Small nucleic acid drug for treating acute lung injury caused by sepsis
A technology for acute lung injury and small nucleic acid drugs, applied in the field of biomedical materials, can solve problems such as designing siRNA, achieve low cost, simple production and synthesis process, and low immunogenicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
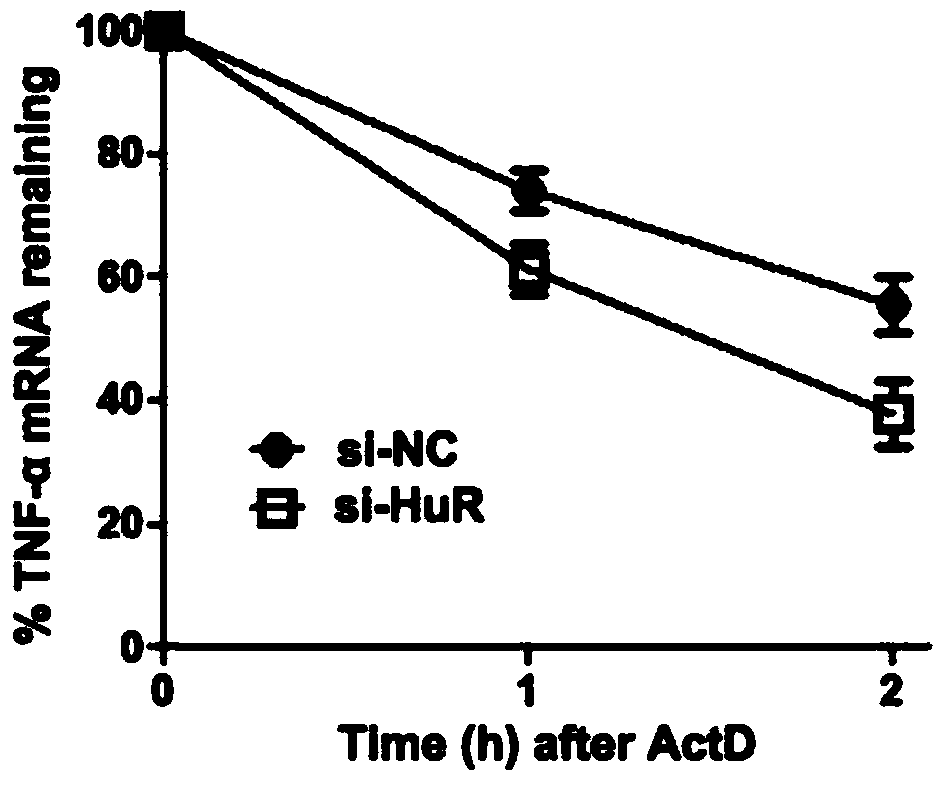
[0031] Example 1: HuR siRNA destabilizes TNF-α mRNA
[0032] In order to determine that HuR is involved in the regulation of TNF-α mRNA stability, we screened and synthesized multiple siRNAs against HuR, and selected a fragment with the best interference effect, which was 5'-AACAUUCAACGCUGUCGGUGAGU-3' (SEQ ID NO.27). This siRNA was transfected into A549 cells with lipofectamine2000, and the protein expression was verified by western blot. It was found that the RNAi almost completely inhibited the expression of HuR ( figure 1 ). In this case, the effect of HuR siRNA on the degradation rate of TNF-α mRNA was studied by reverse transcription PCR method, adding Act D (mRNA synthesis inhibitor) to cells transfected with HuR siRNA or control siRNA, and then collecting Act D treatment After 1 and 2 hours, the total RNA was extracted from the cells, and PCR amplification was carried out after reverse transcription. The experimental results showed that after HuR was interfered, the ha...
