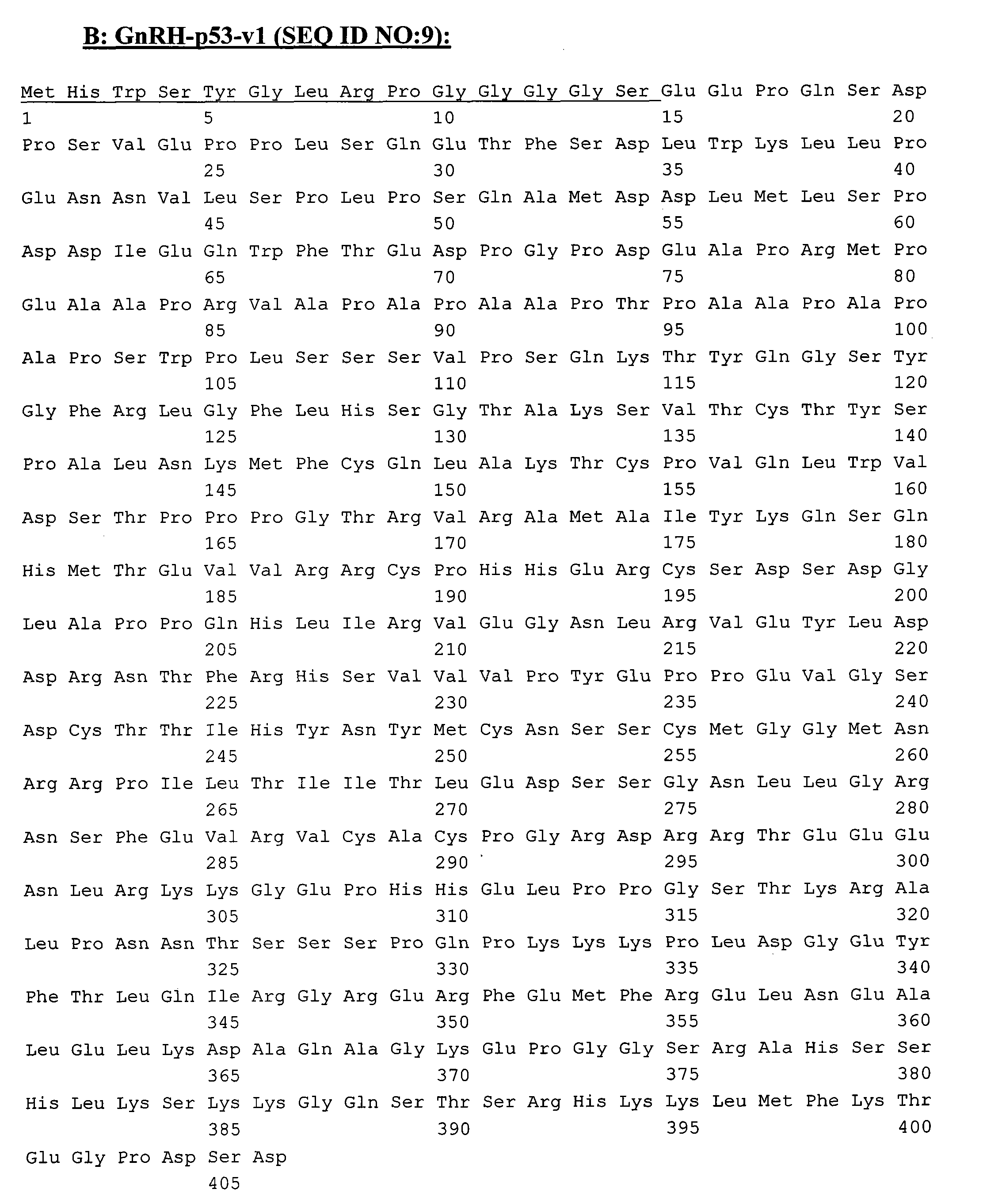
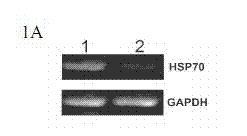
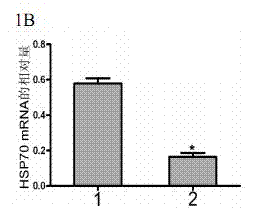
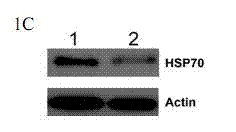
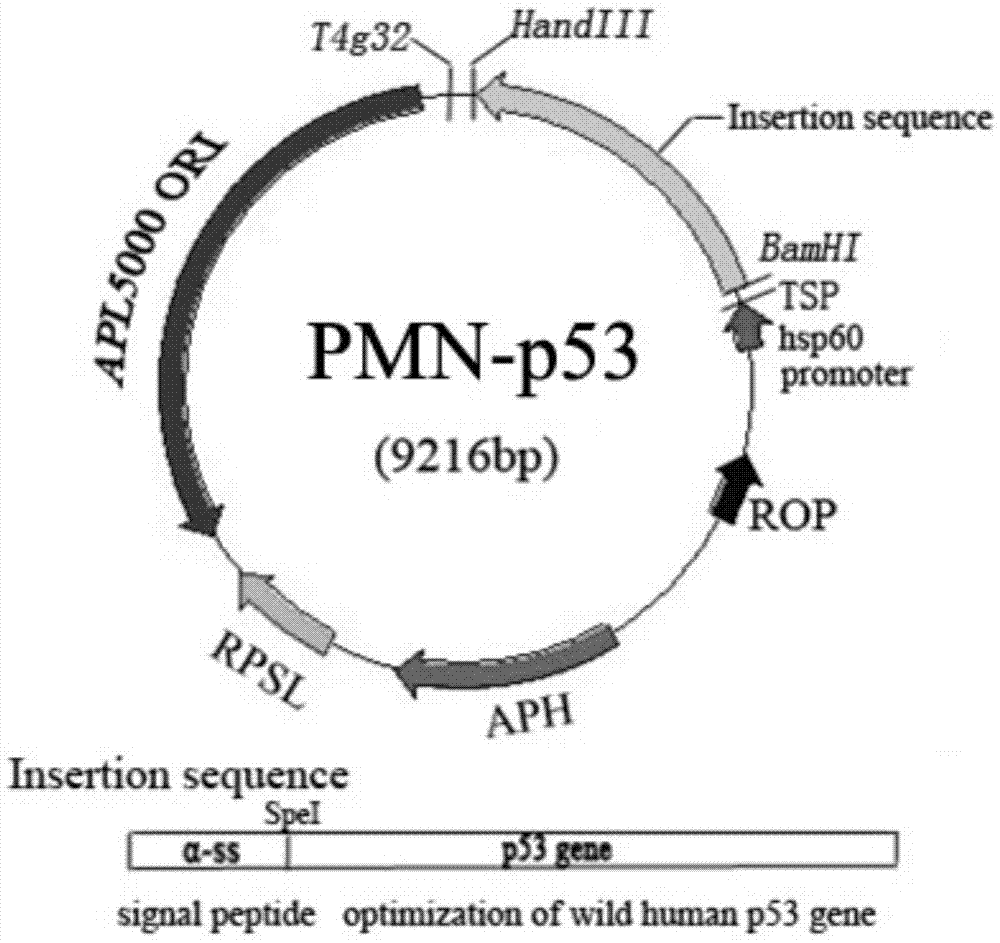
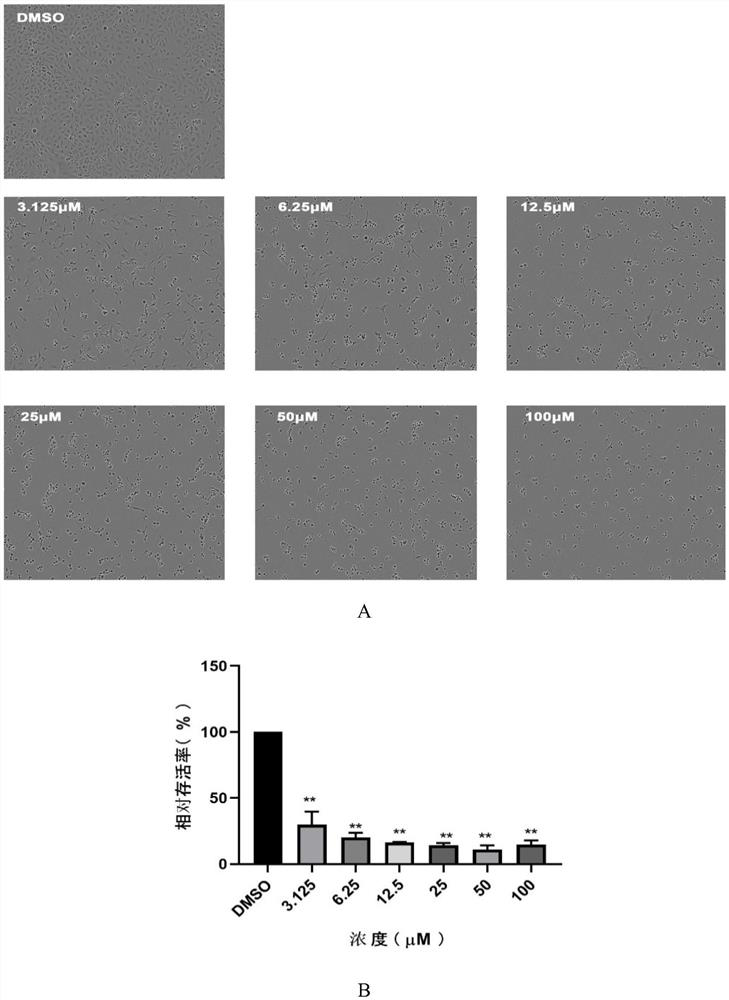
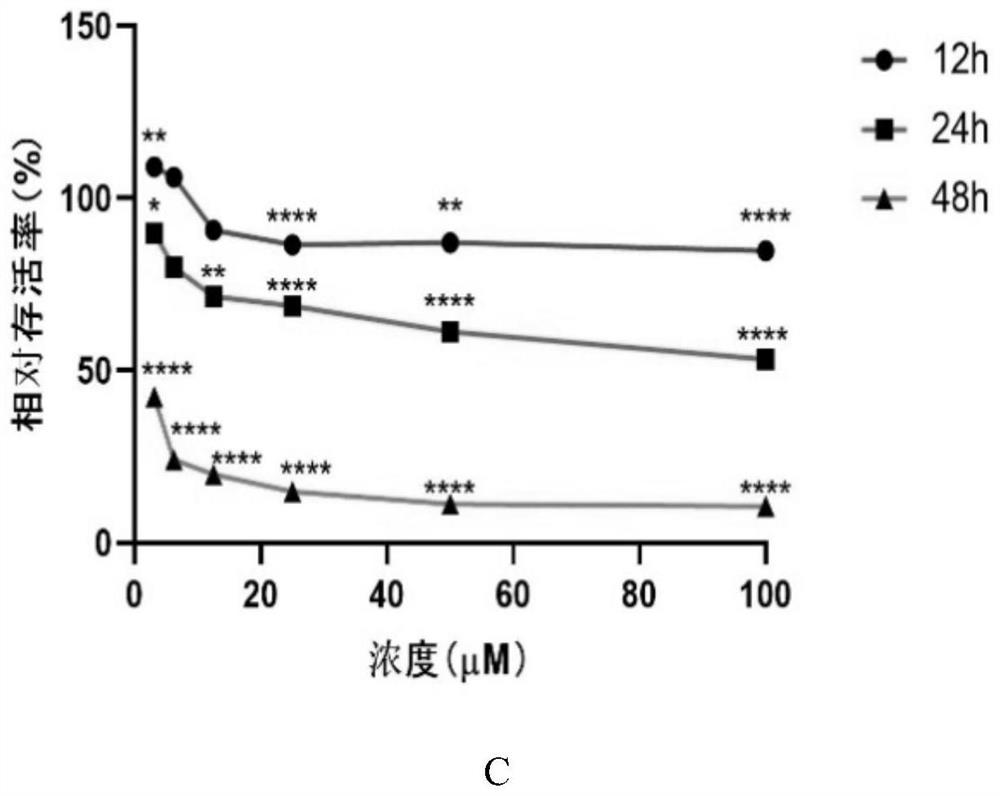
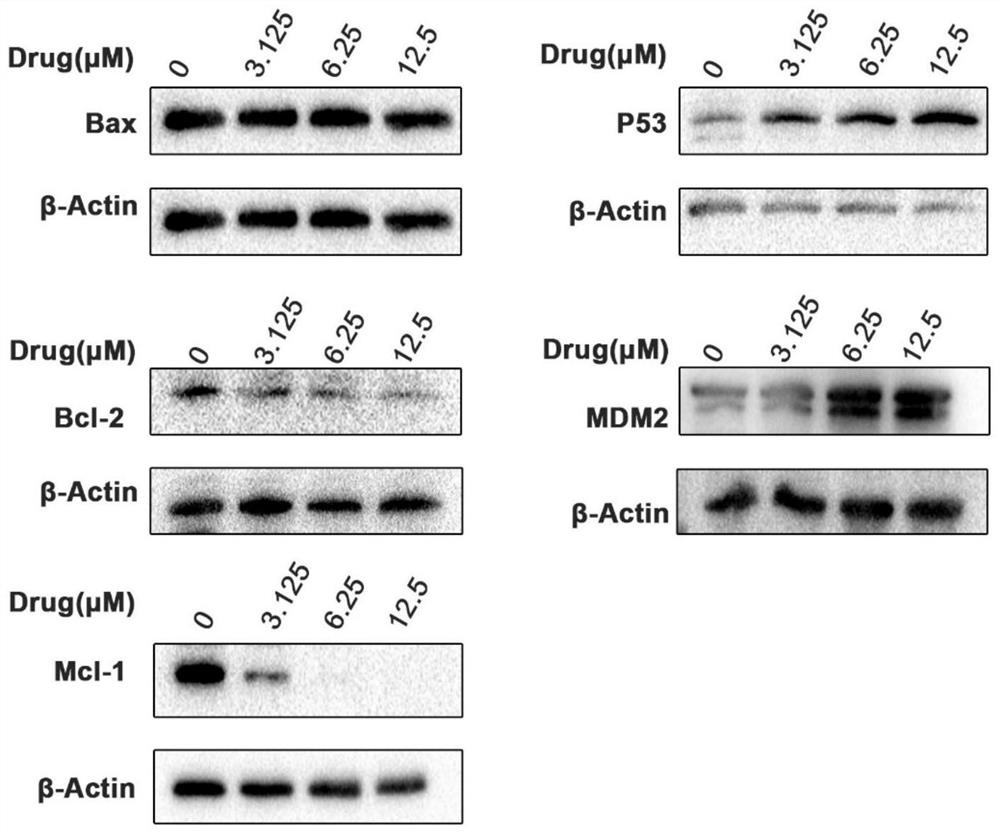
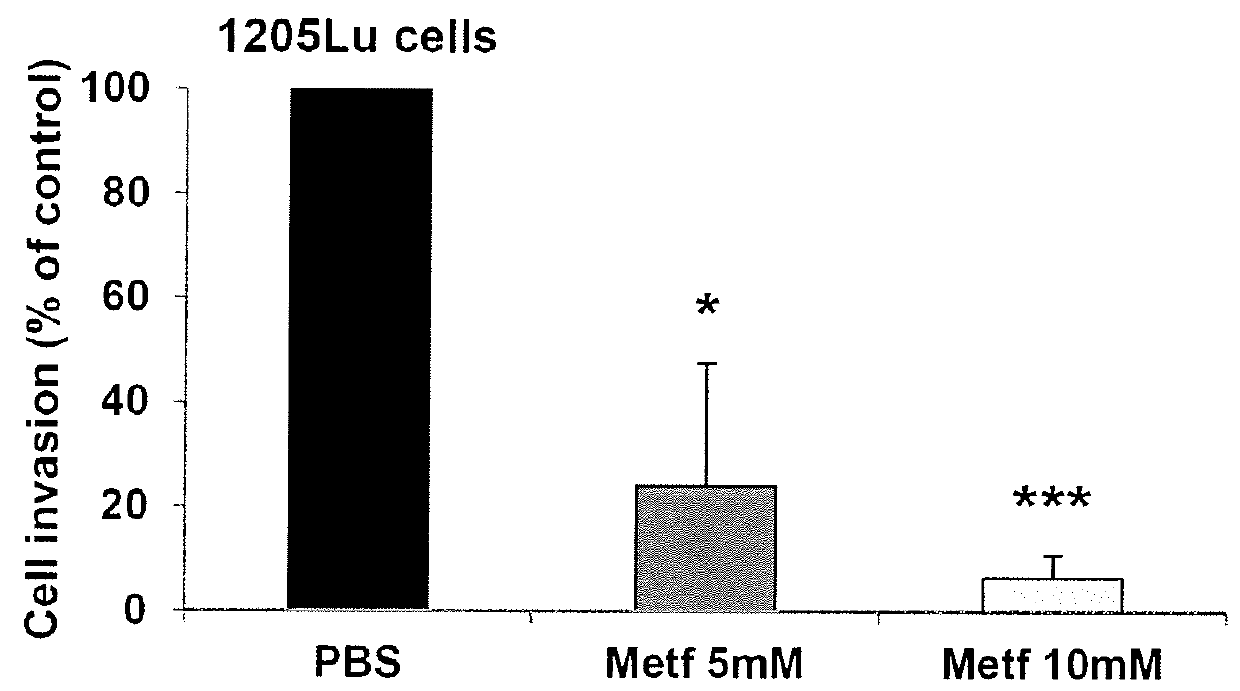
Patents
Literature
65 results about "P53 protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method and system for treating cancer cachexia
ActiveUS9730967B2Foster the retention of muscle mass in the individualRestore healthPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesMuscle tissueCancer cell
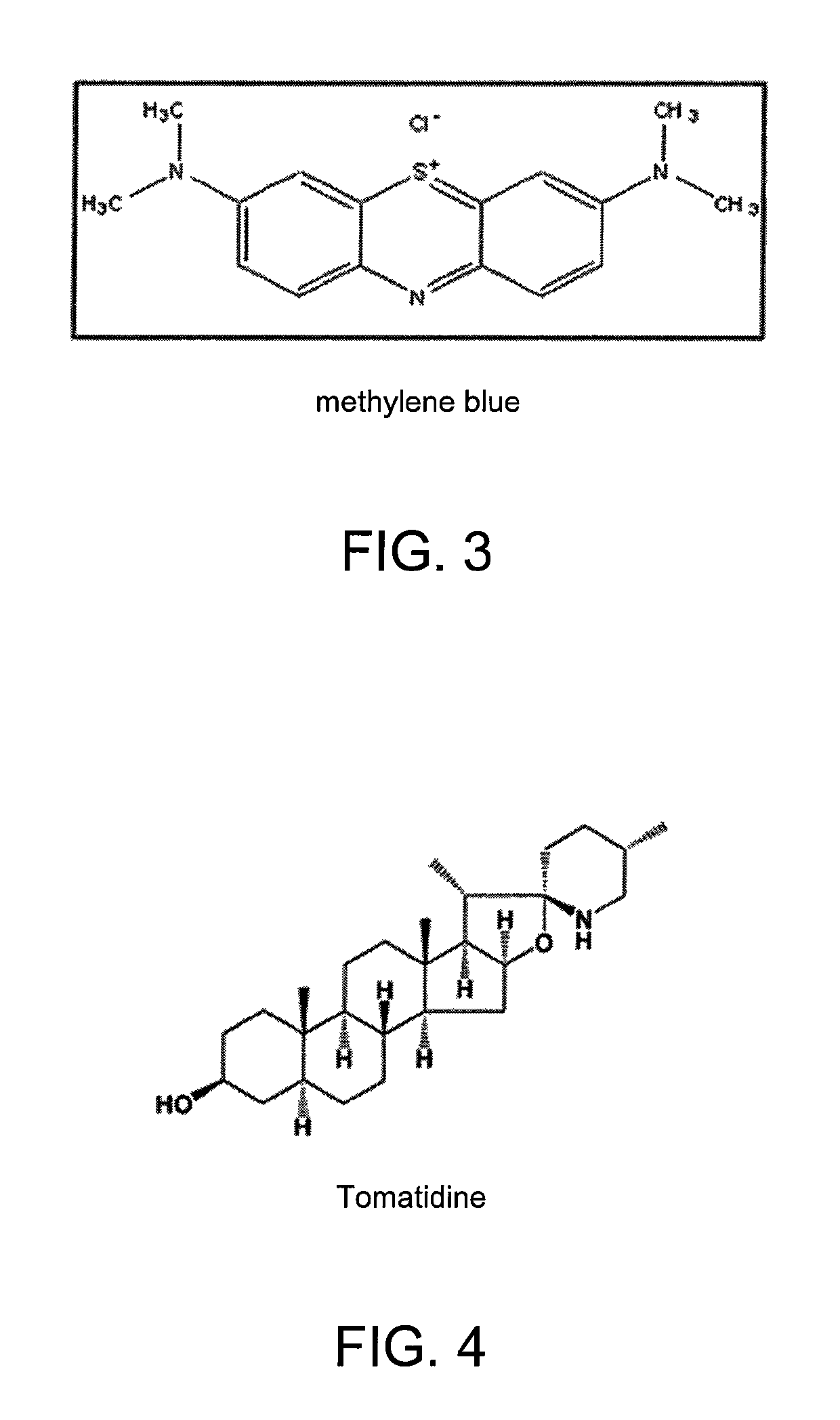
Various embodiments of the present invention are directed to the field of Oncology, and in particular embodiments directed to a method of ameliorating, treating, or preventing a malignancy in a human subject wherein the steps of the method assist or boost the immune system in eradicating cancerous cells. In certain embodiments, administration of beneficial bacteria to an individual's microbiome that have been modified so as to produce effective amounts of desired compositions, compounds, agents, e.g. tomatidine, p53 protein, statins, etc., is employed to address cancerous conditions. In several embodiments, the administration of such beneficial bacteria and microbes to an individual's microbiome invokes either an active (or a passive) immune response to destroy, weaken or render less invasive certain cancerous cells, and preferably maintains muscle tissue to combat cancer cachexia.
Owner:KOVARIK JOSEPH E +1
Method and System for Treating Cancer Cachexia
ActiveUS20170173085A1Good lookingFoster the retention of muscle mass in the individualHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsMuscle tissueCancer cell
Various embodiments of the present invention are directed to the field of Oncology, and in particular embodiments directed to a method of ameliorating, treating, or preventing a malignancy in a human subject wherein the steps of the method assist or boost the immune system in eradicating cancerous cells. In certain embodiments, administration of beneficial bacteria to an individual's microbiome that have been modified so as to produce effective amounts of desired compositions, compounds, agents, e.g. tomatidine, p53 protein, statins, etc., is employed to address cancerous conditions. In several embodiments, the administration of such beneficial bacteria and microbes to an individual's microbiome invokes either an active (or a passive) immune response to destroy, weaken or render less invasive certain cancerous cells, and preferably maintains muscle tissue to combat cancer cachexia.
Owner:KOVARIK JOSEPH E +1
Compounds for use in stabilizing p53 mutants
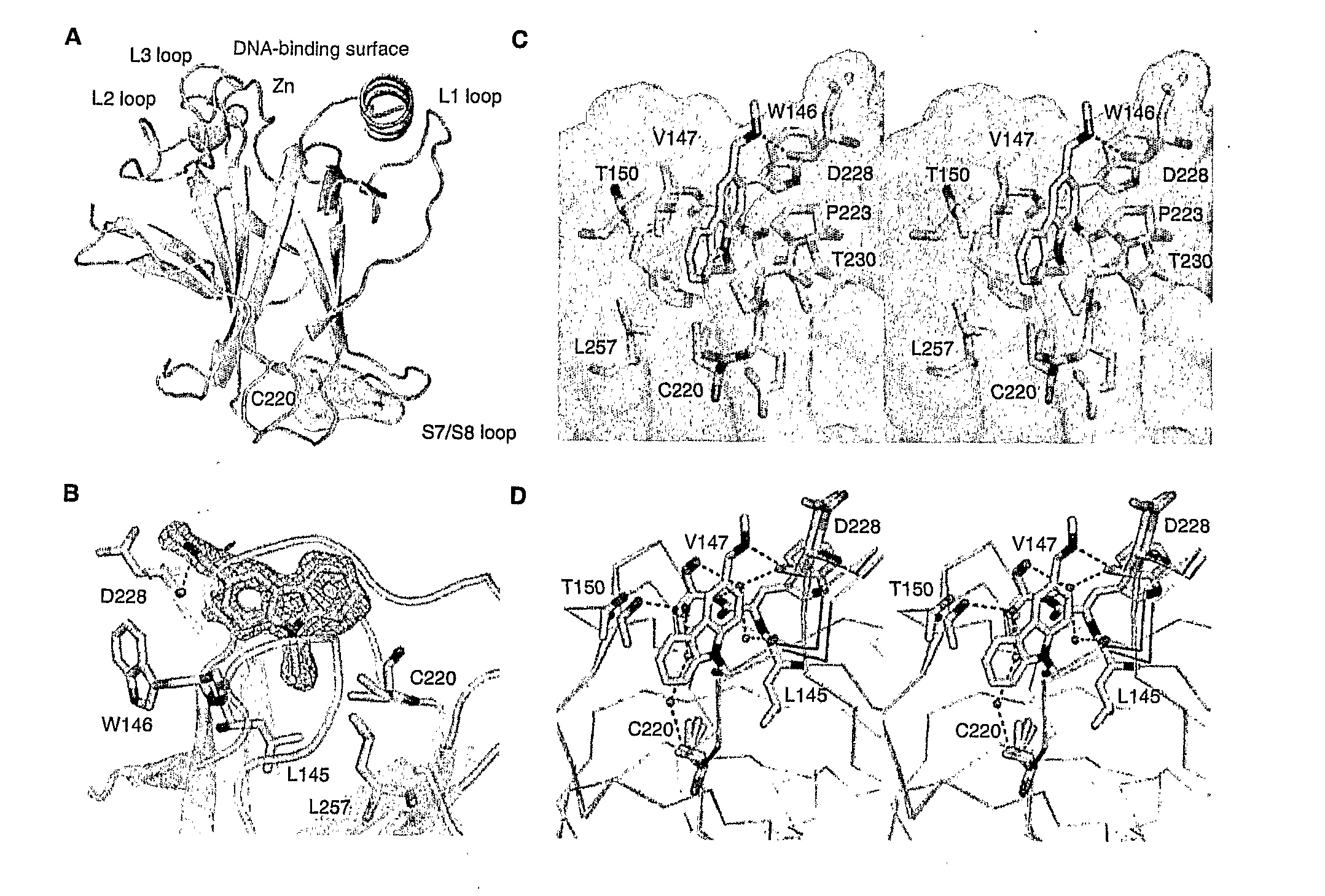
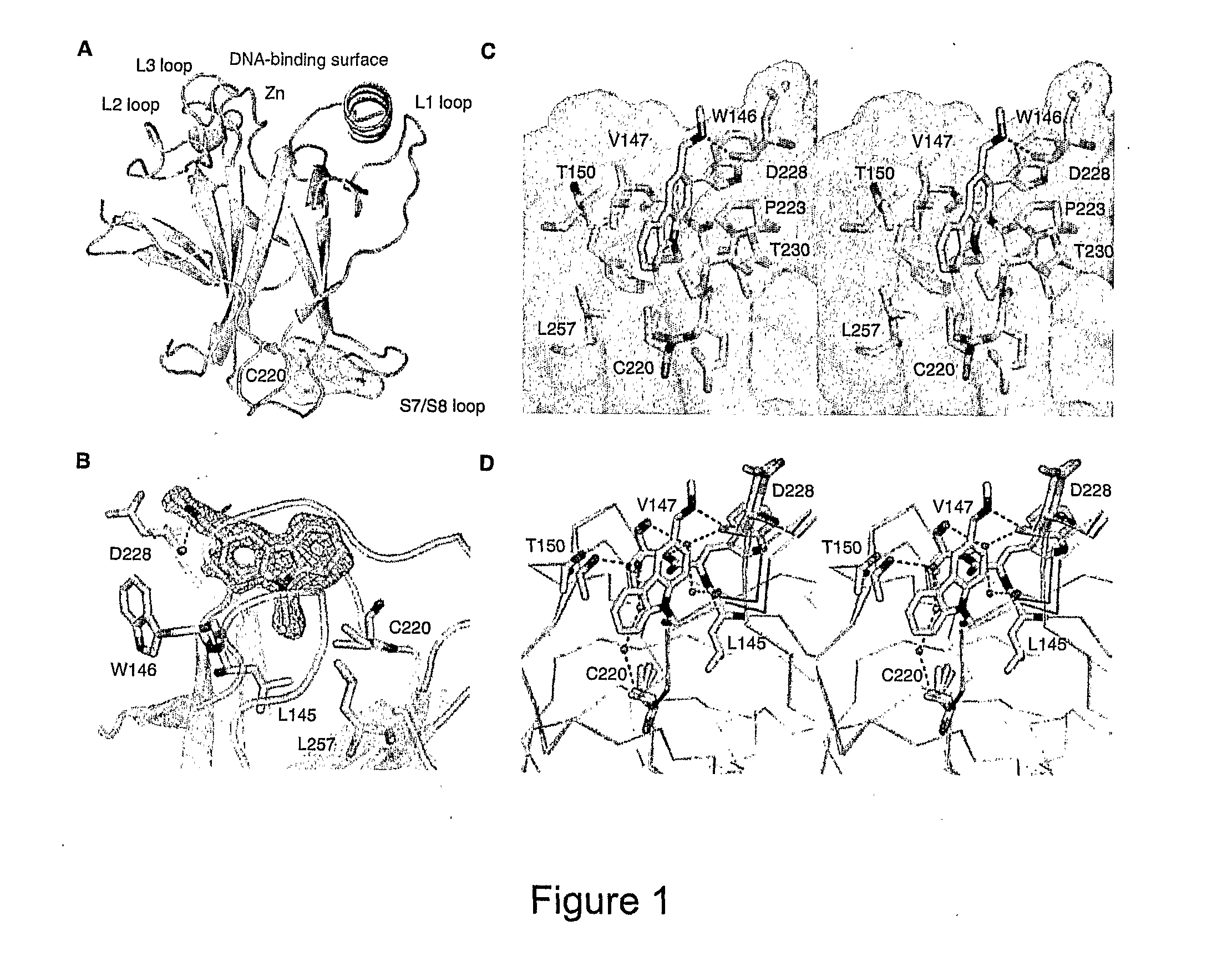
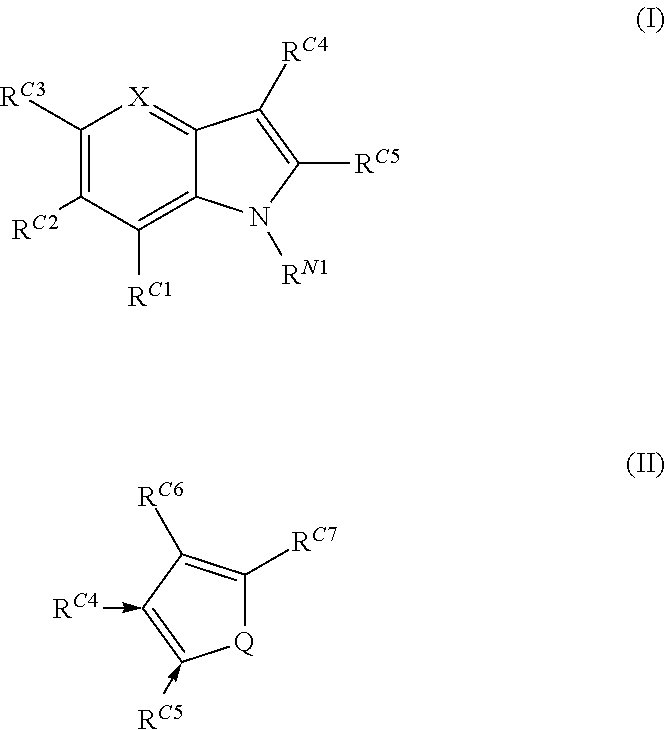
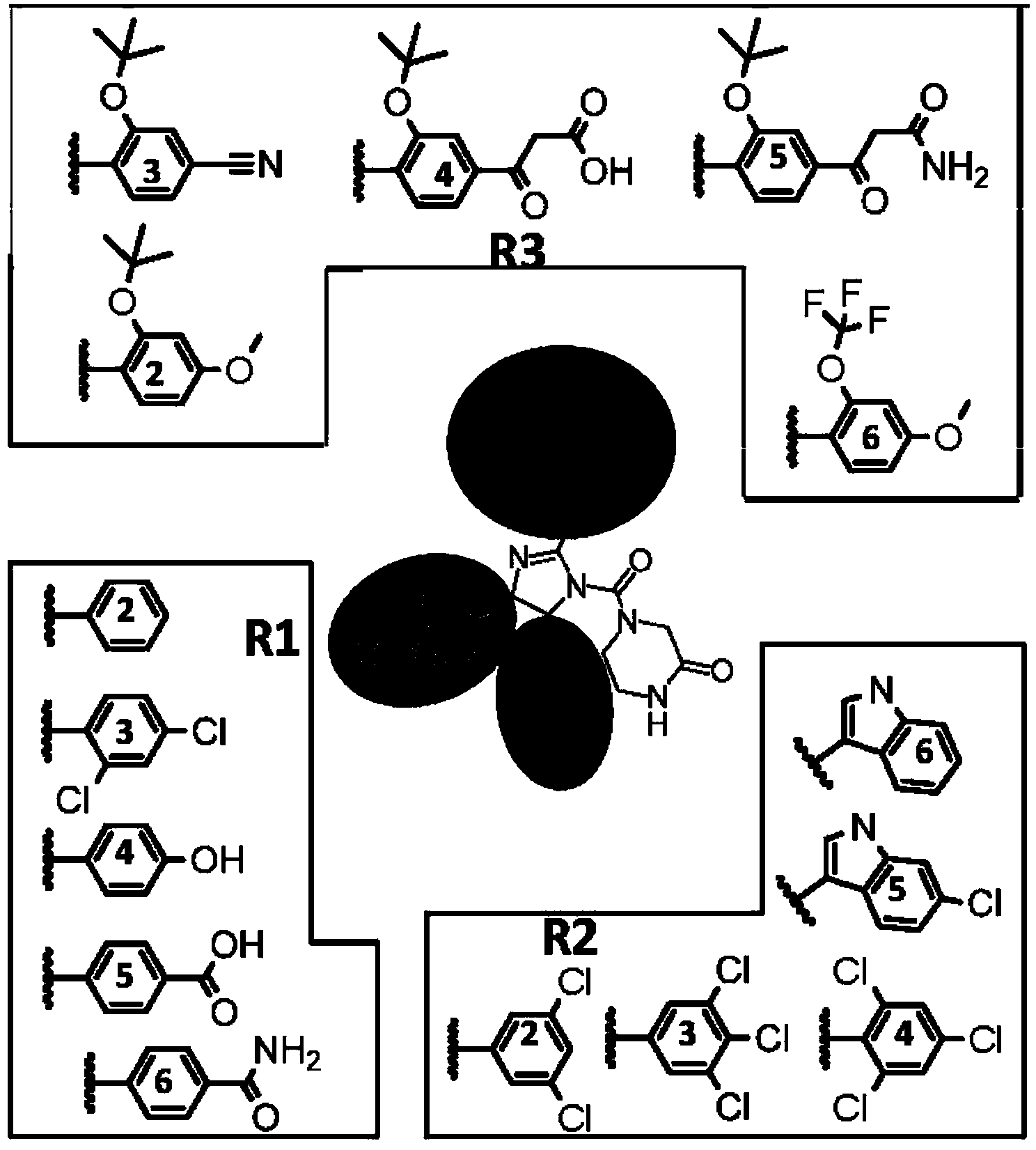
