Process for 6-APA or 7-ADCA production waste water recycling resource and biochemistry pretreatment
A 7-ADCA and 6-APA technology, applied in the chemical industry, can solve the problems of high salinity, waste of resources, and poor biodegradability of wastewater, and achieve the effects of reducing COD, saving resources, and improving biodegradability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
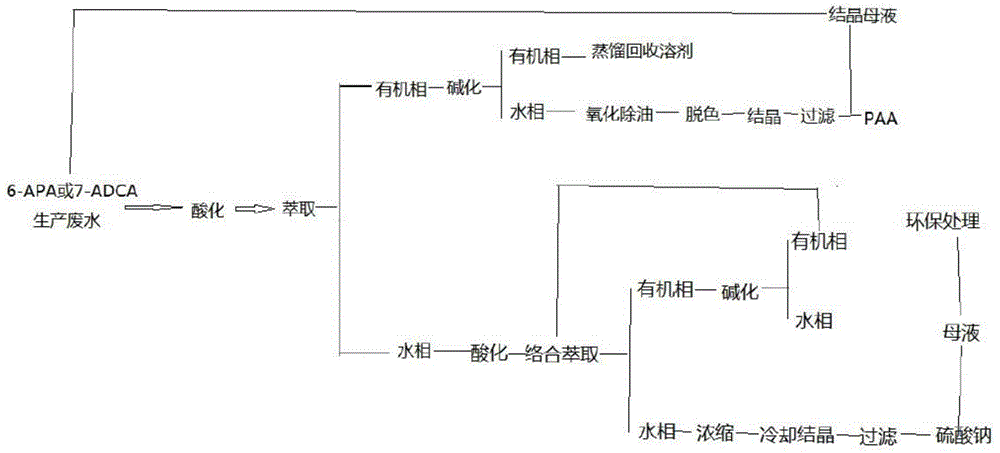
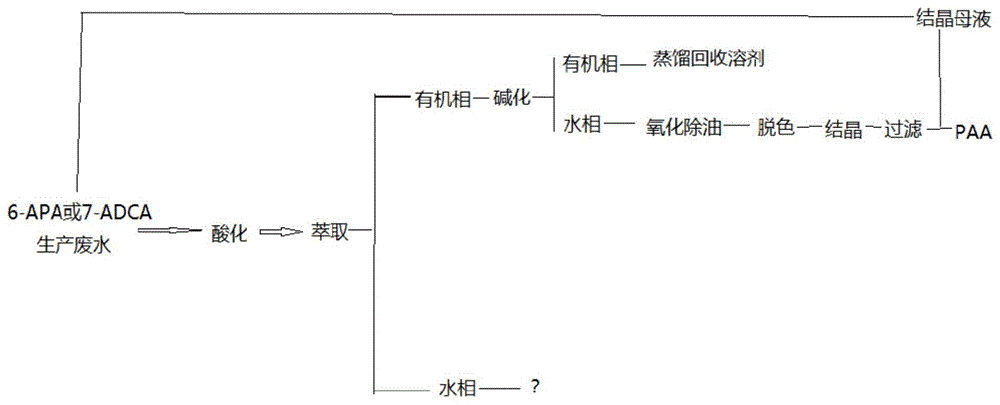
[0023] Embodiment 1 carries out phenylacetic acid recovery to 6-APA or 7-ADCA production waste water
[0024] Take 1L of 6-APA or 7-ADCA production wastewater, add 15% sulfuric acid to make the pH of the solution 2.0, then add 250mL of toluene, stir for 15min, let stand for stratification, and separate the water phase for further processing;
[0025] Add 10% sodium hydroxide solution to the organic phase to make the pH of the solution 10.0, stir for 10 min, let stand to separate the layers, and separate the organic phase, which can be reused after distillation. Add 10% sodium hydroxide solution to the aqueous phase obtained in this step to make the pH 12.0, then add 2mL30%H 2 o 2 After stirring for 10 min, the aqueous phase was heated to 60° C., then 1 g of activated carbon was added, stirred for 30 min, and filtered. Cool the filtrate to room temperature and cool down with an ice-water bath, add 15% sulfuric acid to the filtrate to make the pH of the solution 2.0, grow crys...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Embodiment 2 processes the 6-APA or 7-ADCA production waste water after reclaiming phenylacetic acid
[0027] (1) Adjust the pH value: take 1L of the aqueous phase produced in Example 1, its COD is 56440mg / L, and adjust its pH to 0.5 with 15% sulfuric acid;
[0028] (2) Extraction: add 400mL trialkylphosphine oxide (C 8 -C 10 ) and octanol extractant, trialkylphosphine oxide (C 8 -C 10 ) accounted for 33% by volume in the extractant, stirred for 20min, allowed to stand for stratification, separated the water phase, and set aside, its COD was measured to be 3048mg / L;
[0029] (3) Stripping: Add 80mL of 30% sodium hydroxide solution to the organic phase obtained in step (2), stir for 20 minutes, let stand to separate, and recover the extractant. The COD removal rate of the aqueous phase in this process is 92.4%;
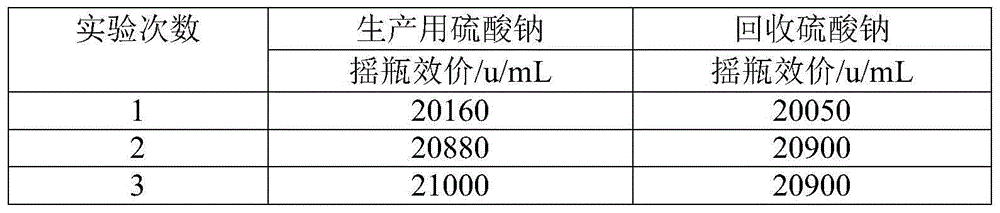
[0030] (4) Recovery of sodium sulfate: Take 1L of the aqueous phase obtained in step (2), and concentrate it with a rotary evaporator. The temperature of th...
Embodiment 3
[0031] Embodiment 3 processes the 6-APA or 7-ADCA production wastewater after reclaiming phenylacetic acid
[0032] (1) Adjust the pH value: take 1L of the aqueous phase produced in Example 1, its COD is 58740mg / L, and adjust its pH to 2.0 with 15% sulfuric acid;
[0033](2) Extraction: Add 200mL of tributyl phosphate and MIBK to the aqueous phase obtained in step (1) as an extractant, the volume ratio of tributyl phosphate in the extractant is 67%, stir for 20min, and let stand Layering, separate the water phase, set aside, measure its COD as 3220mg / L;
[0034] (3) Stripping: Add 66 mL of 30% sodium hydroxide solution to the organic phase obtained in step (2), stir for 20 minutes, let stand to separate, and recover the extractant. The COD removal rate of the aqueous phase in this process is 94.5%;
[0035] (4) Recovery of sodium sulfate: Take 1L of the aqueous phase obtained in step (2), and concentrate it with a rotary evaporator. The temperature of the water bath is 60°C, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com