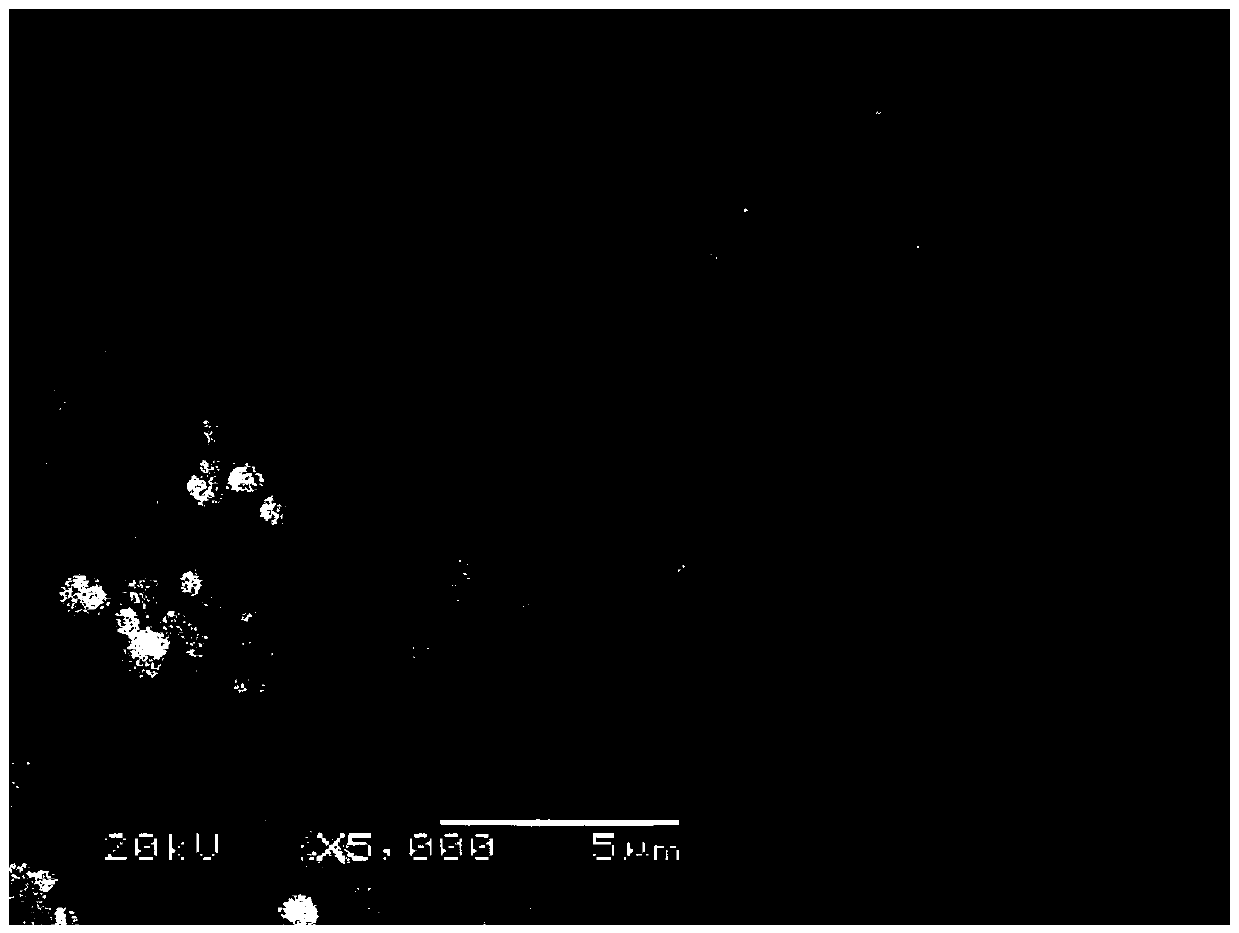
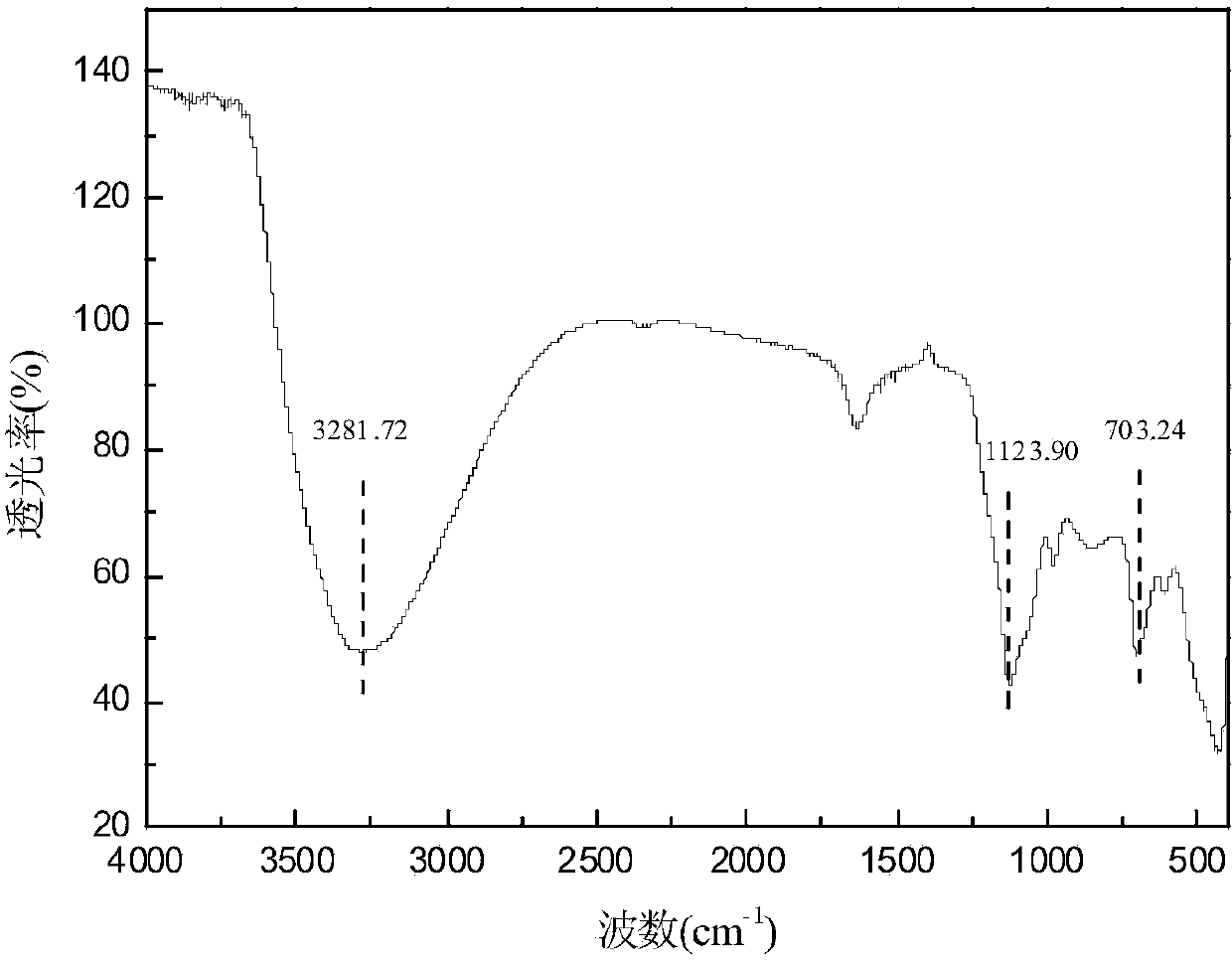
Fixing agent for repairing arsenic-polluted soil, and preparation and application method thereof
A fixative and arsenic-polluted technology, which is applied in the field of fixatives for repairing arsenic-contaminated soil, can solve the problems of pH value influence, inconvenient use, adverse effects of physical and chemical properties, etc., and achieve simple and convenient production operation, low cost, and favorable cultivation of crops Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] To prepare the fixative for repairing arsenic-contaminated soil of the present invention:
[0032] (1) Prepare a ferrous sulfate solution with a ferrous ion concentration of 0.04-1.2mol / L;
[0033] (2) Add oxidant hydrogen peroxide to the above solution while stirring, oxidant and Fe 2+ The molar ratio is 1:1-2; the reaction is 6-24h, and then the residue is washed 2-3 times with an acid with a pH of about 1.5-3 during suction filtration, and then washed 2-3 times with pure water to collect the residue.
[0034] (3) Dissolve the above residue at 30-70℃7 <pH After reacting for 6-24 hours in <9NaOH solution, suction filter, dry the obtained residue at 40-70°C, and grind through a 100-mesh sieve to obtain a chemical fixative.
Embodiment 2
[0036] In this example, weigh 10g of arsenic-contaminated soil in each Erlenmeyer flask, and add the fixative of Example 1 prepared under different temperature conditions with a mass ratio of 4% to the contaminated soil, according to the soil-water mass ratio of 2:1 Add tap water and stir until uniform. After standing for 7 to 14 days, samples were taken to determine the content of water-soluble As and effective As (sodium bicarbonate extractant) in the soil. After testing, the content of water-soluble As and sodium bicarbonate extractable As in the soil after the fixation prepared at a lower temperature was reduced from 27.11mg / kg and 312.49mg / kg to 0.98mg / kg and 156.28mg, respectively / kg, the fixation rate of water-soluble state is 96.38%, and the fixation rate of sodium bicarbonate leaching state is 49.99%; the content of water-soluble As and sodium bicarbonate leaching As in the soil after fixation prepared at higher temperature Reduced from the original 27.11mg / kg and 31...