Compounds of formula (I): wherein X is selected from CRX and N; RN1 is selected from H and C1-4 alkyl, which may be substituted by SH or halo; RG1 is selected from H and SH; RC2 is selected from H and optionally substituted C1-7 alkyl; RC3 is selected from H and optionally substituted C1-7 alkyl; Rx is selected from H, OH and NH2; RC4 is selected from: (i) an optionally substituted C3-12 N-containing heterocyclyl; (ii) C(═O)NRN5RN6, where RN5 and RN6 are independently selected from H, optionally substituted C1-7 alkyl, optionally substituted C3-20 heterocyclyl and optionally substituted C5-20 aryl or RN5 and RN6 and the nitrogen atom to which they are attached form an optionally substituted N-containing C5-7 heterocyclyl group; (iii) C(═O)ORO1, where RO1 is selected from H, optionally substituted C1-7 alkyl, optionally substituted C3-20 heterocyclyl and optionally substituted C5-20 aryl; (iv) C(═O)NHNHSO2RS1, where RS1 is selected from H, optionally substituted C1-7 alkyl, optionally substituted C3-20 heterocyclyl and optionally substituted C5-20 aryl; (v) OC(═O)RC8, where RC8 is selected from H, optionally substituted C1-7 alkyl, optionally substituted C3-20 heterocyclyl and optionally substituted C5-20 aryl; (vi) OC(═O)NRN7RN8, where RN7 and RN8 are independently selected from H, optionally substituted C1-7 alkyl, optionally substituted C3-20 heterocyclyl and optionally substituted C5-20 aryl or RN7 and RN8 and the nitrogen atom to which they are attached form an optionally substituted N-containing C5-7 heterocyclyl group; and (vii) C(═O)CH2NH C(═O)NHNH2, CHC(CN)2, CHC(CN)C(═O)NH2, and carboxy; RC5 is selected from H, OH and NH2; or RC4 and RC5 together with the carbon atoms to which they are bound form an optionally substituted aromatic ring containing either 5 or 6 ring atoms, of formula: where Q represents O, N, or CRQ1═CRQ2, where RQ1 and RQ2 are independently selected from H, OH and NH2; RC6 is selected from H, OH and NH2; and RC7 is selected from optionally substituted C3_12 N-containing heterocyclyl, NHC(═O)RC9, CH2NRN2RN3 and NHC(═S)NHRN4, where RC9 is selected from optionally substituted C1-7 alkyl, optionally substituted C3-20 heterocyclyl and optionally substituted C5-20 aryl, RN2 and RN3 are independently selected from H, optionally substituted C1-7 alkyl, optionally substituted C3-20 heterocyclyl and optionally substituted C5-20 aryl or RN2 and RN3 and the nitrogen atom to which they are attached form an optionally substituted N-containing C5-7 heterocyclyl group, and RN4 is selected from optionally substituted C1-7 alkyl, optionally substituted C3-20 heterocyclyl and optionally substituted C5-20 aryl, and when RC4 and RC5 are not bound together, RC3 may additionally be selected from OR02, where RO2 is a C1-4 alkyl group, and C(═O)ORO3, where RO3 is a C1-4 alkyl group and RC2 may additionally be selected from halo, for use in stabilising a p53 protein carrying a Y220C mutation.
Owner:MEDICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL
