Laser-assisted nano-particle preparation method, and apparatus thereof
A nanoparticle, laser-assisted technology, applied in the direction of microsphere preparation, microcapsule preparation, chemical/physical/physicochemical process of energy application, etc., can solve the problem of high cost of nanoparticle preparation, uncontrollable shape and size, poor stability, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of reducing production costs, high product quality reliability, and good stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
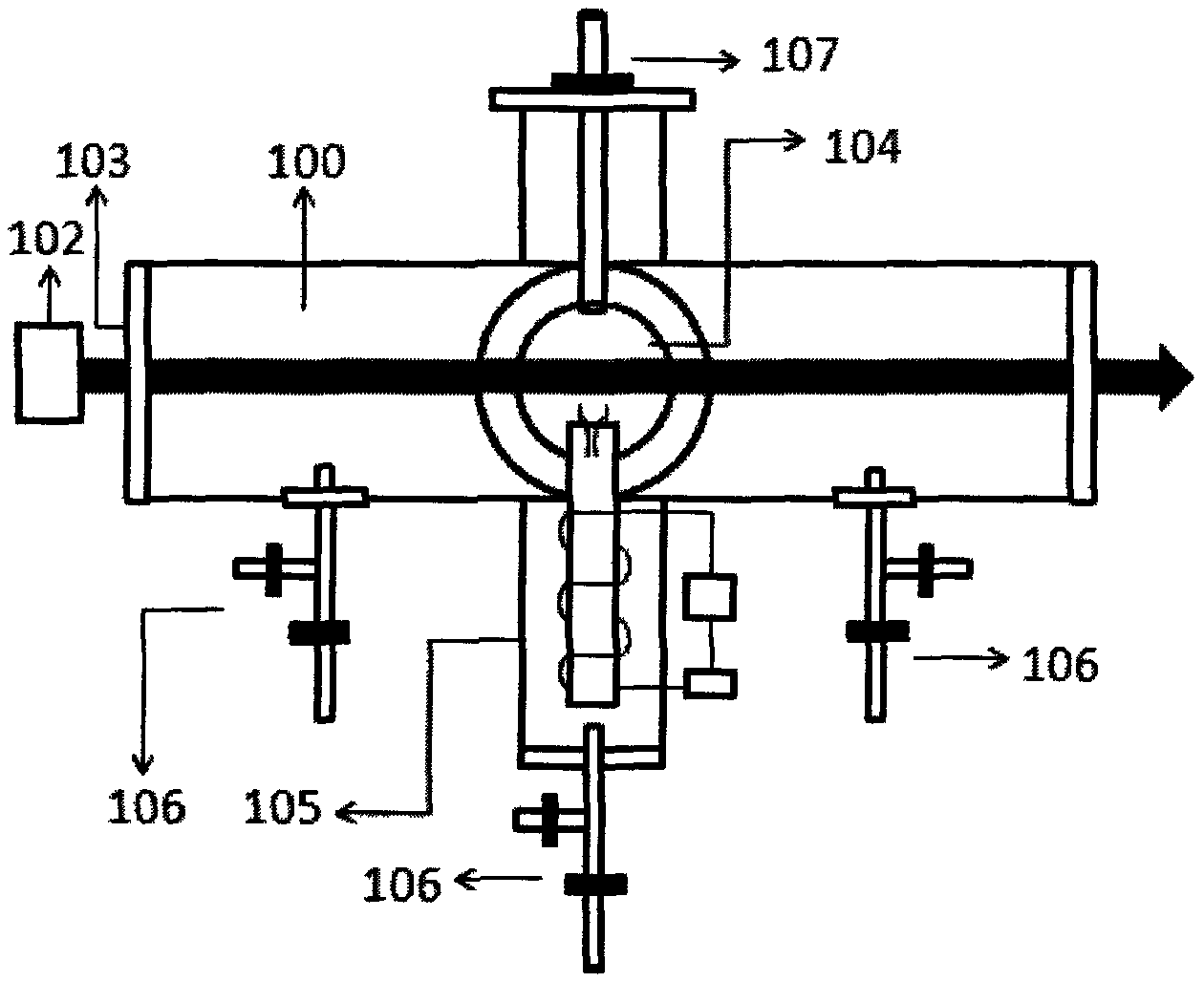
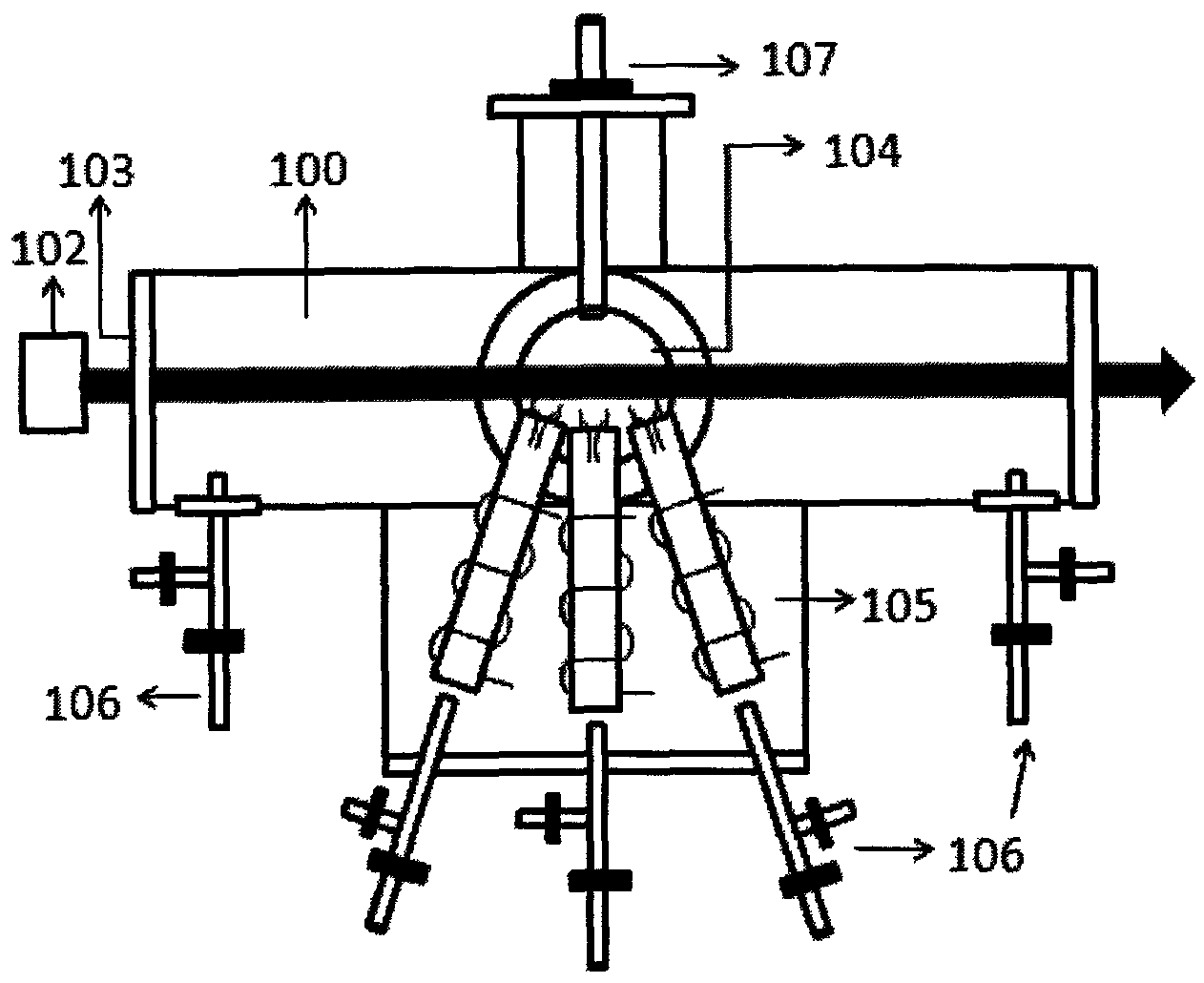
[0026] Taking the preparation of silicon nanoparticles as an example, the method for preparing nanoparticles of the present invention will be described. The preparation of silicon nanoparticles is based on organic precursors of silicon, such as silane, such as but not limited to: SiH 4 、Si 2 h 6 、Si 3 h 8 etc.; chlorosilanes such as SiH 2 Cl 2 , SiHCl 3 、SiCl 4 、Si 2 Cl 6 Wait.
[0027] The organic precursor gas of silicon enters the plasma generator through the gas introduction device, and enters the reaction chamber after being activated by the plasma generator. In the reaction chamber, the laser beam emitted by the laser beam is heated, and the organic silicon is cracked to