Embodiment 3
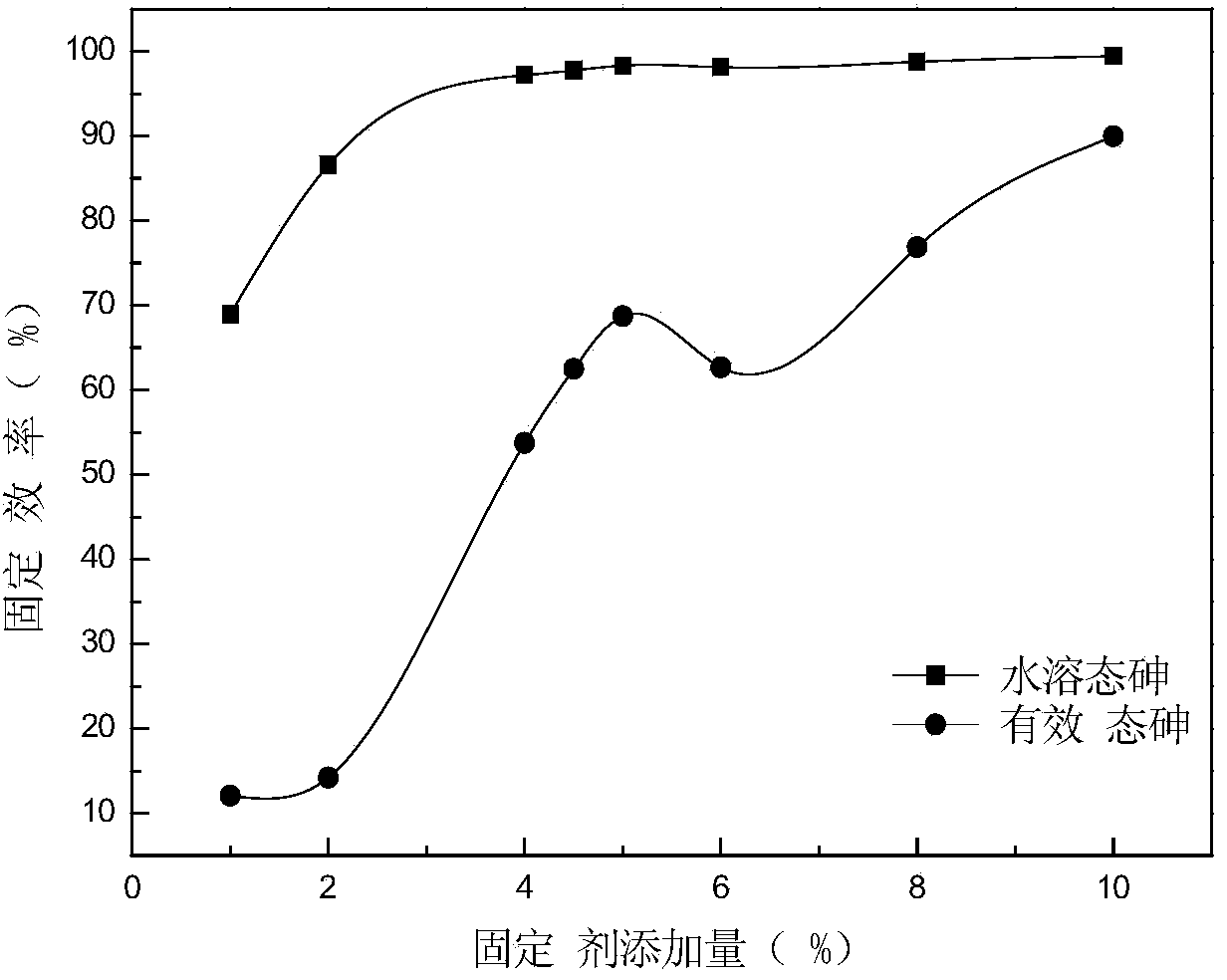
[0038] The experiment soil was collected from Shimen, Hunan Province, and passed through a 20-mesh nylon sieve after air-drying, removing impurities and grinding. In this example, 10g of arsenic contaminated soil is weighed in each Erlenmeyer flask, and chemical fixatives are added to the soil at a mass ratio of 1%, 2%, 4%, 4.5%, 5%, 6%, 8%, and 10%. To the contaminated soil, add tap water according to the soil-water mass ratio of 2:1 and stir until uniform. After standing for 7 to 14 days, samples were taken to determine the content of water-soluble As and effective As (sodium bicarbonate extractant) in the soil. After testing, when the amount of fixative added is 4%, the content of water-soluble As and sodium bicarbonate extractable As in the soil are reduced from 33.17mg / kg and 226.78mg / kg to 0.94mg / kg and 104.86mg / respectively. kg, the fixation rate of water-soluble state is 97.17%, and that of sodium bicarbonate extract state is 53.76%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com