Small-molecule inhibitor of Mdm<X>/Mdm<2>, as well as preparation method and applications
ActiveCN103923067AAvoid interactionProduce toxic side effectsOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsSide effectCancer cell
The invention relates to the technical field of medicinal chemistry, particularly discloses a small-molecule inhibitor of Mdm<X> / Mdm<2>, and also relates to a preparation method of the small-molecule inhibitor of Mdm<X> / Mdm<2>. The small-molecule inhibitor compound can inhibit the interaction of Mdm<X> protein and p53 protein and also can inhibit the interaction of Mdm<2> protein and p53 protein, has antiproliferative activity on cancer cells, and cannot generate toxic and side effects on patients. The small-molecule inhibitor compound can be combined with other therapies for use.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Method and System for Treating Cancer Cachexia
ActiveUS20160339064A1Different mechanism of actionFoster the retention of muscle mass in the individualOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsMuscle tissueMicroorganism
Various embodiments of the present invention are directed to the field of Oncology, and in particular, embodiments directed to a method of ameliorating, treating, or preventing a malignancy in a human subject wherein the steps of the method assist or boost the immune system in eradicating cancerous cells. In certain embodiments, administration of beneficial bacteria to an individual's microbiome that have been modified so as to produce effective amounts of desired compositions, compounds, agents, e.g. tomatidine, p53 protein, etc., is employed to address cancerous conditions. In several embodiments, the administration of such beneficial bacteria and microbes to an individual's microbiome invokes either an active (or a passive) immune response to destroy, weaken or render less invasive certain cancerous cells, and preferably maintains muscle tissue to combat cancer cachexia.
Owner:KOVARIK JOSEPH E +1
Methods for diagnosis and treatment of chronic immune diseases
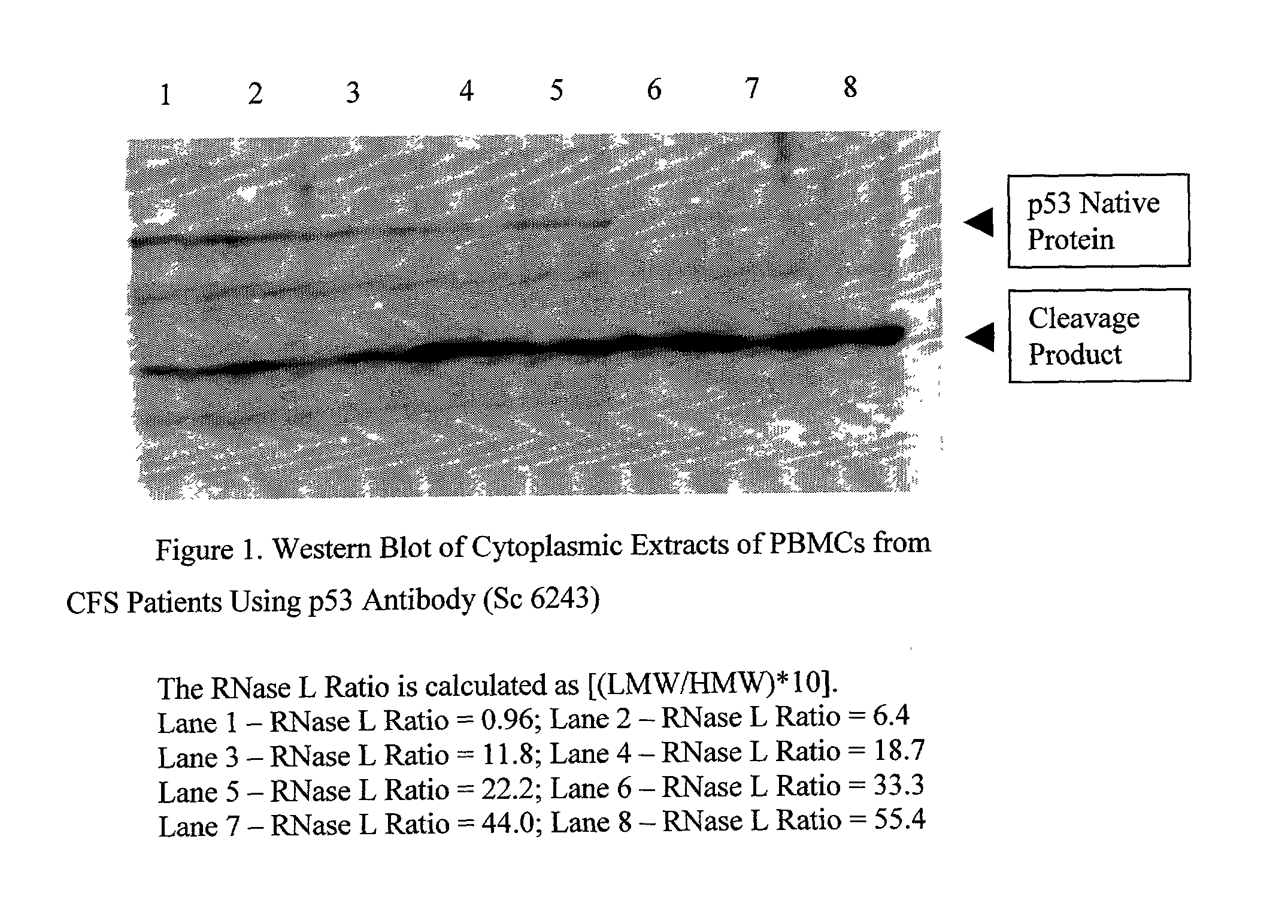
InactiveUS20030017492A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingProper treatmentP53 protein
Methods are provided for diagnosing / characterizing chronic immune disease activity in a subject. In the subject methods, a sample is obtained from a subject suspected of having or known to have a chronic immune disease. The sample is then assayed for the presence and amount of intact (i.e., native) p53 protein and / or fragments thereof. The assay results are used to diagnose the presence of chronic immune disease and / or characterize chronic immune disease activity in a subject, and / or to determine appropriate treatments protocols. Also provided by the subject invention are methods of treating chronic immune disease conditions by enhancing p53 activity. Also provided by the subject invention are kits for practicing the methods.
