Thyristor with buffer layer structure
A buffer layer, thyristor technology, applied in the direction of thyristor, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve the problem of increased power loss of devices, and achieve the effect of reducing on-state voltage drop, improving on-state capability, and optimizing internal structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
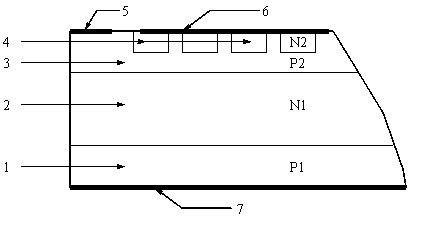
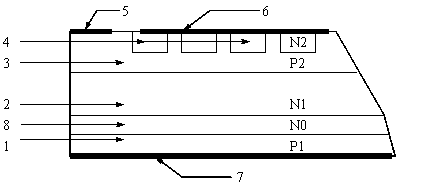
[0014] like figure 2 shown. The buffer layer structure thyristor of the present invention includes a tube shell and a PNPN four-layer three-terminal structure semiconductor chip packaged in the tube shell, and the four layers are P1 anode area 1, N1 long base area 2, cathode end P2 area 3 and N2 cathode area 4. The three terminals are anode A, cathode K and gate G. The junction depth of P1 anode region 1 is 15-50 μm; the junction depth of P2 region 3 at the cathode end is 45-130 μm; the thickness of N1 long base region 2 is 100-500 μm; the thickness of buffer layer N0 region 8 is 10-60 μm. The impurity concentration of the N0 region 8 of the buffer layer is higher than that of the N1 long base region 2 but lower than that of the P1 anode region 1 . The N0 region 8 of the buffer layer is formed by impurity diffusion, and may also be formed by epitaxy.
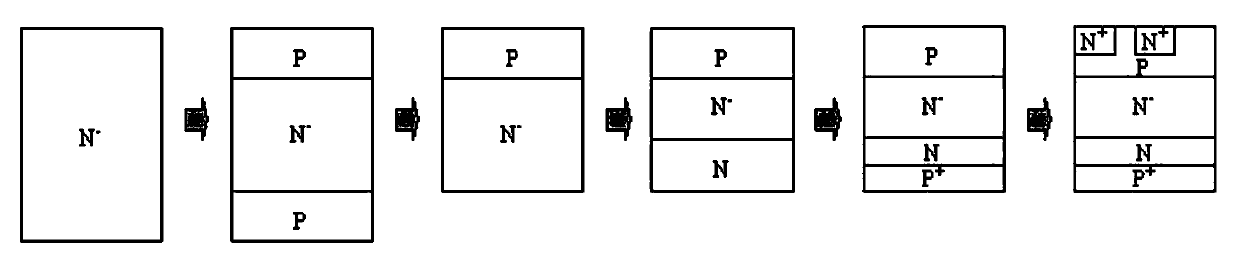
[0015] The silicon chip manufacturing process flow chart of thyristor with buffer layer structure is as follows image 3 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com