Method for separating and purifying astaxanthin from antarctic krill shells
A technology for separation and purification of Antarctic krill, applied in chemical instruments and methods, organic chemistry, organic dyes, etc., can solve problems such as high production costs, protein waste, and industrial production restrictions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
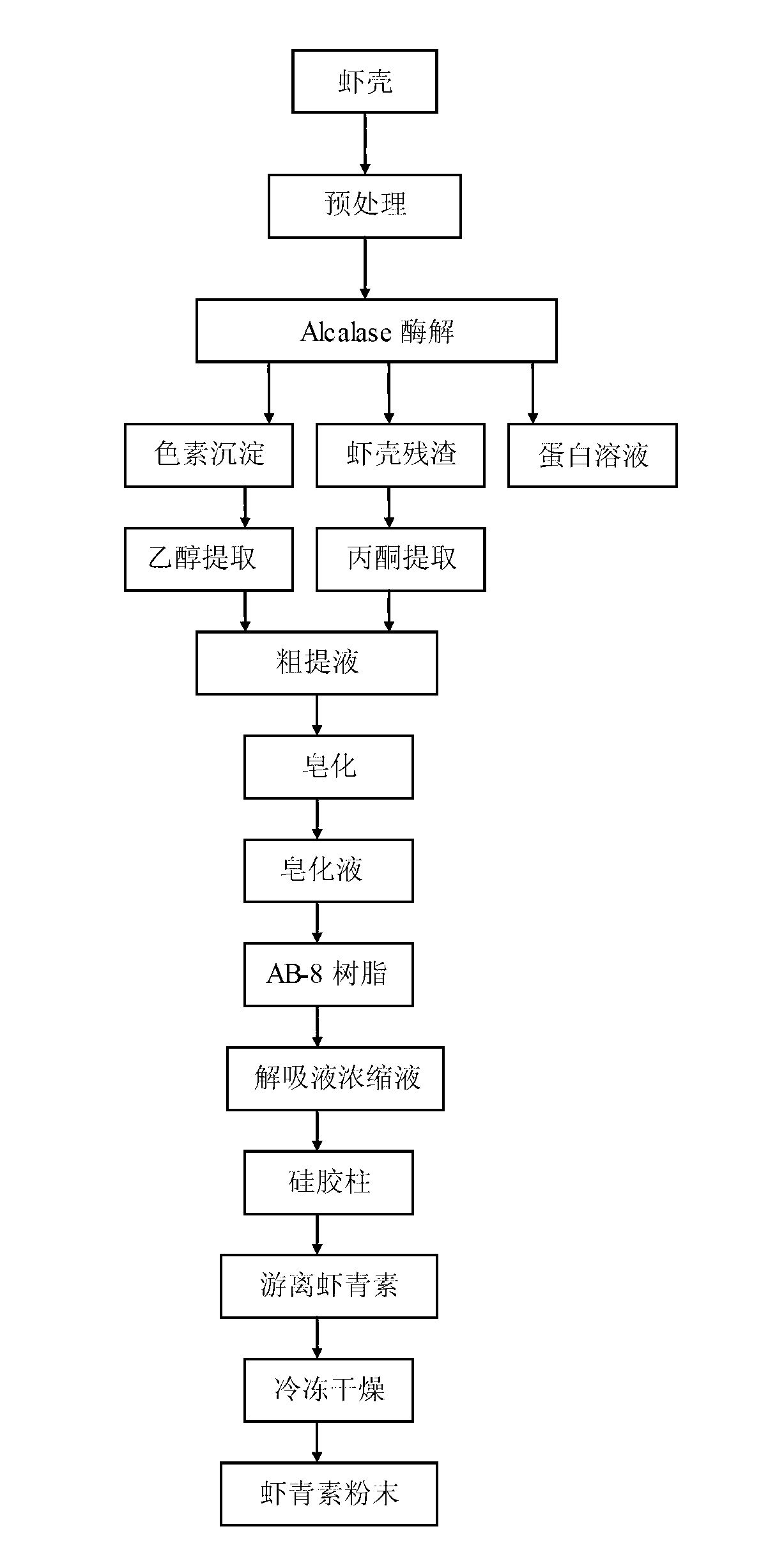
[0023] Take 100g of Antarctic krill shells, the moisture content is about 78.2%. Adjust the pH to 8.2, add Alcalase enzyme at an enzyme-to-substrate ratio of 3000U / g, and shake in a dark water bath at 55°C for 2.5h; the enzymolysis solution is filtered through gauze to obtain 74.2g of shrimp shell residue and filtrate, and the filtrate is centrifuged (4°C, 6000rap / min, 20min), to obtain 16.5g of enzymatic hydrolysis supernatant and pigment precipitate. Add acetone to the shrimp shell residue at a material-to-liquid ratio (w:v) of 1:5, shake in a water bath at 40°C in the dark for 3.5 hours, and filter to obtain the extract; Add ethanol, shake in a dark water bath at 40°C for 2.0 h, and filter with suction to obtain an extract. Combine the extracts of the shrimp shell residue and the pigment precipitation, concentrate at 40°C to remove the solvent, and obtain 0.70 g of crude pigment oil. Then dilute the crude pigment oil with absolute ethanol to a concentration of 0.1 g / mL, ...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Take 100g of Antarctic krill shells with a moisture content of 75.3%. Adjust the pH to 8.5, add Alcalase enzyme at an enzyme-to-substrate ratio of 3000U / g, and shake in a dark water bath at 55°C for 3.0h; the enzymolysis solution is filtered through gauze to obtain 72.6g of shrimp shell residue and filtrate, and the filtrate is centrifuged (4°C, 7000rap / min, 20min), to obtain 20.8g of enzymatic hydrolysis supernatant and pigment precipitate. Add acetone to the shrimp shell residue at a material-to-liquid ratio (w:v) of 1:4, shake in a water bath at 40°C in the dark for 4.0 hours, and filter to obtain the extract; Add ethanol, shake in a dark water bath at 40°C for 1.5 hours, and filter with suction to obtain the extract. Combine the extracts of shrimp shell residues and pigmentation, and concentrate at 40°C to remove the solvent to obtain 0.75 g of crude pigment oil. Then dilute the crude pigment oil with absolute ethanol to a concentration of 0.1 g / mL, add 1 / 5 volum...
Embodiment 3
[0029] Take 100g of Antarctic krill shells with a moisture content of 79%. Adjust the pH to 8.0-8.5, add Alcalase enzyme at an enzyme-to-substrate ratio of 3000U / g, and shake in a dark water bath at 55°C for 3.5h; the enzymolysis solution is filtered through gauze to obtain 70.5g of shrimp shell residue and filtrate, and the filtrate is centrifuged (4°C, 8000rap / min, 20min), to obtain 18.2g of enzymatic hydrolysis supernatant and pigment precipitate. Add acetone to the shrimp shell residue with a material-liquid ratio (w:v) of 1:6, shake in a water bath at 40°C for 3.0 hours, and filter to obtain the extract; Add ethanol, shake in a dark water bath at 40°C for 2.5 hours, and filter with suction to obtain the extract. Combine the extracts of the shrimp shell residue and the pigment precipitation, concentrate at 40°C to remove the solvent, and obtain 0.72 g of crude pigment oil. Then dilute the crude pigment oil with absolute ethanol to a concentration of 0.1 g / mL, add 1 / 5 vol...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com