Owner:PROTEA BIOPHARMA
Nanometer vesica capable of detecting wild type p53 protein and variant p53 protein in cells simultaneously
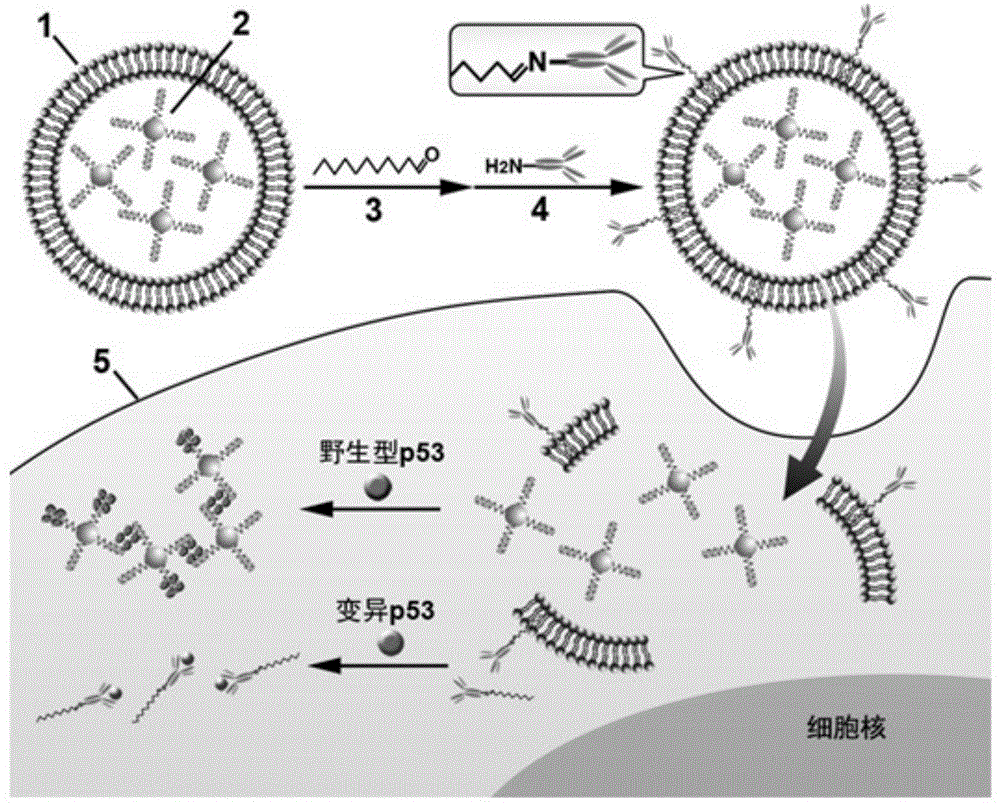
InactiveCN104977277AAchieving Simultaneous DetectionImprove featuresFluorescence/phosphorescenceCell layerWild type
The invention discloses a nanometer vesica capable of detecting wild type p53 protein and variant p53 protein in cells simultaneously. Nanogold capable of specifically recognizing wild type p53 protein wraps inside the vesica, and an antibody resisting variant p53 protein marked by fluorescein isothiocyanate decorates the surface of the vesica. The nanometer vesica has the advantages that (1) the nanometer vesica recognizes different types of tumor suppressor proteins p53 with high specificity, and the detection specificity and the sensitivity are improved; (2) plasma resonance imaging and fluorescence imaging technologies are adopted, after the vesica enters the cell, the cell is subjected to in-situ imaging by adopting a microscope, and wild type p53 protein and variant p53 protein on the single-cell layers are detected simultaneously; (3) the nanometer vesica designed according to the technical scheme is capable of carrying out in-situ monitoring on variation of expression of p53 protein in the cell under the action of medicine, and a novel method is provided for researching physiological process in the cell participated by the vesica.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method and system for treating cancer and other age-related diseases by extending the healthspan of a human
ActiveUS10314865B2Extend healthy lifespanProlong lifeBacterial antigen ingredientsHydrolasesCancer preventionMicrobiome
Owner:SEED HEALTH INC +1
Method of expanding nk cell and composition for culturing
InactiveUS20170119865A1Increase the number of cellsEfficiently obtainedHydroxy compound active ingredientsCulture processP53 proteinTumor cytotoxicity
Provided are a method of ex-vivo culture of natural killer (NK) cells by treating the cells with a reactive oxygen species (ROS) inhibitor and / or a p53 protein inhibitor; and a composition comprising the cultured NK cells. By reducing the activity of ROS and p53 proteins during ex-vivo culture, NK cells may have achieved greater expansion efficiency without altering their anti-tumor cytotoxicity.
Owner:KOREA UNIV RES & BUSINESS FOUND
Peptides selectively lethal to malignant and transformed mammalian cells
The present invention provides peptides corresponding to all or a portion of amino acid residues 12-26 of human p53 protein, which peptides are lethal to malignant or transformed cells when fused to a membrane-penetrating leader sequence. The subject peptides are thus useful in treating neoplastic disease in an animal, preferably a human. Also provided are pharmaceutical compositions comprising the subject peptides admixed with a pharmaceutical acceptable carrier. Methods of treating neoplastic disease in a patient by administering a subject peptide fused at its carboxy terminal end to a membrane penetrating leader sequence are also provided. The present invention also provides replication incompetent Adenovirus (AdV) vectors comprising a promoter sequence operably linked to a nucleotide sequence encoding a subject peptide. Methods of selectively killing cancer cells in a subject by administering a therapeutically effective amount of a subject AdV vector are also provided by the present invention.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Method for establishing colon cancer prognosis prediction model
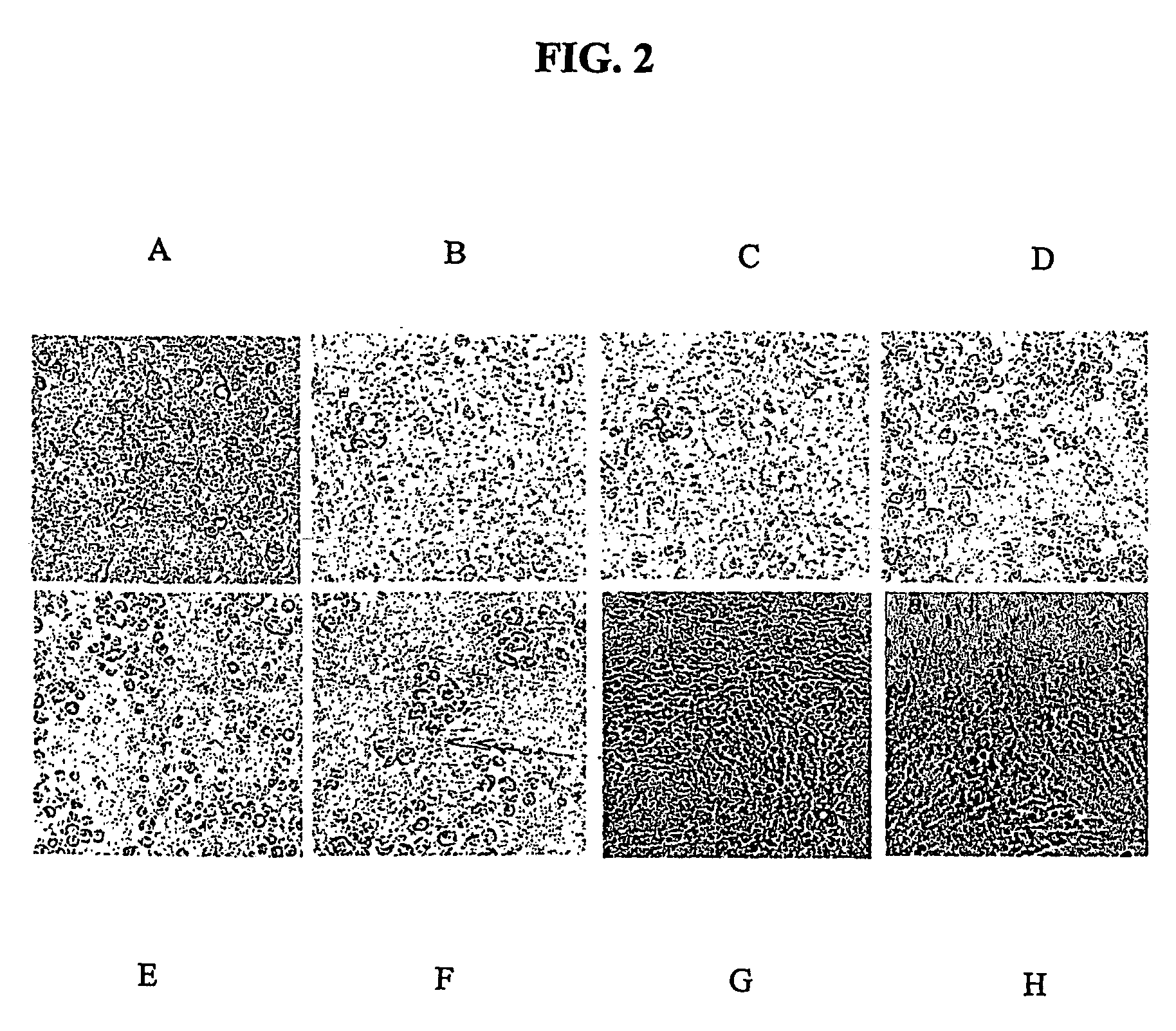
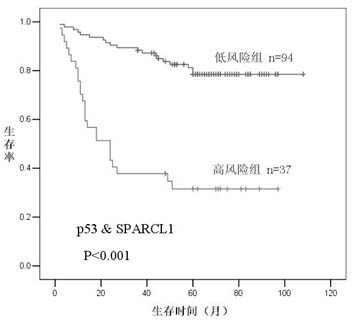
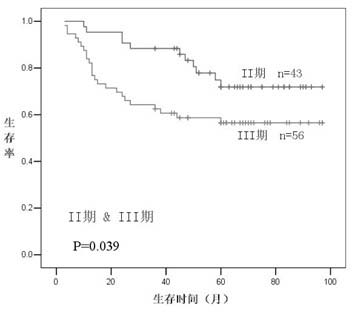
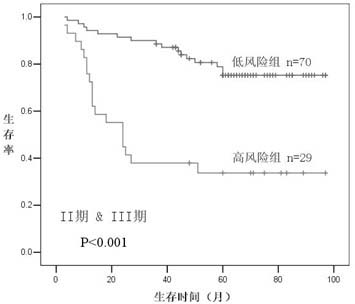
The invention provides a method for establishing a colon cancer prognosis prediction model. The method comprises the following steps of: detecting the expression levels of SPARCL1 and P53 proteins in colon cancer tissues by immunohistochemistry; grading the tissue expression levels of the SPARCL1 and P53 proteins by a semi-quantitative method; and combining, analyzing and verifying the expression levels of the SPARCL1 and P53 proteins through a support vector machine, and finally establishing a judgment model. Immunohistochemistry detection, marker combination and support vector machine analysis are combined for establishing the colon cancer prediction model. The research shows that the model constructed by using the composition of the SPARCL1 and the P53 as a marker has experiment aid effect of predicting the prognosis of colon cancer patients. The model can be applied in postoperative transfer relapse risk prediction experiments of the colon cancer patients.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method and system for treating cancer cachexia
ActiveUS9585920B2Foster the retention of muscle mass in the individualRestore healthOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsMuscle tissueCancer cell
Various embodiments of the present invention are directed to the field of Oncology, and in particular, embodiments directed to a method of ameliorating, treating, or preventing a malignancy in a human subject wherein the steps of the method assist or boost the immune system in eradicating cancerous cells. In certain embodiments, administration of beneficial bacteria to an individual's microbiome that have been modified so as to produce effective amounts of desired compositions, compounds, agents, e.g. tomatidine, p53 protein, etc., is employed to address cancerous conditions. In several embodiments, the administration of such beneficial bacteria and microbes to an individual's microbiome invokes either an active (or a passive) immune response to destroy, weaken or render less invasive certain cancerous cells, and preferably maintains muscle tissue to combat cancer cachexia.
Owner:KOVARIK JOSEPH E +1
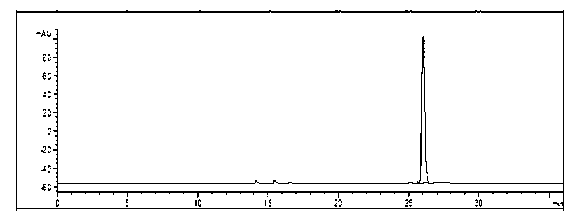
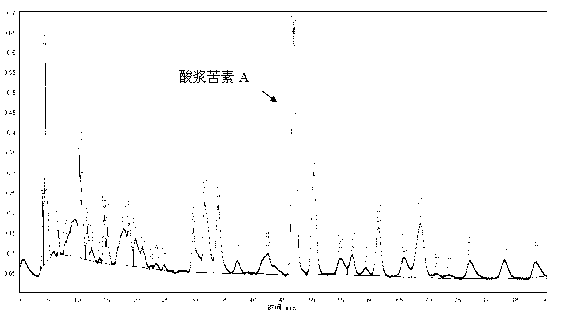
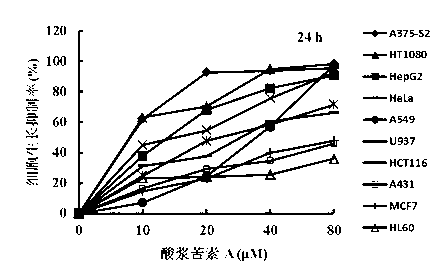
Physalin A extracting process and medical application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicines, in particular relates to a physalin A extracting process and medical application thereof, in particular relates to a novel application of physalin A in preparation of an anti-tumor dug and in particular relates to the use of physalin A in treatment of human fibrosarcoma and human malignant melanoma. After process optimization, the extracting rate of physalin A is 0.2133%. Physalin A can be used for inhibiting the growth of various tumor cells, particularly has obvious inhibiting action on the growth of the human fibrosarcoma and human malignant melanoma, but does not inhibit the activities of the human normal cells obviously. The mechanism is that the downstream caspase family-associated protein is activated by activating Fas death receptors, so that the tumor cells are induced to generate apoptosis. Meanwhile, the physalin A can be used for inducing the tumor cells to generate autophagy for achieving autophagy antagonism apoptosis in the HT1080 and the A375-S2 cells; and the p53 protein and the MAPK (Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase)-familty p38 protein have a key regulation effect. The physalin A can be used for preparing a digestive tract dosage form or a non-digestive tract dosage form, which can be used for treating tumors including the human fibrosarcoma and human malignant melanoma.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
P53 fusion protein and application thereof
InactiveCN101987873APeptide/protein ingredientsMacromolecular non-active ingredientsEscherichia coliInclusion bodies
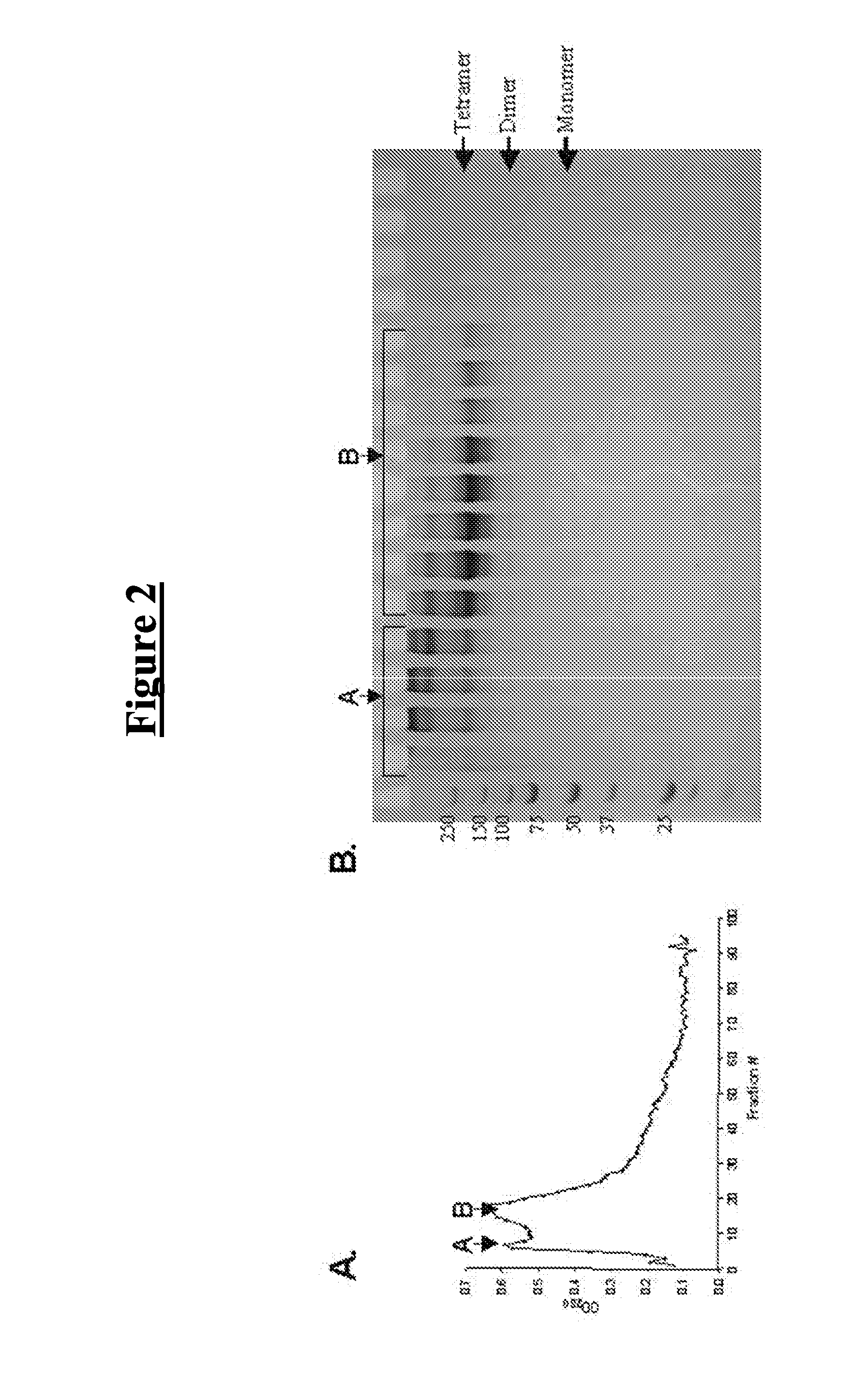
The invention relates to a p53 fusion protein and an application thereof. The invention provides the p53 protein and the p53 fusion protein in the tetrameric shape having the bioactivity. In the invention, the p53 protein and the p53 fusion protein inclusion body is produced by using the recombination expression by escherichia coli, and the inactivated p53 protein and the p53 fusion protein in the tetrameric shape and having the bioactivity are prepared by the renaturation and other steps. The invention also provides the medical application of the p53 protein and the p53 fusion protein.
