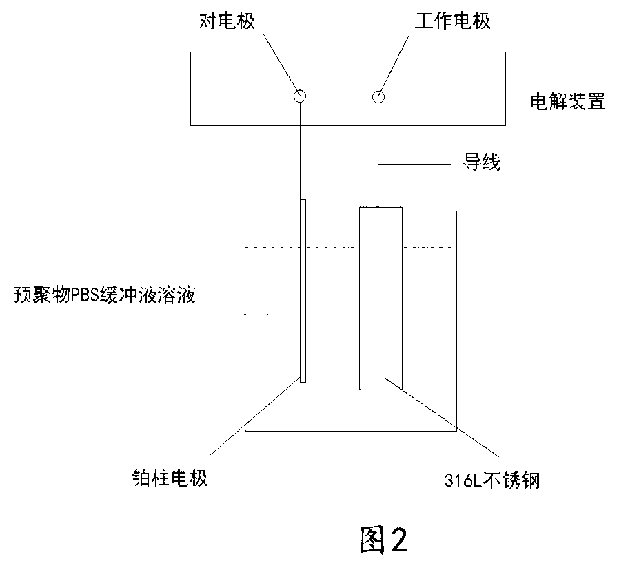
[0035] 5) Dissolve an appropriate amount of dopamine-hyaluronic acid polymer in 40ml of PBS buffer solution with pH=8.0, adopt a three-electrode system, use the 316L stainless steel to be modified as the working electrode, and the platinum column electrode as the counter electrode. The mercury electrode is the reference electrode, and the electrochemical reaction occurs at the...
Embodiment 3
[0038] 1) Weigh 300mg of sodium hyaluronate at room temperature and dissolve in 30ml of 2-(N-morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid buffer solution with pH=5.5;
[0039] 2) Then add 500mg 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride and 400mg N-hydroxysuccinimide, mix the three and stir at room temperature for 1~2h;
[0040] 3) Add 150mg of dopamine after 1~2h, water is the solvent, dopamine is the modification medium, the concentration is 5mg / ml, and the reaction time is 8h. ;
[0041] 4) The reaction product was extracted with acetone, and the dopamine-hyaluronic acid polymer was freeze-dried;
[0042] 5) Dissolve an appropriate amount of dopamine-hyaluronic acid polymer in 50ml of PBS buffer solution with pH = 8.0, adopt a three-electrode system, use the 316L stainless steel to be modified as the working electrode, and the platinum column electrode as the counter electrode. The mercury electrode is the reference electrode, and the electrochemical reaction occurs at...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com