Embodiment 2
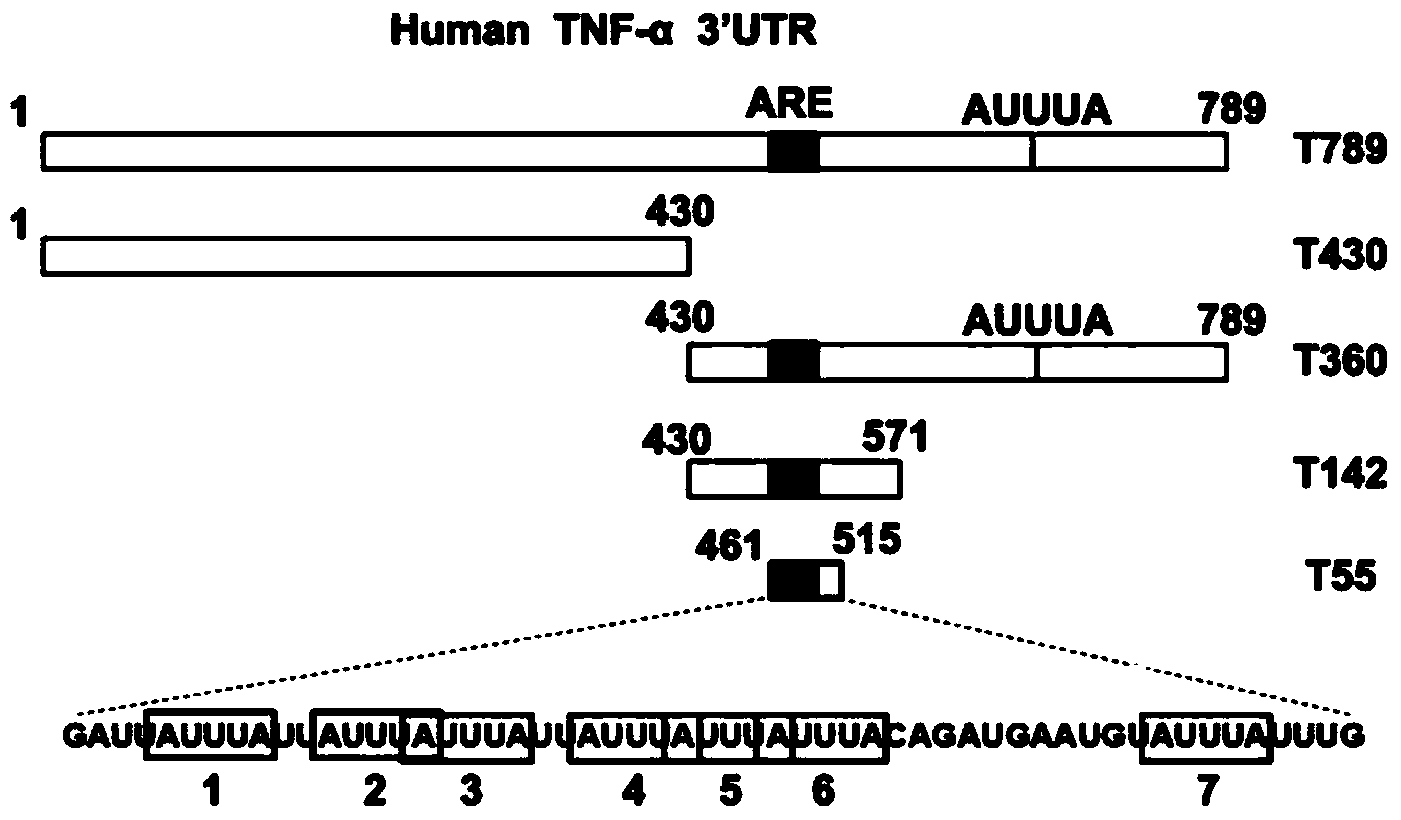
[0033] Example 2: HuR can bind TNF-α mRNA 3'UTR to play a stabilizing role
[0034] TNF-α3'UTR plays a key role in mRNA stability. In order to determine the minimum sensitive response element on TNF-α3'UTR, the present invention adopts PCR and molecular cloning methods to construct human TNF3'-UTR full length and 4 truncated variants. The luciferase reporter plasmids of the body were named T789, T430, T360, T142 and T55 ( Figure 4 ). The PCR primers involved in its construction are as follows:
[0035]
[0036] These reporter plasmids and renillia plasmids (purchased by Invitrogen) were co-transfected into cells using lipofectamine2000, and the luciferase activity was determined. The results showed that TNF-α 3'UTR full-length (T789) had obvious destabilizing effect, and T55 could Destabilization of the full-length TNF-α 3'UTR by partial substitution ( Figure 4 ). In order to further study the function of T55, we transfected the cells with the above variants and then ...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Example 3: In vivo knock-down HuR inhibits acute lung injury
[0043] 3.1 Experimental method
[0044] 3.1.1 Modeling of LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice
[0045] The experiment was divided into PBS negative control group and LPS treatment group. The PBS and LPS (500ug / ml) solution was stimulated by ultrasonic atomization for 30 minutes, and the mice were inhaled. After an interval of 1 hour, they were atomized again for 30 minutes. The mice were killed at 8 hours, and the lungs were taken. A part of the lung tissue was fixed in 4% neutral paraformaldehyde and stained with H&E, and the remaining part of the tissue was homogenized for MPO activity determination. 3.1.2 In vivo detection of HuR siRNA fragments with Cy5 fluorescence
[0046] Mice were injected with Cy5-labeled HuR siRNA into the tail vein. After 24 hours, the lung tissue was taken out and placed on a fluorescence imager to observe the distribution of HuR siRNA in the lung tissue. Take out a small pi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com