Owner:PROTEOMTECH
Application of icariside II in preparation of anti-melanoma medicament
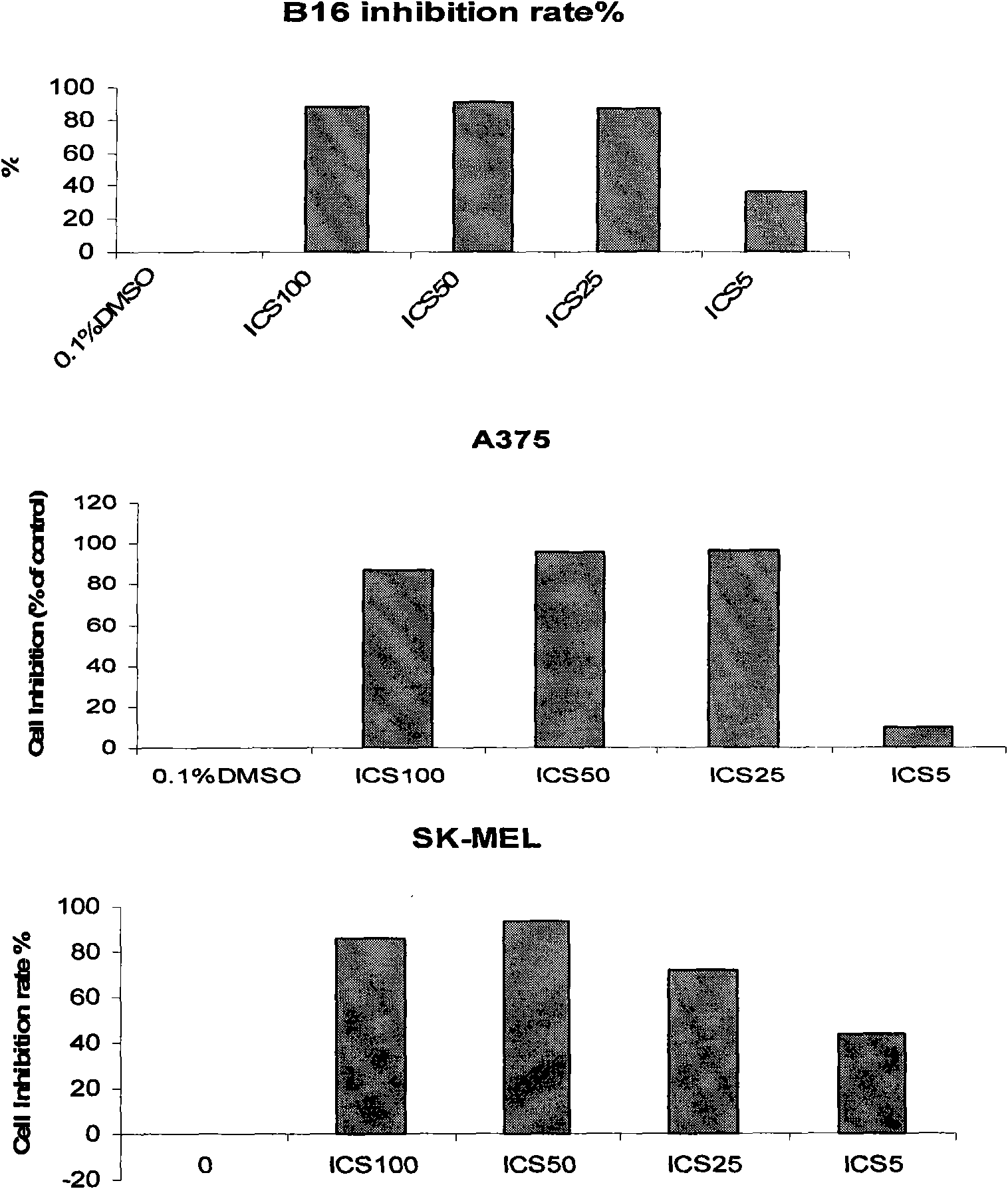
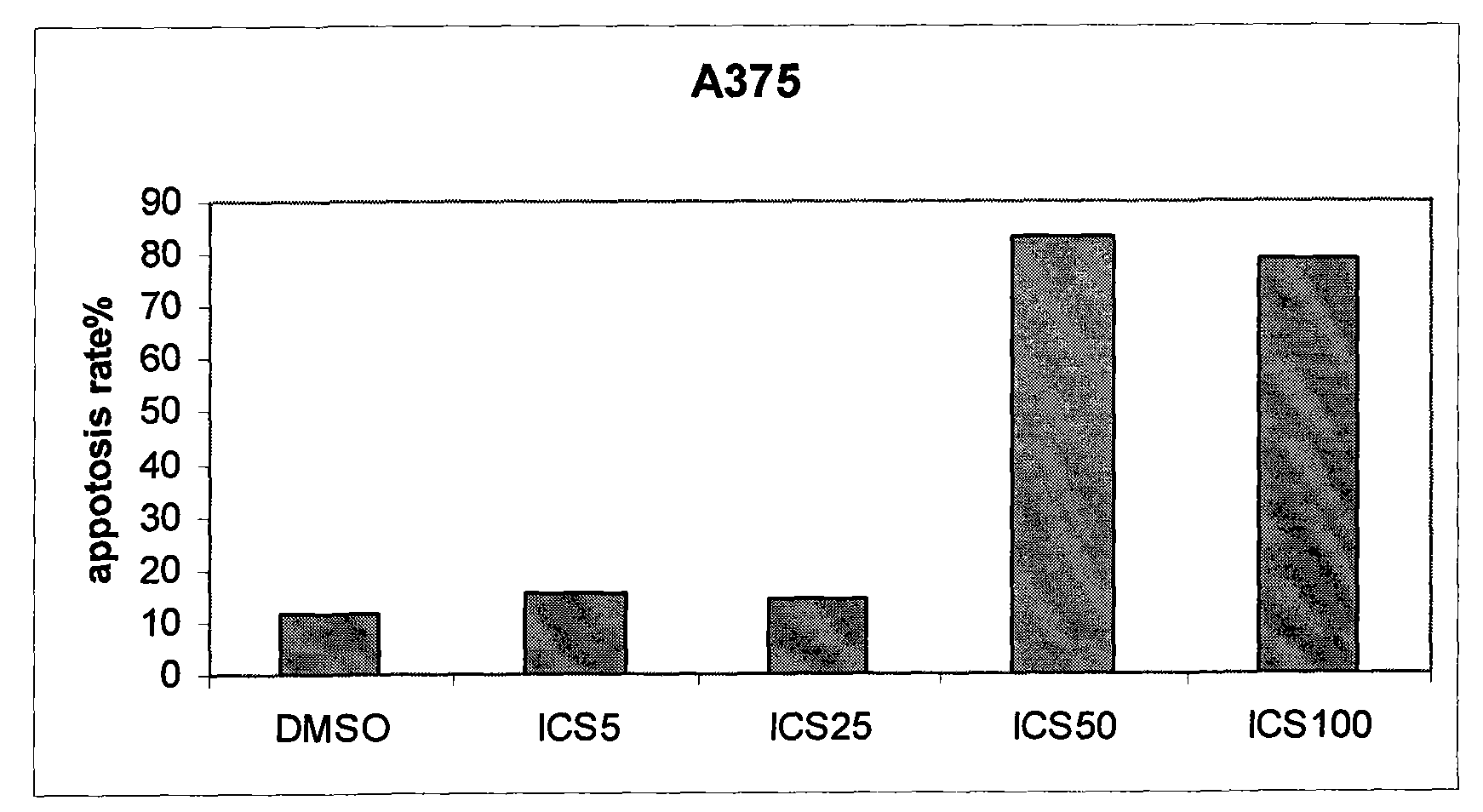
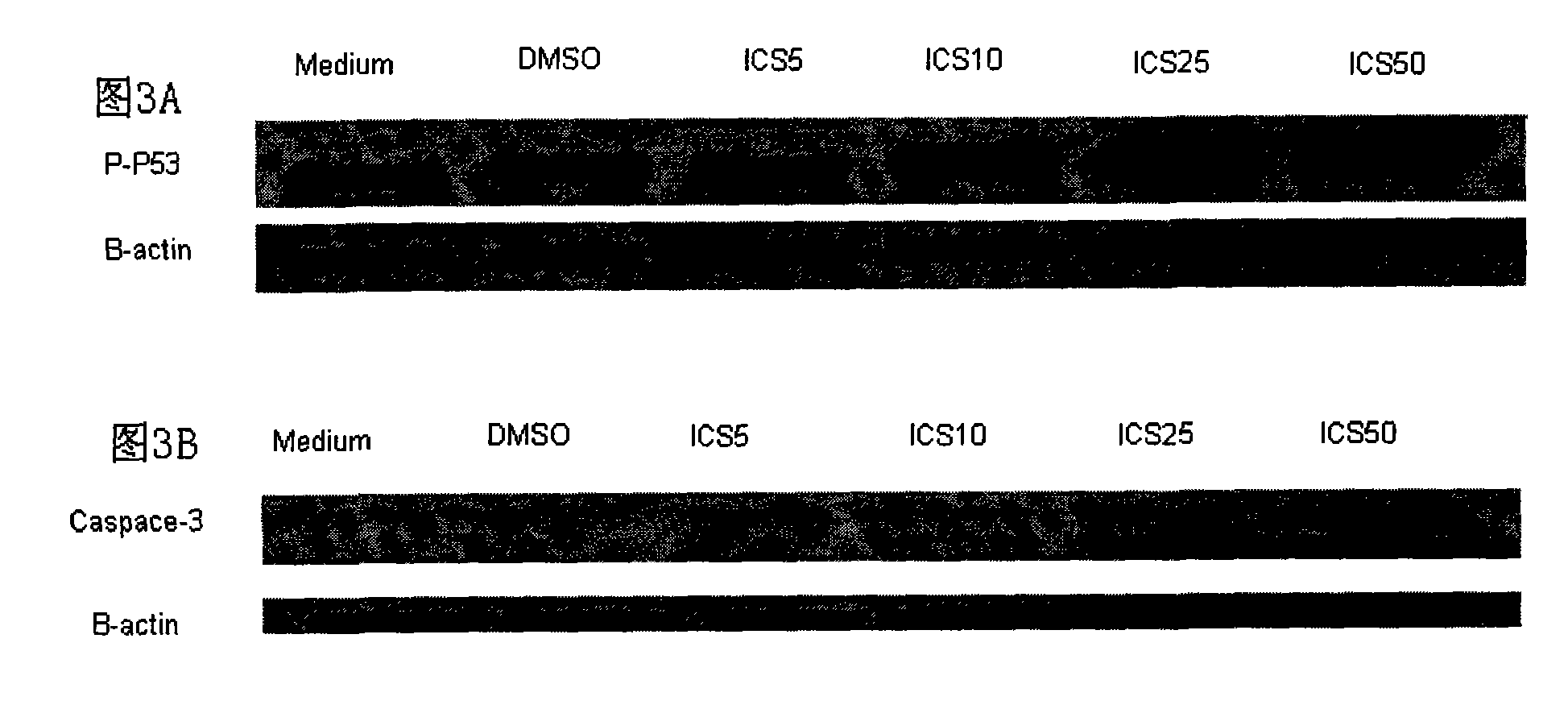
The invention belongs to the field of medicament preparation, relates to new medicinal application of icariside II, and particularly relates to application of icariside II in preparation of an anti-melanoma medicament. The icariside II is adopted for intervention experiments of mouse melanoma cell strains and human melanoma cell strains; by observing the inhibiting condition of the icariside II on cell proliferation, the results show that the icariside II can remarkably inhibit the proliferation of B16, A375 and SK-MEL-2 cells in vitro, obviously promote apoptosis of the cells and increase P53 protein phosphorylation and caspace protein expression; and the icariside II can remarkably inhibit loaded B16 mouse subcutaneous transplant tumor volume. Experiment results prove that the icariside II can effectively inhibit the melanoma. The icariside II can further be used for preparing the anti-melanoma medicament by adding proper pharmaceutically-acceptable carriers.
