Low temperature sintered Ni metal fiber composite ceramic substrate
A technology of composite ceramics and metal fibers, applied in the field of metal fiber composite ceramic substrates, can solve the problems of low thermal conductivity and large thermal expansion coefficient of metal substrates, and achieve the effects of reducing sintering temperature, reducing preparation cost and improving thermal conductivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
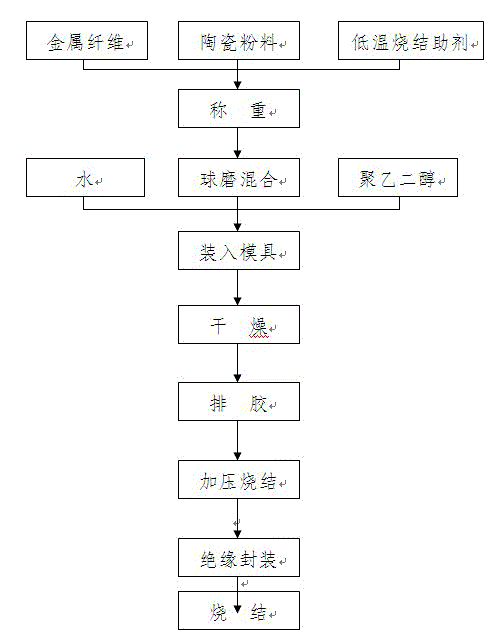
[0032] see figure 2 flow chart. Will Al 2 o 3 400g of powder, 200g of Ni metal fiber with a diameter of 1μm and an aspect ratio of 30~35, 370g of Al-Mg-Si glass additive, 30g of cerium oxide rare earth additive, and ball milling for 12 hours. After adding 50 g of water and 50 g of polyethylene glycol to the resulting mixture, mix it, let it stand for 15 minutes, and place it in a graphite mould. Send the graphite mold into the hot-press sintering equipment, pressurize in stages, dry at 120°C for 0.5 hours, raise the temperature to 600°C for heating and debinding, and keep for 0.5 hours. At a temperature of 1200°C and a pressure of 100 MPa, pressurize for 2 hours to obtain Ni / Al with uniform distribution of Ni metal fibers 2 o 3 Composite ceramic material matrix. The low-melting point insulating glass powder is made into slurry, and a thin layer of insulating glass slurry is evenly coated on the surface of the sintered composite ceramic material by spraying, and sintere...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Mix 350g of SiC ceramic powder, 280g of Ni metal fibers with a diameter of 5μm and an aspect ratio of 15-25, and 370g of Ca-Al-Si series low-temperature sintered glass additives, and mix them by ball milling for 12 hours. After adding 50 g of water and 50 g of polyethylene glycol to the resulting mixture, mix it, let it stand for 15 minutes, and place it in a graphite mould. Send the graphite mold into the hot-press sintering equipment, pressurize in stages, dry at 120°C for 1 hour, heat up to 600°C for heating and debinding, and keep for 0.5 hours. At a temperature of 1150° C. and a pressure of 120 MPa, the pressure is applied for 2 hours to obtain a composite ceramic material matrix uniformly distributed with Ni metal fibers. The low-melting point insulating glass powder is made into slurry, and a thin layer of insulating glass slurry is sprayed on the surface of the sintered composite ceramic material matrix, and sintered at 650°C for 1 hour to obtain a low-temperatu...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Si 3 N 4 350g of ceramic powder, 325g of Ni metal fibers with a diameter of 10μm and an aspect ratio of 16~18, 300g of Ca-Al-B-Si series low-temperature sintered glass additives, and 25g of yttrium oxide rare earth additives were ball milled and mixed for 12 hours. After adding 50 g of water and 50 g of polyethylene glycol to the resulting mixture, mix it, let it stand for 15 minutes, and place it in a graphite mould. Send the graphite mold into the hot-press sintering equipment, pressurize in stages, dry at 120°C for 0.6 hours, raise the temperature to 600°C for heating and debinding, and keep for 0.5 hours. At a temperature of 1100° C. and a pressure of 150 MPa, the pressure is applied for 2 hours to obtain a composite ceramic material matrix uniformly distributed with Ni metal fibers. The low-melting point insulating glass powder is made into a paste, and a thin layer of insulating glass paste is coated on the surface of the sintered composite ceramic material subs...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| sintering temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| aspect ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com