produce Silicon nanoparticles are collected by a collection device above the reaction chamber. In addition, the protective gas H 2 and sensitizing gas SF 6 , H 2 Confine the reactive gas and sensitizing gas near the center of the reaction chamber to prevent them from accumulating in the cor...
Embodiment 2
[0033] The present invention will be further described by taking the preparation of copper indium gallium selenide nanoparticles as an example.
[0034] Copper indium gallium selenide nanoparticles are compounds composed of various elements, and the precursor gases include organic copper, organic indium, organic gallium, and selenium vapor. For example, copper-containing organic precursors include, but are not limited to: Cu(C 11 h 19 o 2 ) 2 , Cu(CF 3 COCHCOCF 3 ) 2 , (C 5 h 5 )CuP(C 2 h5 ) 3 , Cu(CF 3 COCHCOCH 3 ) 2 , Cu(CF 3 COCHCOCF 3 )P(CH 3 ) 3 etc.; Indium-containing organic precursors include, but are not limited to: triphenylindium (C 18 h 15 In), triphenylpyridine indium (C 23 h 20 InN), p-tolyl indium (C 21 h 21 In) etc.; gallium-containing organic precursors include but are not limited to: dimethylgallium fluoride (C 2 h 6 FGa), trimethylgallium (C 3 h 9 Ga), triethylgallium (C 6 h 15 Ga), tripropylgallium (C 9 h 21 Ga), triisopropylga...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com