Owner:AFFILIATED HUSN HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV
A kind of small molecule inhibitor of mdmx/mdm2 and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN103923067BAvoid interactionProduce toxic side effectsOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsCancer cellSide effect
The invention relates to the technical field of medicinal chemistry, particularly discloses a small-molecule inhibitor of Mdm<X> / Mdm<2>, and also relates to a preparation method of the small-molecule inhibitor of Mdm<X> / Mdm<2>. The small-molecule inhibitor compound can inhibit the interaction of Mdm<X> protein and p53 protein and also can inhibit the interaction of Mdm<2> protein and p53 protein, has antiproliferative activity on cancer cells, and cannot generate toxic and side effects on patients. The small-molecule inhibitor compound can be combined with other therapies for use.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Method for regulating expression, quantity and activity of heat shock protein 70 and application thereof
ActiveCN102816792AIncreased sensitivityAdded treatment strategyPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsDeath ReceptorsTranscription Factor NF-kB
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and in particular relates to a method for regulating expression, quantity and activity of a heat shock protein 70 and application thereof. The method provided by the invention can also regulate tumor tissue, activity of a transcription factor NF-kB, expression and activity of a death receptor DR4 and DR5, phosphorylation and activity of JNK and c-Jun, expression and activity of a p53 protein, expression and proapoptotic activity of proapoptotic molecules Bax, Bid, t-Bid, capsase 3, capsase 8 and capsase 9, and expression and activity of c-FLIP and Bcl-2, and promote apoptosis of tumor tissues and cells. The invention also relates to application of the above method to preparation of drugs cooperatively applied with cell apoptosis induced drug.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
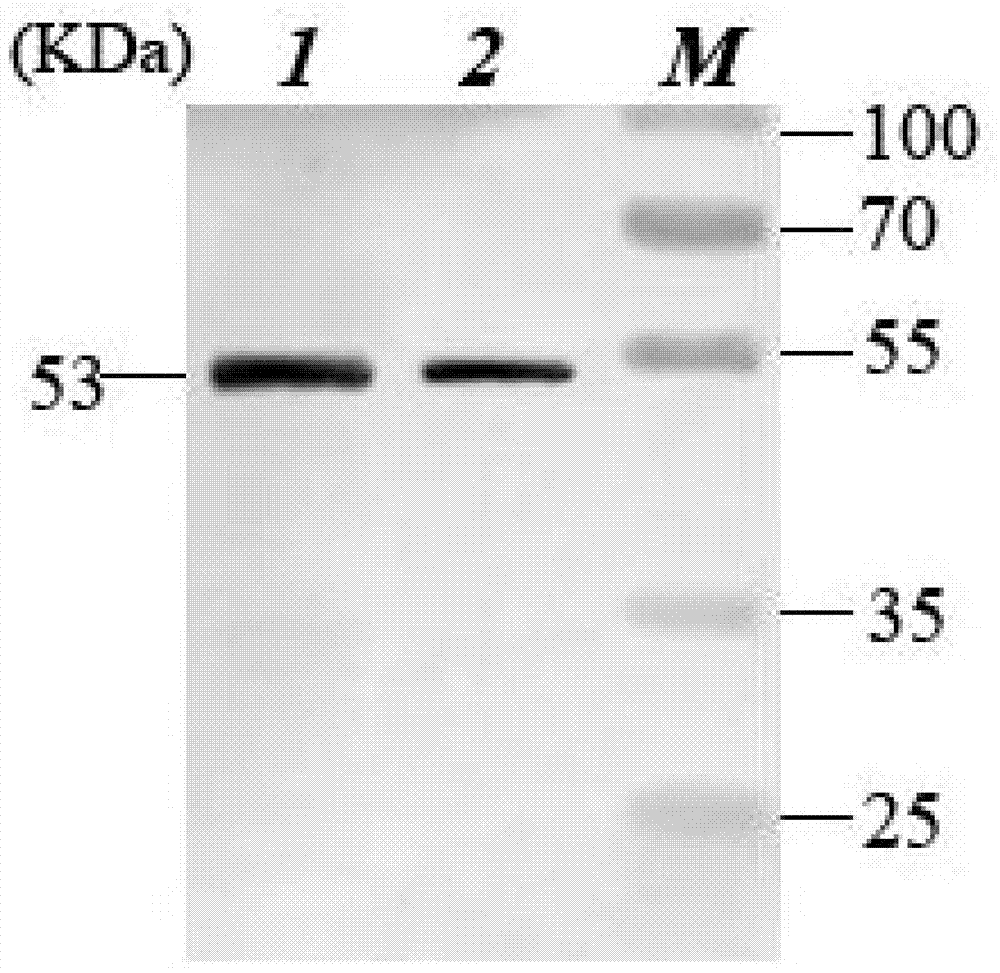
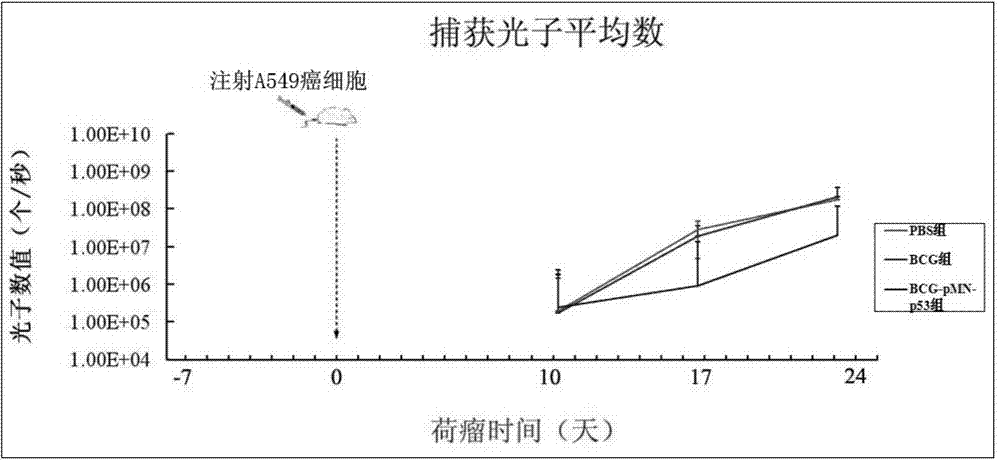
Recombination BCG viable bacterium strain capable of expressing and secreting human p53 protein, viable bacterium vaccine and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN103497926APlay a role in preventioPlay a therapeutic roleBacteriaGenetic material ingredientsVaccinationHuman tumor
The invention provides a recombination BCG viable bacterium strain capable of expressing and secreting human p53 protein, a viable bacterium vaccine and a construction method and application thereof, and relates to the technical field of biology, in particular to the technical field of genetic engineering. The novel viable bacterium vaccine capable of being used for prevention and treatment of human tumor diseases is provided. The recombination BCG viable bacterium strain is provided first, and the recombination BCG viable bacterium strain is a recombination strain which is obtained after a human p53 optimization gene sequence obtained after the preference of a codon is modified by a human p53 gene sequence for coding the human p53 protein referring to a BCG genome is led into the BCG viable bacterium strain. The invention further provides the construction method of the recombination strain and the viable bacterium vaccine obtained through the construction method. The viable bacterium strain can express and secrete the human p53 protein in cells, and zoology experiments show that the function for prevention and treatment of cancers can be achieved after the viable bacterium strain is used as a vaccination organism.
Owner:深圳市微宇生物科技有限公司
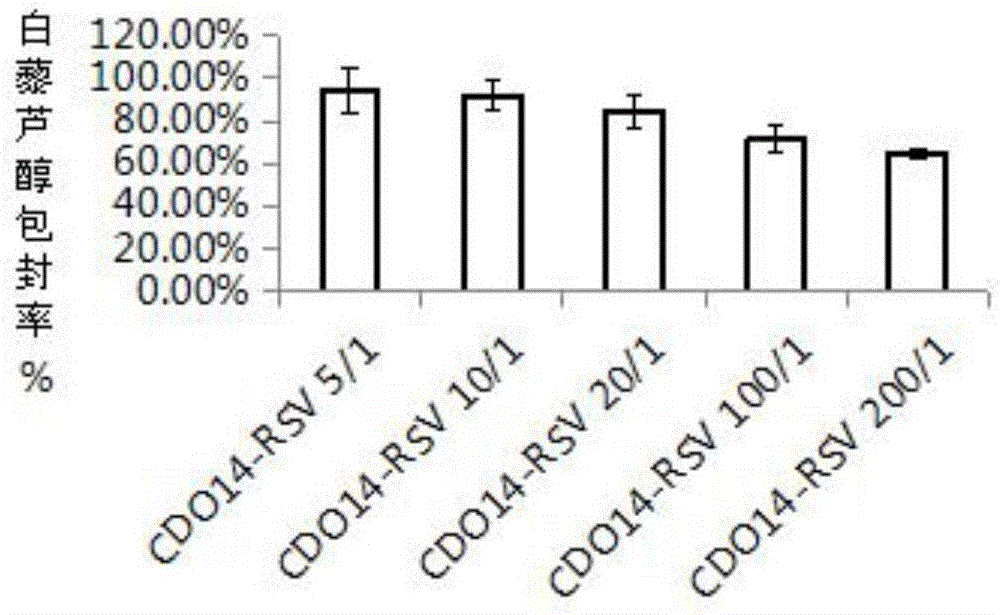
Drug liposome/p53 gene compound and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106692989ALow toxicityTo achieve the purpose of tumor treatmentHydroxy compound active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsWild typeP53 protein
The invention provides a drug liposome / p53 gene compound and a preparation method and application thereof. The compound is composed of a drug liposome containing resveratrol and a p53 gene. The invention further provides the preparation method of the drug liposome / p53 gene compound. The preparation method comprises the following steps: taking polypeptide type positive ion lipoid, auxiliary lipoid and the resveratrol as main raw materials, orderly adopting a film dispersion method, an ultrasonic hydration method and a gel chromatographic column separation method to prepare a drug liposome, and then mixing the drug liposome with the p53 gene to prepare the drug liposome / p53 gene compound through an electrostatic compounding method. The drug liposome / p53 gene compound provided by the invention activates the p38MAPK kinase activity through the resveratrol so as to induce the activation of the p53 gene, the p53 gene is enabled to express a wild type p53 protein, the antitumor effects of the resveratrol and the p53 gene are synergistically played to trigger the apoptosis of tumor cells, thereby achieving an aim of treating the tumor. The in vitro biological study shows that the compound has a certain cell proliferation inhibition ability, has high wild type p53 protein expression, provides a new thought for the tumor treatment and has a potential application value.
