Hydrometallurgy industry raffinate waste water COD removal method
A technology of hydrometallurgy and raffinate, applied in metallurgical wastewater treatment, chemical instruments and methods, water/sewage multi-stage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of no obvious removal effect, difficult degradation, and inability to further remove COD, etc., to achieve The effect of small dosage, lower COD, and low overall operating cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
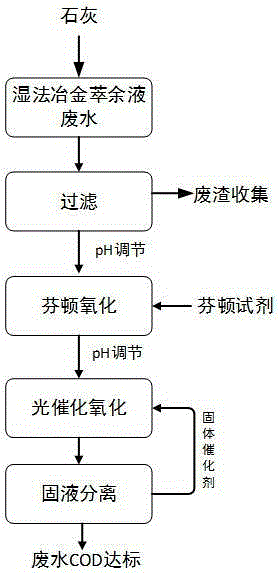
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Mixed waste water from copper and molybdenum extraction and recovery system of an enterprise, pH=0.69, COD1240mg / L, SO 4 2- The content is 109.5g / L, Cl - The content is 7.8g / L, NO 3 - The content is 210.5g / L. The main components of COD are a small amount of disperse oil, extractant N235 and LIX984, sulfonated kerosene and copper-molybdenum extract.
[0030] (1) Take 5000mL of the above wastewater, add slaked lime powder according to 1% of the theoretical dosage for removing all sulfate radicals, stir for 30 minutes, then let stand for 20 minutes, and filter to remove the generated calcium sulfate slag;
[0031] (2) The filtrate obtained in step (1) was adjusted to pH=1 with 10% dilute hydrochloric acid solution, the COD content was 1010mg / L, and the SO 4 2- The content is 108.5g / L;
[0032] (3) The solution obtained in step (2) is first added with 30% hydrogen peroxide, wherein H 2 o 2 The amount added is 1 times the mass concentration of COD, that is, 1.01g / L,...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Cobalt raffinate wastewater from a metallurgical enterprise in Zhejiang, pH=9.80, COD4580mg / L, SO 4 2- The content is 158.4g / L. The main components of COD are a small amount of dispersed oil, extractant P204, a small amount of emulsified and soluble sulfonated kerosene, and blue cobalt extract.
[0038] (1) Take 5000mL of the above wastewater, add slaked lime powder according to 50% of the theoretical dosage for removing all sulfate radicals, stir for 30 minutes, then let it stand for 20 minutes, and filter to remove the generated calcium sulfate slag;
[0039] (2) The filtrate obtained in step (1) was adjusted to pH=8 with 10% dilute hydrochloric acid solution, the COD content was 2540mg / L, and the SO 4 2- The content is 82.3g / L;
[0040] (3) The solution obtained in step (2) is first added with 30% hydrogen peroxide, wherein H 2 o 2 The amount added is twice the mass concentration of COD, that is, 5.08g / L, followed by the rapid addition of 30% ferrous sulfate so...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Raffinate wastewater from a rare earth company in Jiangxi, pH=6.58, COD960mg / L, PO 4 3- The content is 78.2g / L, Cl - The content is 18.3g / L, NO 3 - The content is 165.2.5g / L. The main components of COD are a small amount of dispersed oil, extractant TBP, sulfonated kerosene and rare earth extracts.
[0046] (1) Take 5000mL of the above wastewater, add slaked lime powder according to 100% of the theoretical amount for removing all phosphate radicals, stir and react for 30 minutes, then let it stand for 20 minutes, and filter to remove the generated calcium phosphate slag.
[0047] (2) The pH of the filtrate obtained in step (1) is 12, the COD content is 752mg / L, and the PO 4 3- The content is 1.7g / L;
[0048] (3) The solution obtained in step (2) is first added with 30% hydrogen peroxide, wherein H 2 o 2 The amount added is 5 times the mass concentration of COD, that is, 3.76g / L, followed by the rapid addition of 30% ferrous sulfate solution, Fe 2+ with H 2 o ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com