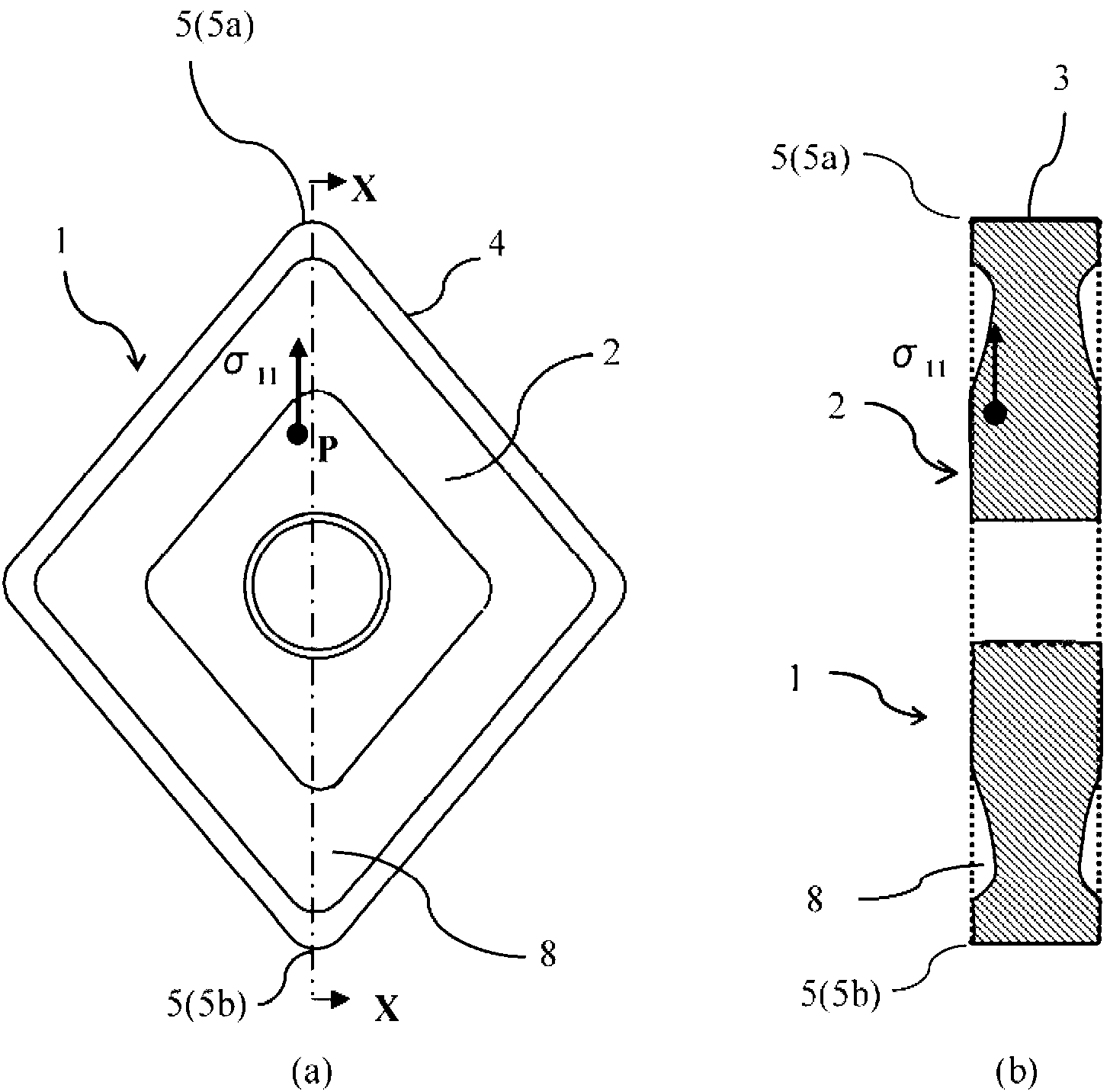
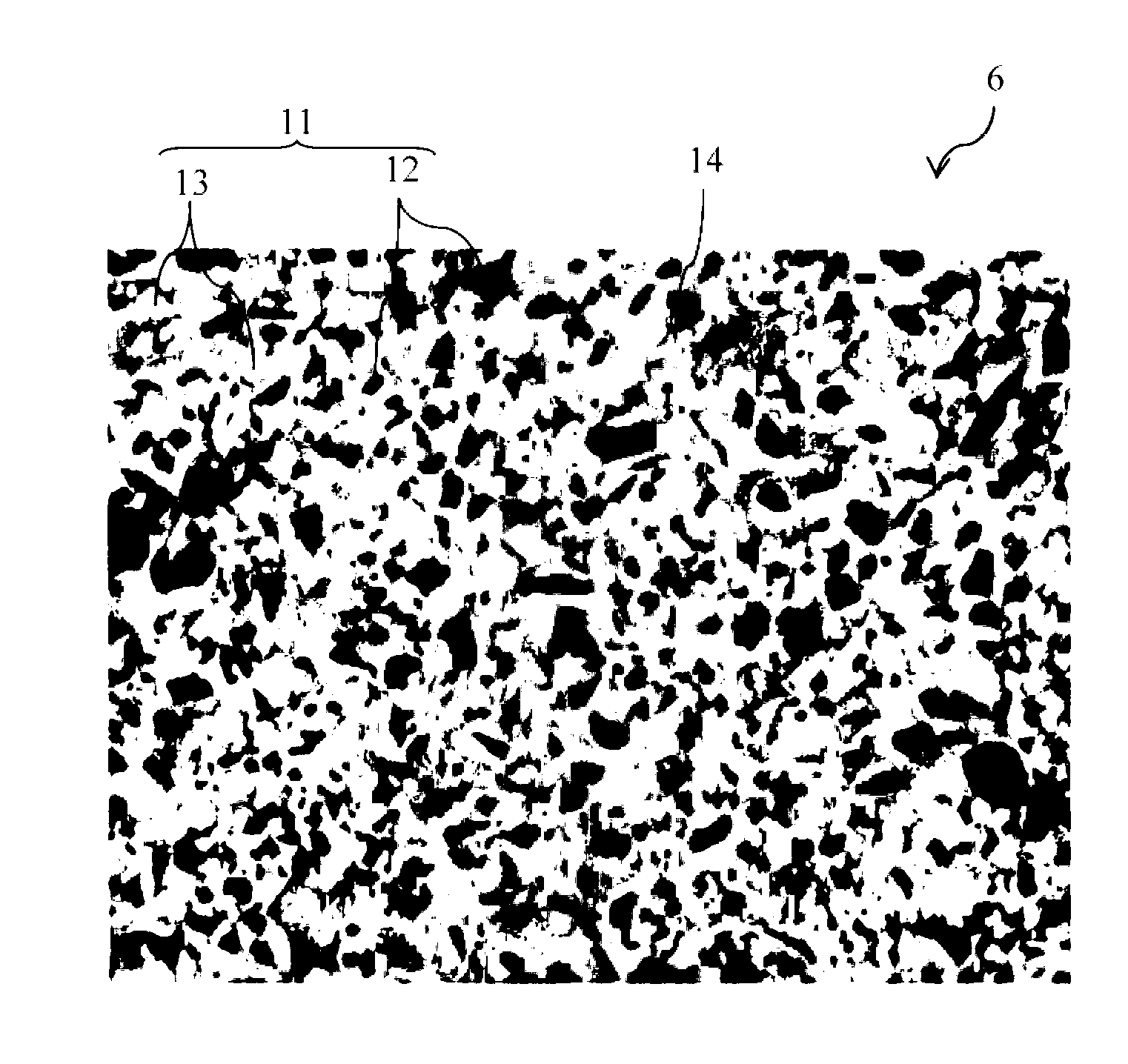
Cutting tool
A cutting tool, hard phase technology, used in the manufacture of tools, workpieces, turning equipment, etc., can solve problems such as limitations, different sizes, and difficulty in obtaining toughness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
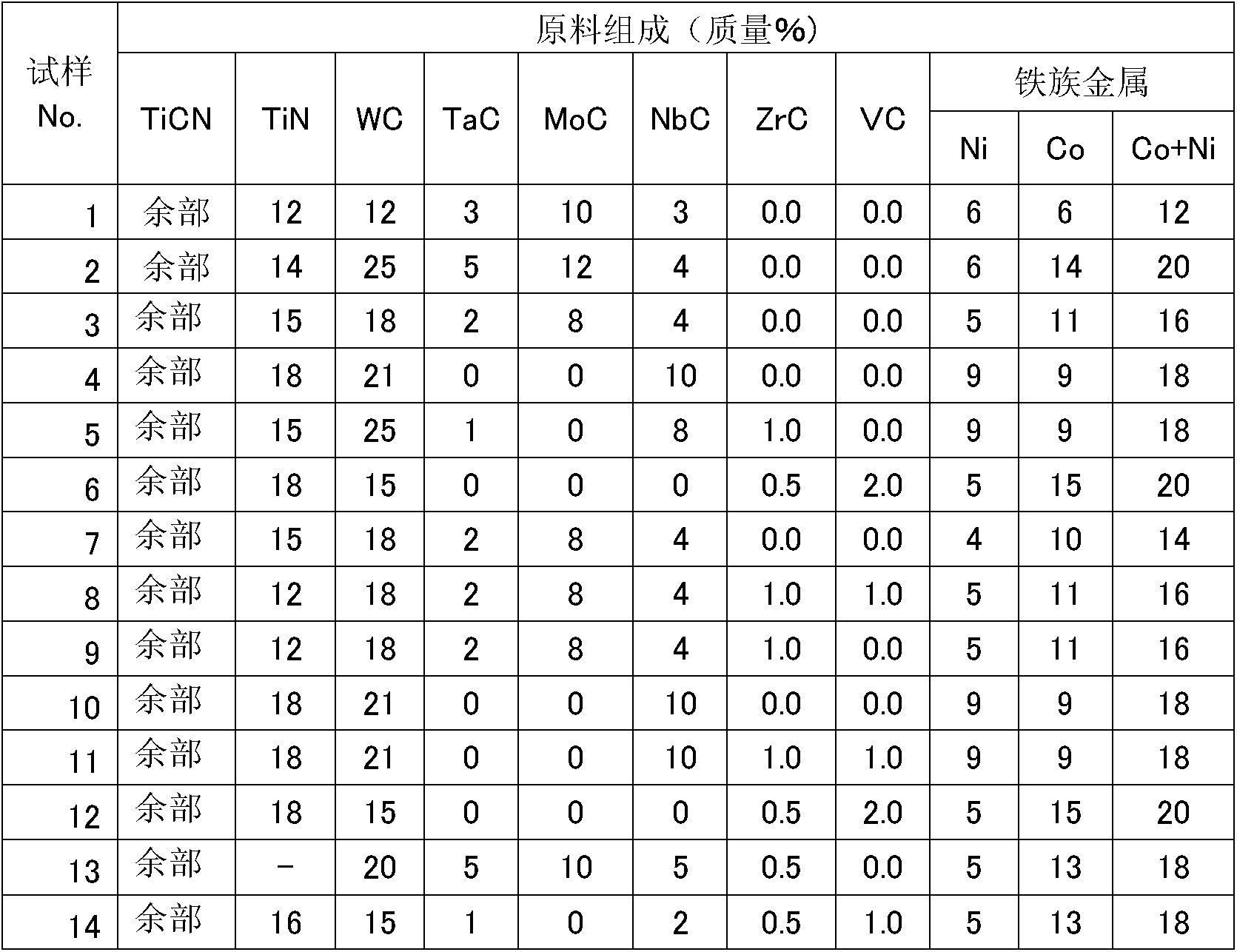
[0066] In the measurement of laser particle size (Japanese: Microtrac) method, the average particle diameter (d 50 value) TiCN powder with an average particle diameter of 1.1 μm, WC powder with an average particle diameter of 1.1 μm, TiN powder with an average particle diameter of 1.5 μm, VC powder with an average particle diameter of 1.0 μm, TaC powder with an average particle diameter of 2 μm, and MoC powder with an average particle diameter of 1.5 μm powder, NbC powder with an average particle diameter of 1.5 μm, ZrC powder with an average particle diameter of 1.8 μm, Ni powder with an average particle diameter of 2.4 μm, Co powder with an average particle diameter of 1.9 μm, and MnCO powder with an average particle diameter of 5.0 μm 3 The powders were adjusted in the ratio shown in Table 1 to form a mixed powder, which was wet-mixed by adding isopropyl alcohol (IPA) using a stainless steel ball mill and superhard balls, and mixed by adding 3% by mass of paraffin wax. Then...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| compressive stress | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com