Owner:DALIAN NATIONALITIES UNIVERSITY
Methods for diagnosis and treatment of chronic immune diseases
Methods are provided for diagnosing / characterizing chronic immune disease activity in a subject. In the subject methods, a sample is obtained from a subject suspected of having or known to have a chronic immune disease. The sample is then assayed for the presence and amount of intact (i.e., native) p53 protein and / or fragments thereof. The assay results are used to diagnose the presence of chronic immune disease and / or characterize chronic immune disease activity in a subject, and / or to determine appropriate treatments protocols. Also provided by the subject invention are methods of treating chronic immune disease conditions by enhancing p53 activity. Also provided by the subject invention are kits for practicing the methods.
Owner:PROTEA BIOPHARMA
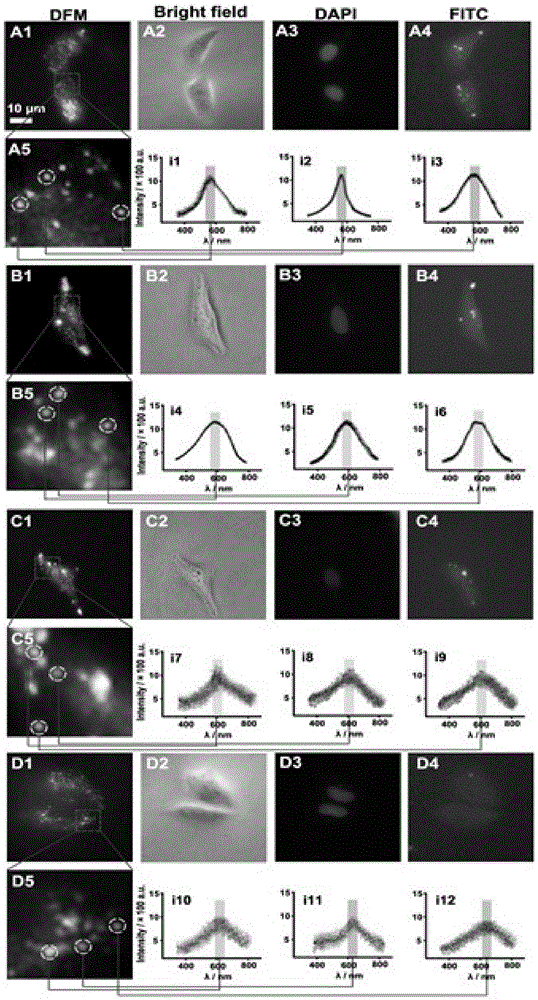
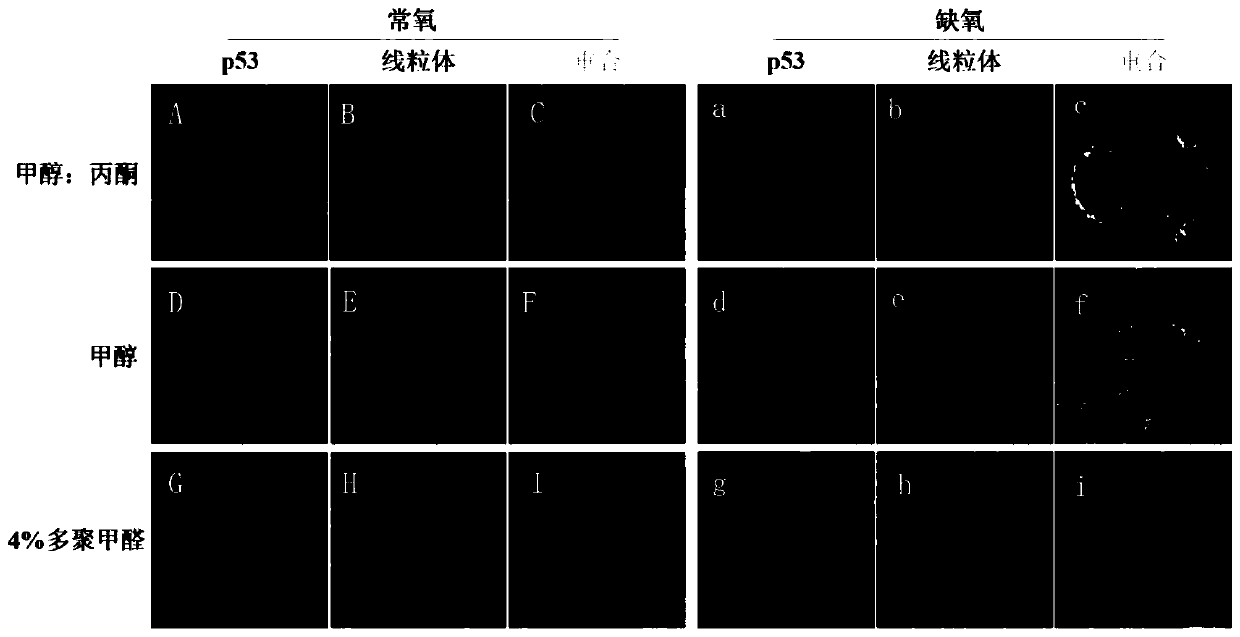
P53 protein and mitochondria double-labeled immunofluorescence detection method and kit thereof
The invention discloses a p53 protein and mitochondria double-labeled immunofluorescence detection method and a kit thereof. The detection method comprises the steps of: preparing a cell climbing piece, and performing cleaning; fixing the cell climbing piece with cell fixing liquid, and performing cleaning; sealing the cell climbing piece with cell confining liquid; adding primary antibodies for incubation, and performing rinsing, wherein the primary antibodies comprise an antibody combined with p53 protein and an antibody combined with mitochondria; adding a fluorescently labeled secondary antibody for dyeing, and performing incubation and cleaning; performing redyeing by using cell nucleus fluorochrome, and performing cleaning; sealing the piece, and observing a dyeing result via microscopic examination of a fluorescence microscope or via the microscopic examination of a confocal microscopy; and performing superposed analysis on fluorescent pictures. Only a cytomembrane is broken, anuclear membrane is not broken, intranuclear signal interference can be avoided, co-localization of p53 protein and mitochondria is realized, and basis and reference are provided for the positioning of the mitochondria of protein and the positioning study of the protein and other non-nuclear organelles.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
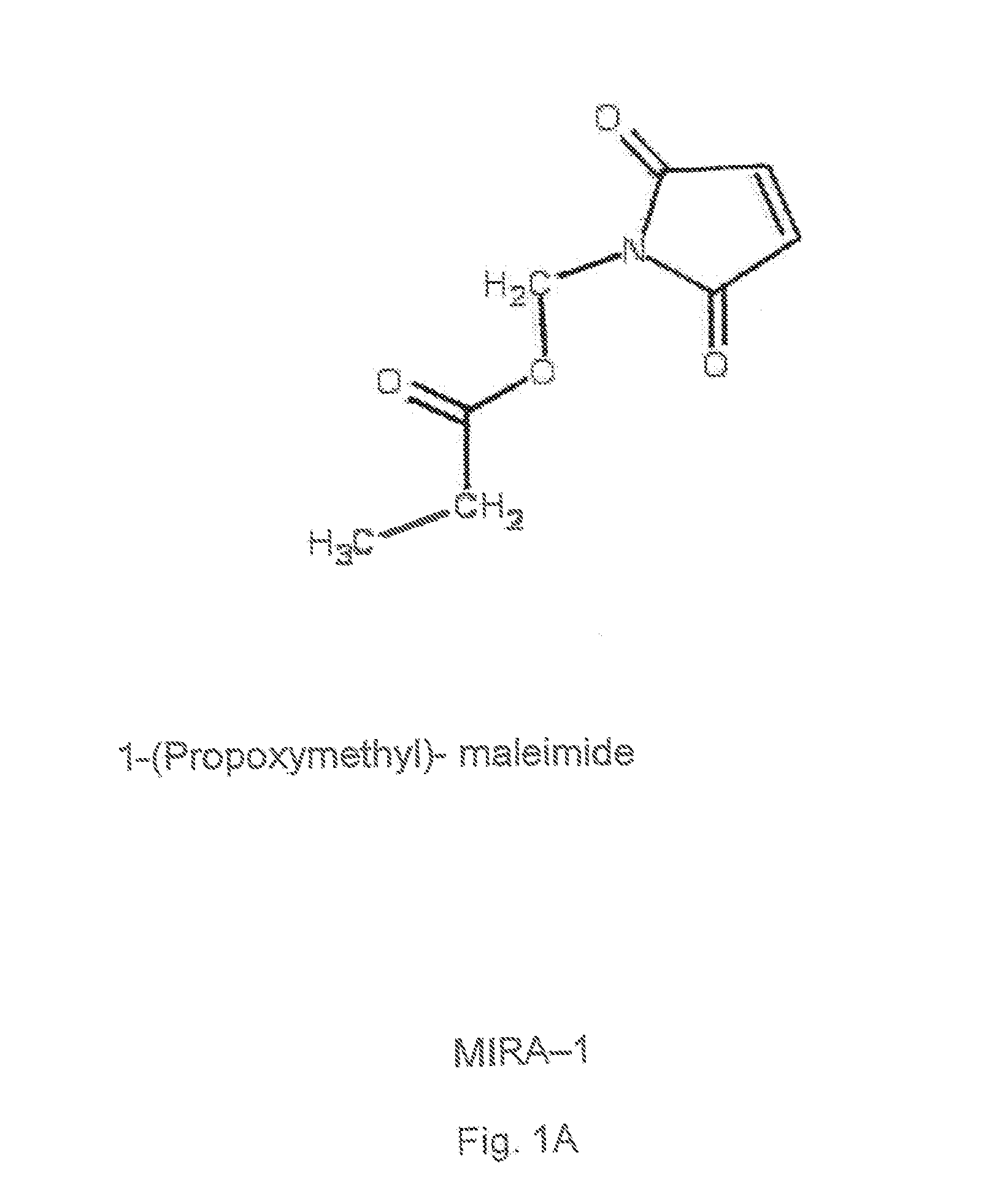
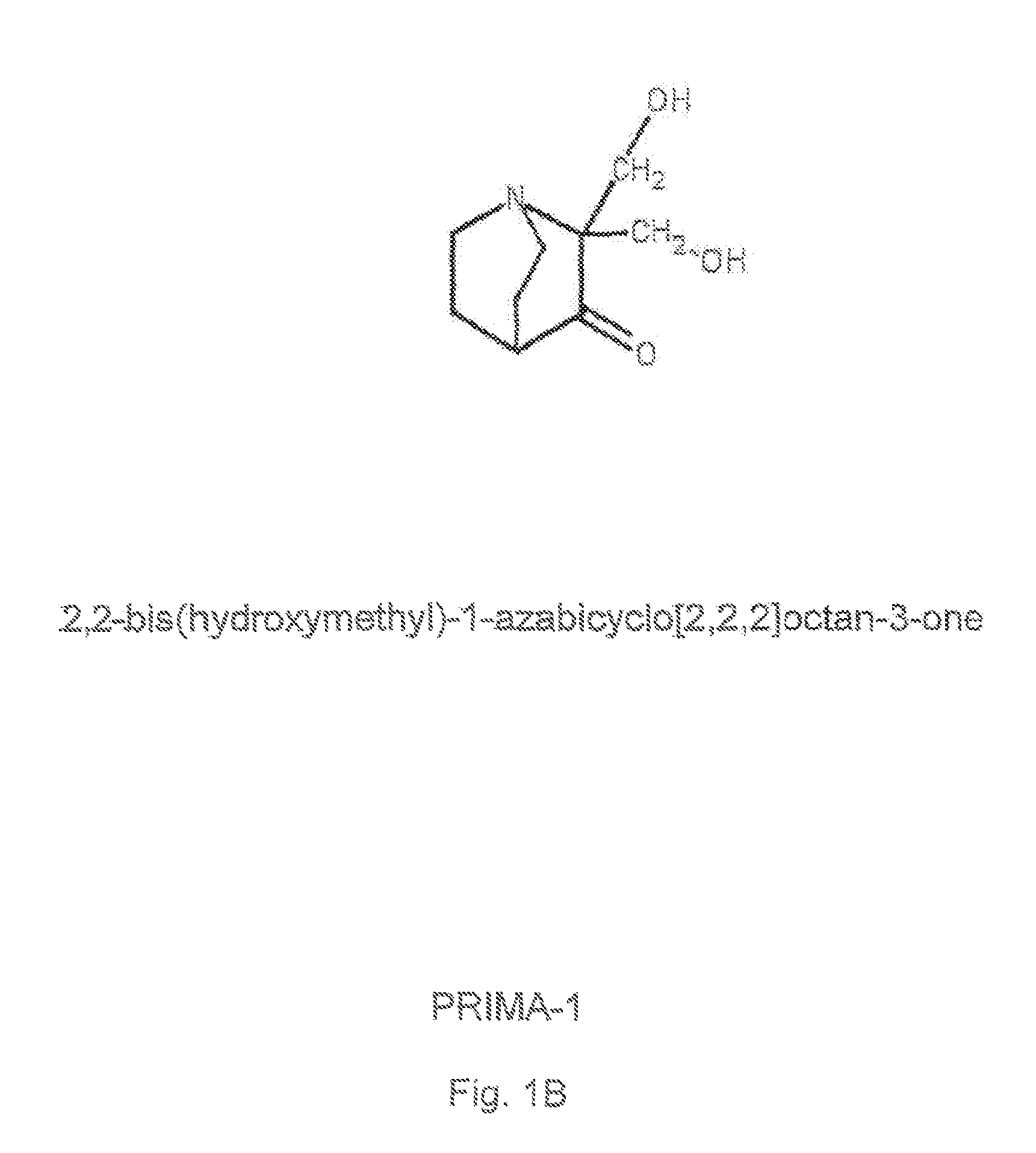
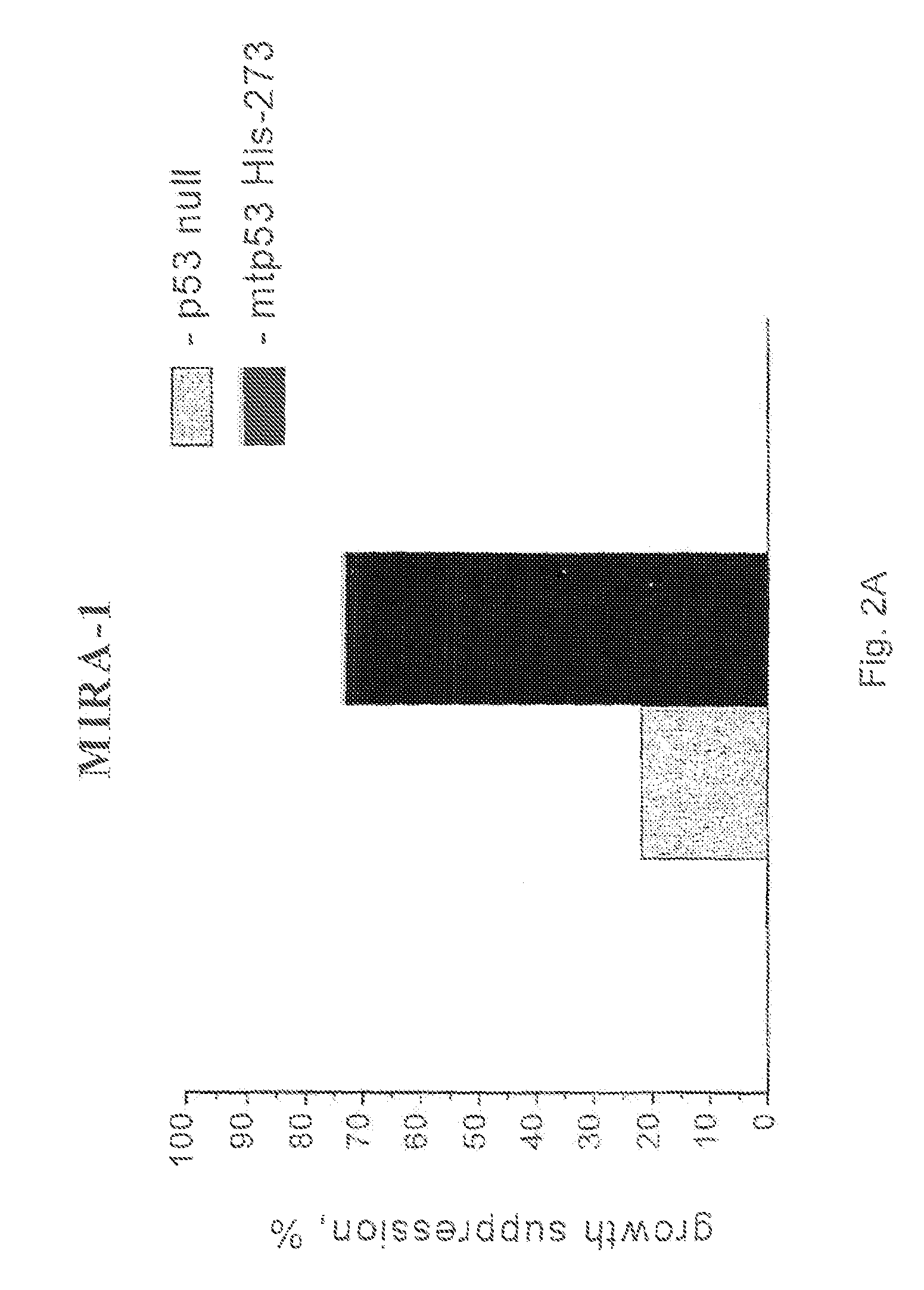
Use of low molecular weight compounds for preparing a medicament useful in treating mutant p53 mediated diseases
The present invention provides novel compounds, corresponding to formulae I and II, respectively, which are able to reactivate the apoptosis-inducing function of mutant p53 proteins. This reactivation is provided by restoration of sequence-specific DNA-binding activity and transcriptional transactivation function to mutant p53 proteins, and modulation of the conformation-dependent epitopes of the p53 protein. Accordingly, the substances according to the invention will be used in pharmaceutical compositions and methods for treatment of patients suffering from various types of tumours.
Owner:APREA THERAPEUTICS AB
Stable polypeptide protein targeted inhibitor and application thereof
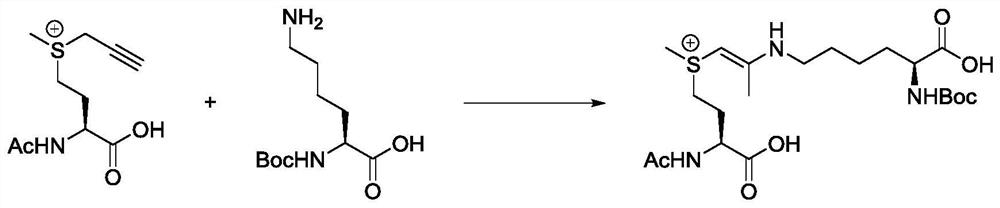
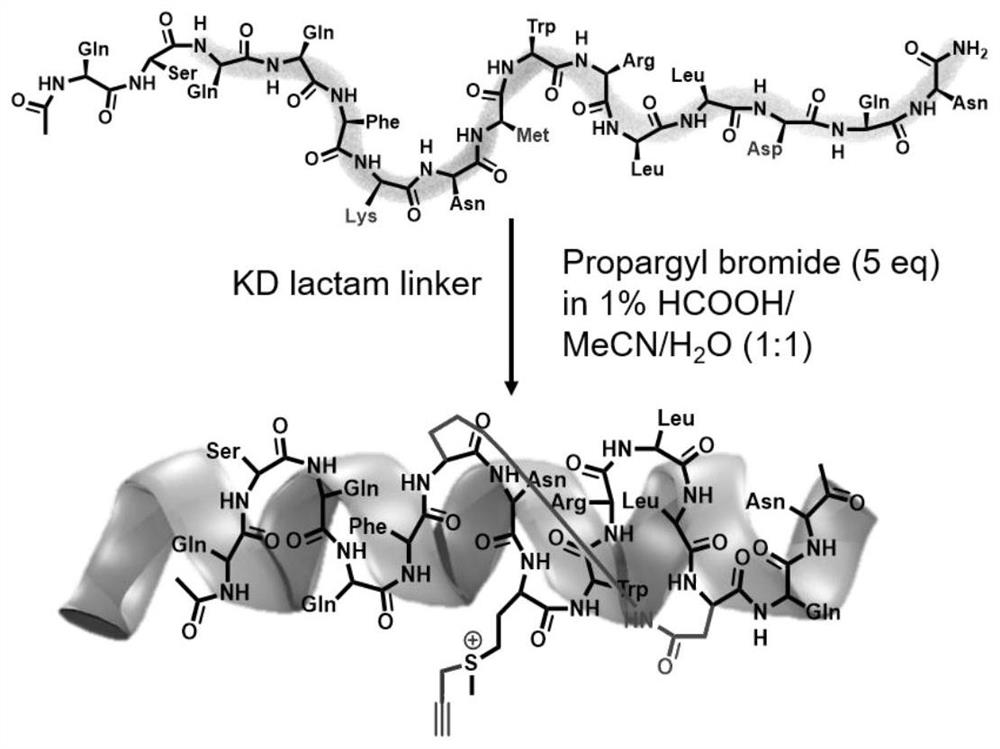
ActiveCN112794880AGrowth inhibitionAchieve covalent modificationPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptidesProtein targetMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
The invention provides a stable polypeptide protein targeted inhibitor, the amino acid sequence of the stable polypeptide protein targeted inhibitor is as shown in the specification: Ac-Q-S-Q-Q-F-K-N-Mq-W-R-L-L-D-Q-N-NH2, and Mq is as shown in the specification. The invention also provides application of the stable polypeptide protein targeted inhibitor in preparation of drugs for inhibiting MDM4 protein. Nuclear magnetism, secondary mass spectrometry and the like prove that polypeptide disclosed by the invention can be covalently bound with lysine on the MDM4 protein, so that the binding activity of the MDM4 protein and the p53 protein is influenced. Meanwhile, cell proliferation experiments also prove that the polypeptide can inhibit proliferation of breast cancer cells.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL +1
