Preparation method ofzinc cobaltatenanometer material doped with zinc oxide
A technology of nanomaterials and zinc oxide, applied in chemical instruments and methods, nanotechnology for materials and surface science, nanotechnology, etc., can solve the problems of high reaction temperature, high equipment cost, high production cost, etc., and achieve simplified operation The steps and conditions are easy to control and the effect of low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Add 2.0×10 -3 mol of zinc oxide and dicobalt trioxide were dissolved in 75ml of deionized water, and the reaction kettle was sealed and mixed evenly; the reaction kettle was placed in a constant temperature box and heated at a constant temperature of 120°C for 12 hours; the reaction kettle was taken out and cooled to room temperature naturally , take out the precipitate obtained in the reaction, wash with deionized water and absolute ethanol alternately for 3 times, and then dry at low temperature to obtain zinc cobaltate nanomaterials.
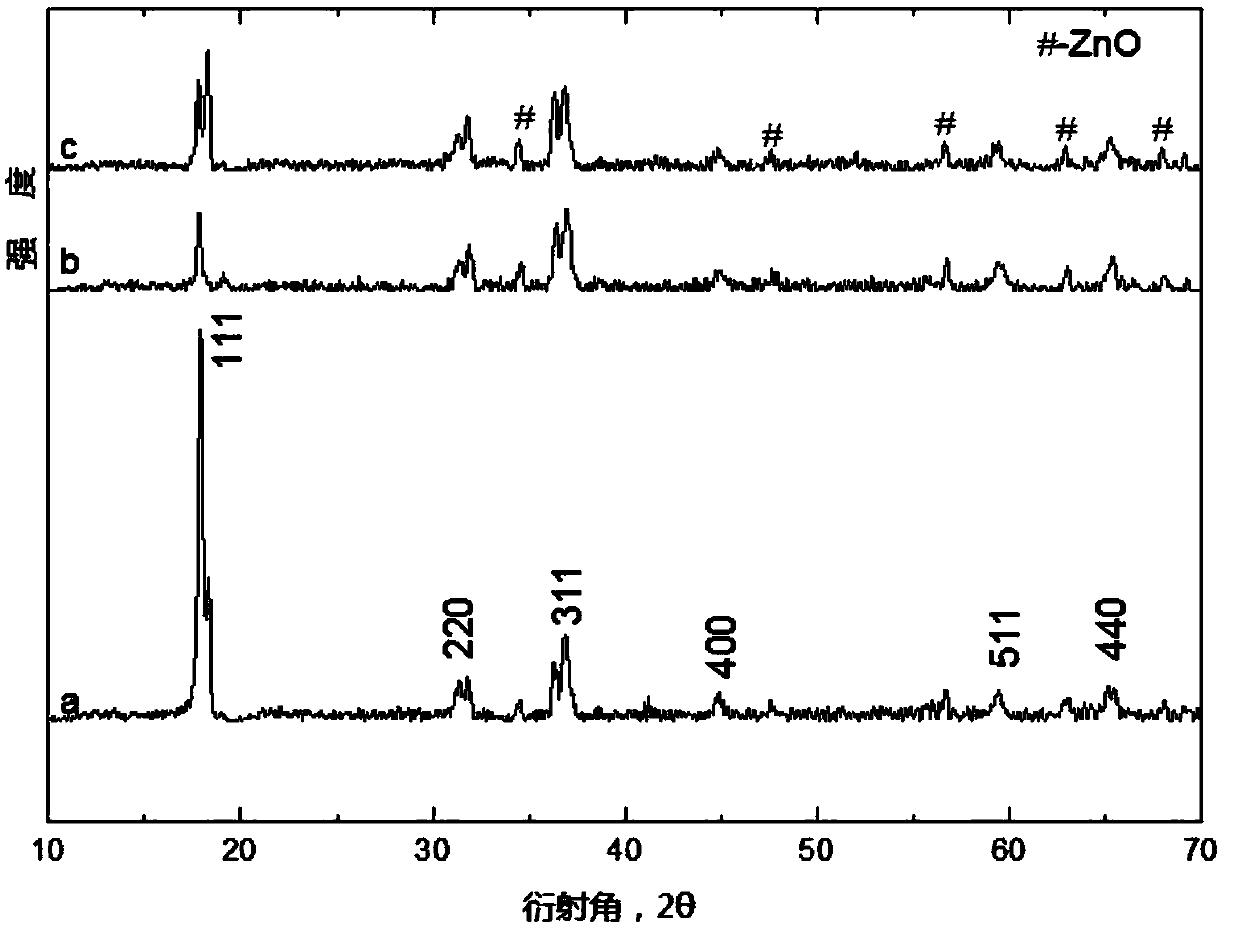
[0023] figure 1 It is the XRD spectrogram of the zinc cobaltate nanomaterial doped with zinc oxide prepared under different reaction temperatures and reaction times in Examples 1, 2, and 3.
[0024] Such as figure 1 The XRD spectrum of the zinc cobaltate nanomaterial doped with zinc oxide obtained under different reaction temperatures and reaction times shown, wherein a is the doped zinc oxide obtained when heated at a constant tempe...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Add 2.0×10 -3 mol of zinc oxide and cobalt trioxide were dissolved in 75ml of deionized water, and the reaction kettle was sealed and mixed evenly; the reaction kettle was placed in a constant temperature box and heated at a constant temperature of 180°C for 12 hours; the reaction kettle was taken out and cooled to room temperature naturally , take out the precipitate obtained in the reaction, wash with deionized water and absolute ethanol alternately for 3 times, and then dry at low temperature to obtain zinc cobaltate nanomaterials.
[0030] figure 1 It is the XRD spectrogram of the zinc cobaltate nanomaterial doped with zinc oxide prepared under different reaction temperatures and reaction times in Examples 1, 2, and 3.
[0031] Such as figure 1 The XRD spectrum of the zinc cobaltate nanomaterial doped with zinc oxide obtained under the different reaction temperatures and reaction times shown, wherein c is the X-ray diffraction spectrum of the zinc cobaltate nanoma...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Add 2.0×10 -3 mol of zinc oxide and cobalt trioxide were dissolved in 75ml of deionized water, and the reaction kettle was sealed and mixed evenly; the reaction kettle was placed in a constant temperature box and heated at a constant temperature of 180°C for 48 hours; the reaction kettle was taken out and cooled to room temperature naturally , take out the precipitate obtained in the reaction, wash with deionized water and absolute ethanol alternately for 3 times, and then dry at low temperature to obtain zinc cobaltate nanomaterials.
[0037] figure 1 It is the XRD spectrogram of the zinc cobaltate nanomaterial doped with zinc oxide prepared under different reaction temperatures and reaction times in Examples 1, 2, and 3.
[0038] Such as figure 1 The XRD spectrogram of the zinc cobaltate nanomaterial doped with zinc oxide obtained under different reaction temperatures and reaction times shown, wherein b is the X-ray diffraction spectrum of the zinc cobaltate nanomat...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Average size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Average size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Average size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com