Human breast cancer cell acetylation p53 protein isotope labeling quantitative method
A technology of human breast cancer cells and isotope labeling, which can be used in measurement devices, material analysis by electromagnetic means, instruments, etc., and can solve problems such as inability to quantify acetylated sites.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
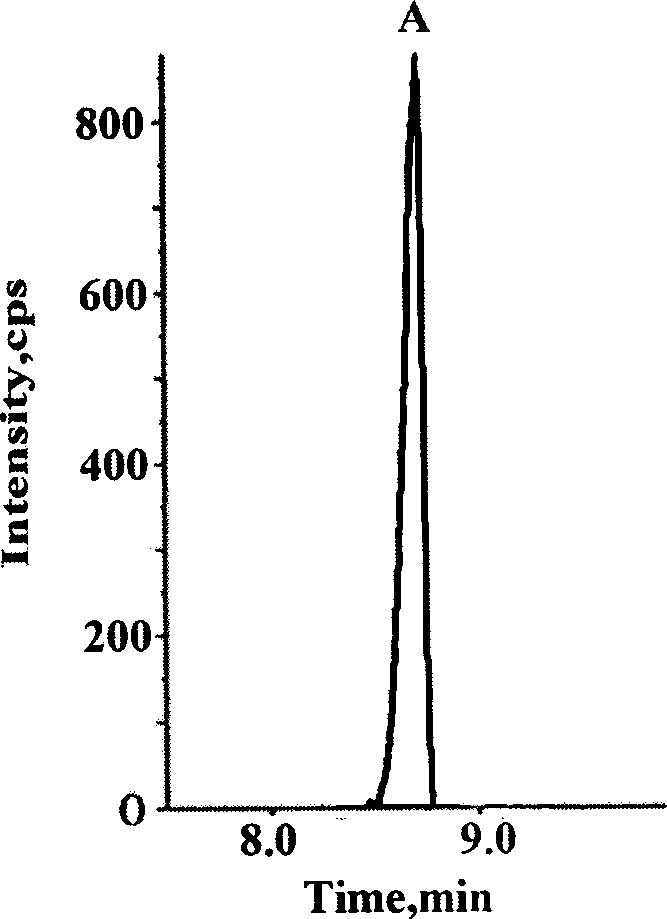
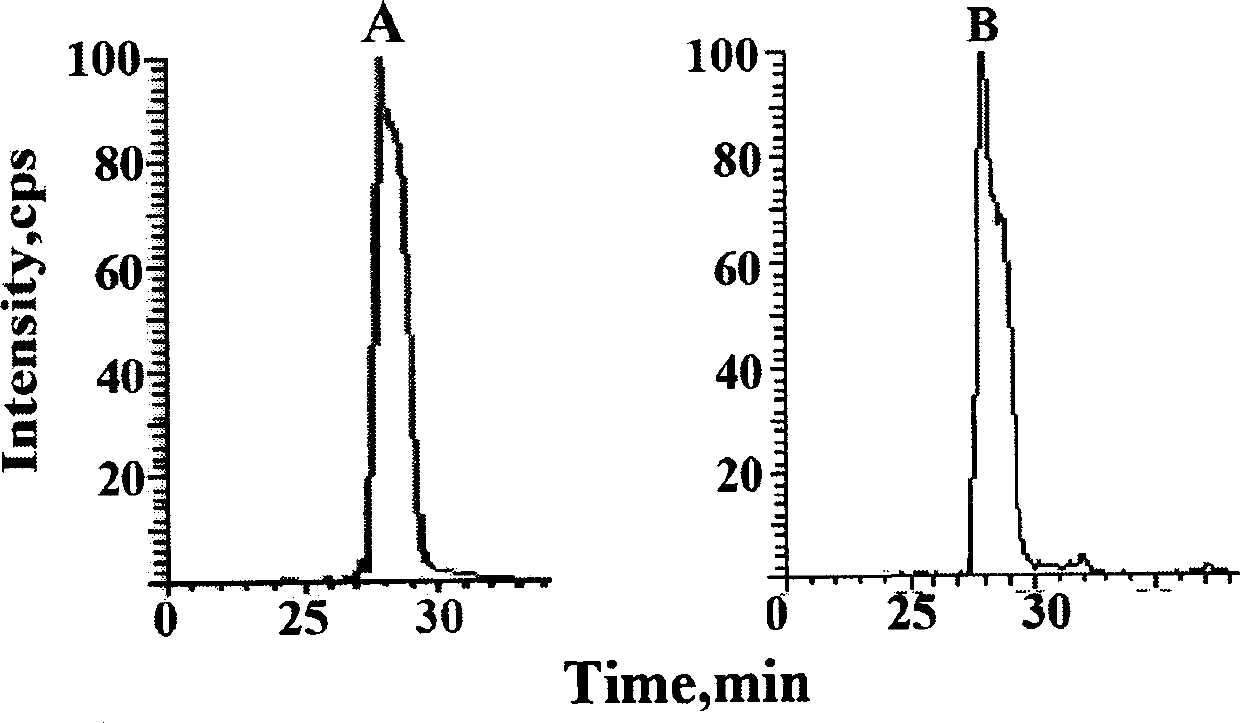
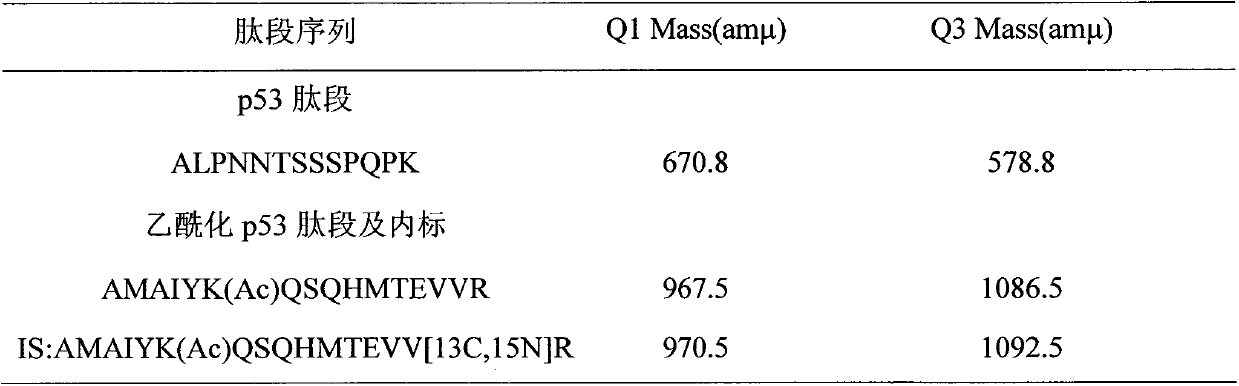
[0034] Example 1: Determination of the amount of acetylated p53 protein in human breast cancer cells at different times after administration of the chemotherapy drug adriamycin
[0035] The main steps are as follows:
[0036] Take the MCF-7 sensitive cells of human breast cancer cells in logarithmic growth phase, digest the cells with 0.1% trypsin, resuspend the cells in complete medium after centrifugation, and count on a blood cell counter to 1×10 4 Each / well was inoculated in a 6-well culture plate. After 24 hours, change the medium after the cells have basically adhered to the wall, and add 200 μl of adriamycin-containing serum-free medium to each well at a concentration of 10 μM. A solvent control administration group (0.1% DMSO) was set for each cell at the same time, and each group had 3 replicate wells. After administration, the cell culture plate is placed in an incubator at 37°C, containing 5% CO 2 , Cultivate in an environment with a relative humidity of 90%. The cells...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com