Kit for detecting prognosis of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Xinjiang region
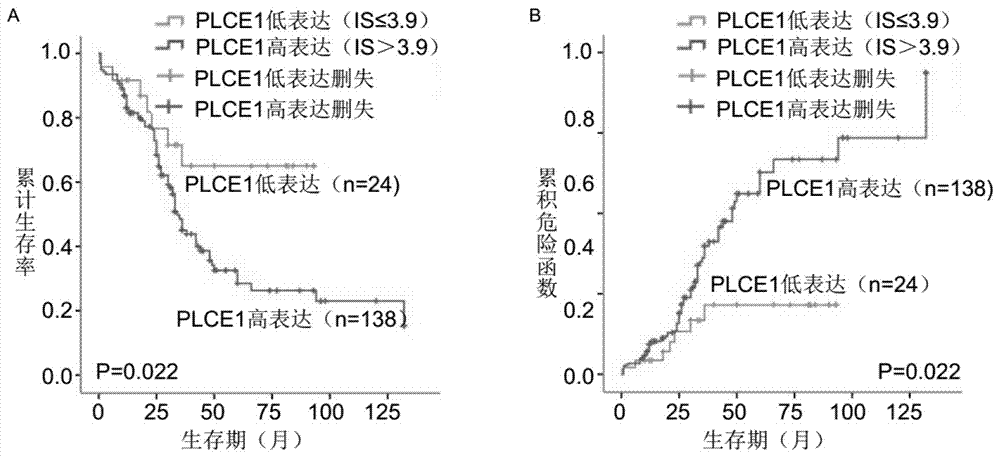
InactiveCN107966566AImprove predictive performanceSolve the current situation of lack of prognostic evaluation toolsBiological testingPhospholipasePhosphate
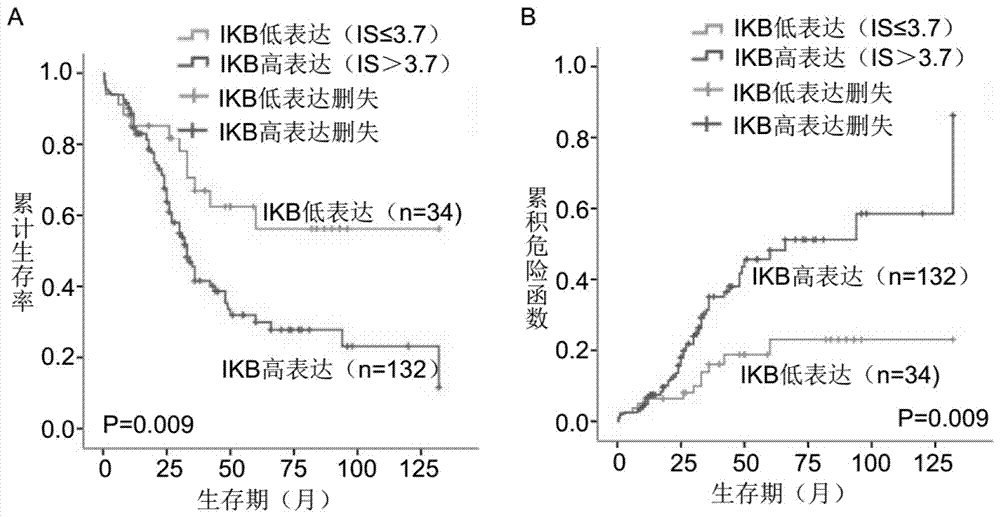
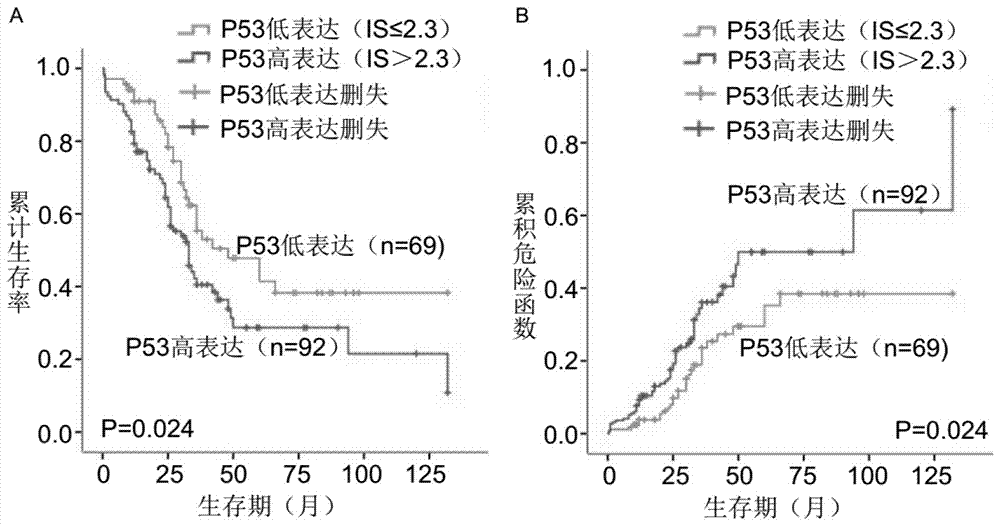
The invention provides a kit for detecting the prognosis of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in the Xinjiang region. The kit comprises a phospholipase epsilon 1 protein, an IKB alpha protein and a mutant P53 protein. The kit also comprises a citrate buffer solution with the content of 0.01M, an ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid repair solution with the content of 10mM, a H2O2 solution with the mass concentration of 3%, a phosphate buffer solution with the content of 0.01M, a BSA blocking solution with the mass concentration of 5%, an immunohistochemical Envision kit and a DAB developing reagent. The kit can forecast the prognosis of patients through detecting the expression case of the paraffin-embedded surgical specimen of the patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinomathrough PLCE1, IKB alpha and P53 proteins. Compared with the existing kit realizing single index detection, the kit has higher prediction effects and has the prediction ability similar to the TNM staged prediction ability. The two-step immunohistochemical method using the kit is a mature and reliable method that can be widely used in primary hospitals.
Owner:SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
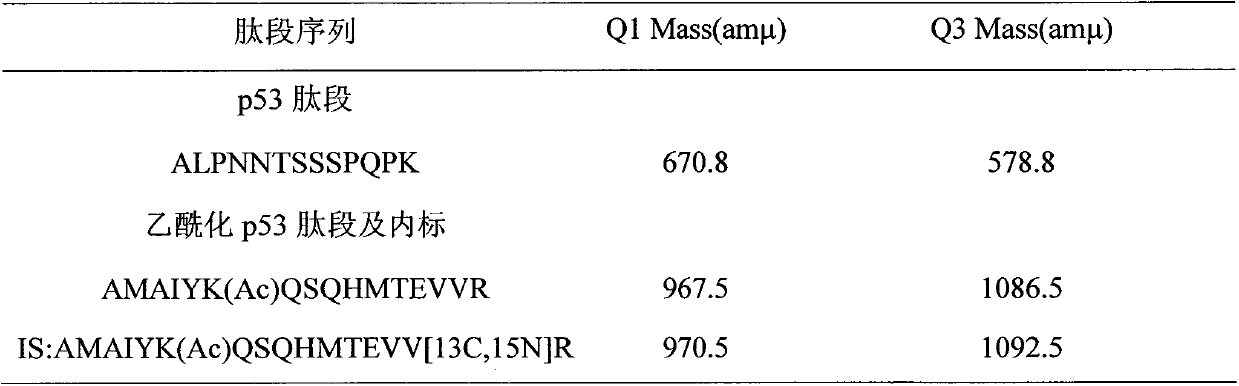
Human breast cancer cell acetylation p53 protein isotope labeling quantitative method
The invention belongs to the field of analysis and relates to breast cancer cell endogenous biological macromolecule acetylation p53 protein isotope quantitative analysis. The acetylation p53 protein in a complex cell matrix sample is extracted, separated and purified by utilizing the technical means such as co-immunoprecipitation and gel electrophoresis. The method comprises the following steps: by utilizing a strategy for performing qualitative and quantitative analysis on specific peptide fragments generated by performing trypsin hydrolysis on recombinant human p53 proteins and p53 proteins in breast cancer cells, by taking synthetic peptide fragments generated by performing stable carbon 13 and nitrogen 15 isotope labeling on amino acids in the specific peptide fragment sequence as interior labels, realizing quantitative analysis of acetylation p53 proteins on specific sites in a DNA binding domain in a breast cancer cell sample. The method mainly comprises a sample extraction and gel electrophoresis method, an Obitrap measurement method, preparation of a standard curve and measurement of precision and density. The method is good in linear relationship, high in accuracy and high in reproducibility and can be used for quantitative analysis of acetylation p53 proteins in cells.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
High-sensitivity protein detection method
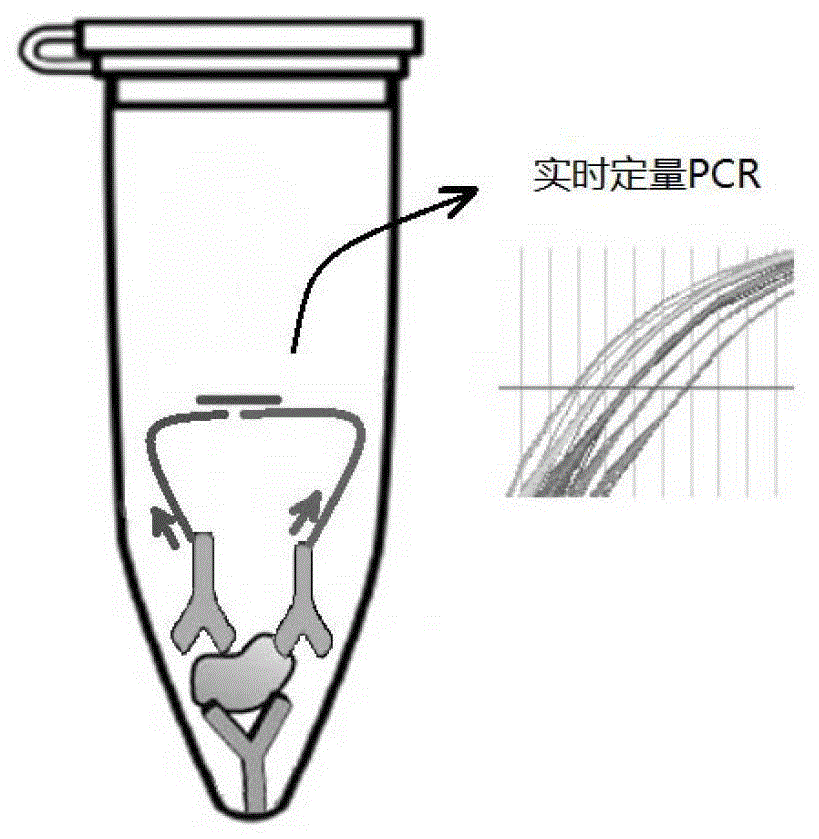
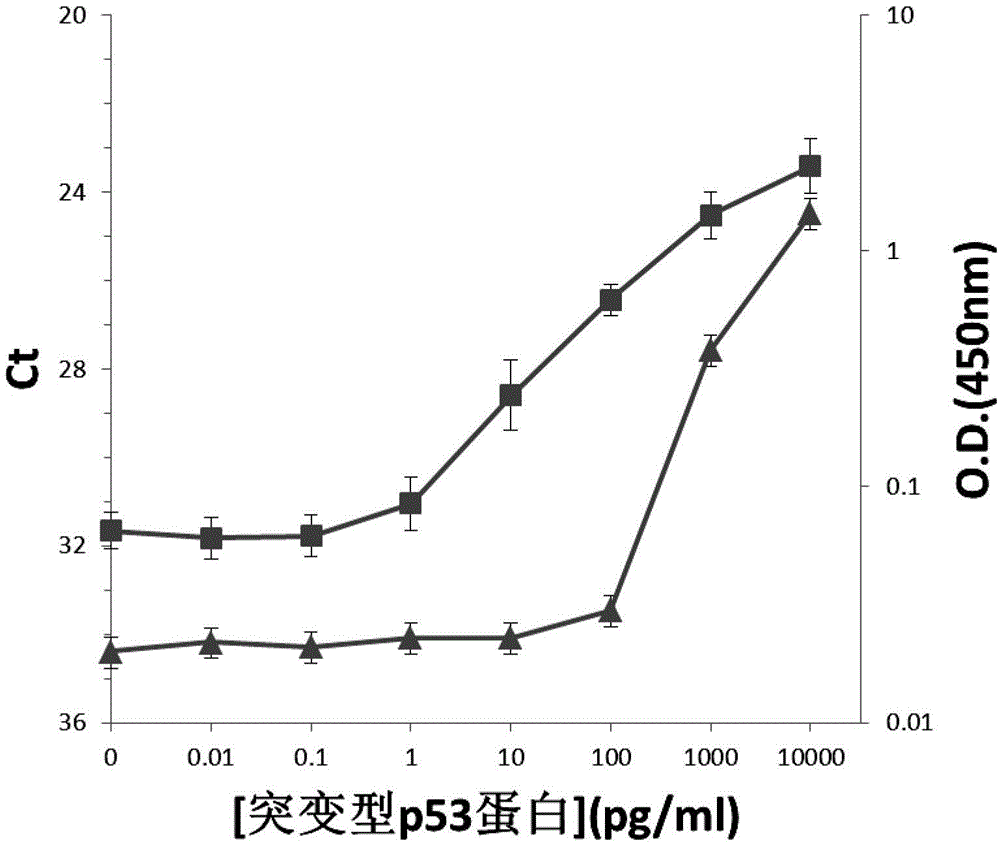
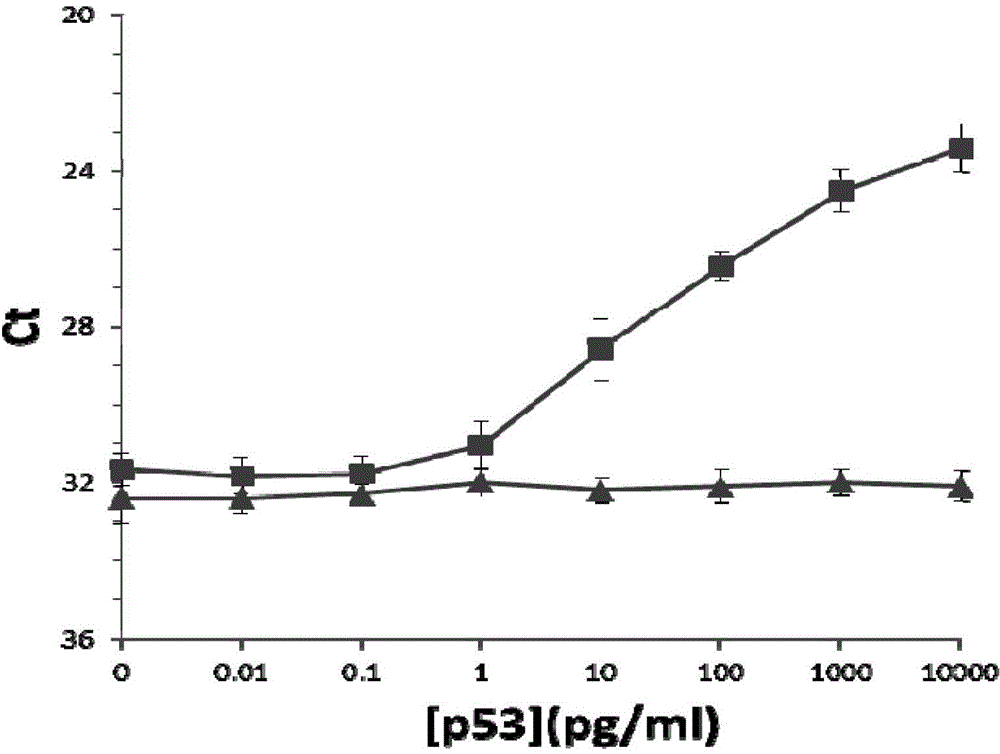
InactiveCN103276087BLow costGood effectMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingCross-linkProtein detection
The invention discloses a high-sensitivity protein detection method, wherein one of the following modes is selected optionally: mode 1, performing a tube wall solid phase PLA (proximity ligation assay) by a direct coating method, namely, directly adsorbing the protein or the antibody to a real-time fluorescence quantification PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) tube wall to perform PLA detection; and mode 2, performing a tube wall solid phase PLA by a cross-linking agent fixing method, namely, cross-linking the protein or the antibody to the real-time fluorescence quantification PCR tube wall by glutaraldehyde to perform PLA detection. Specifically, the method comprises the following steps of: using a monoclonal antibody pab240, and sequentially establishing PLA detection of P53 protein (P53 protein mutant) and cTnI (cardiac troponin I). According to the method disclosed by the invention, the antibody is fixed on a PCR tube so as to perform protein PLA detection, magnetic beads are not needed in the detection process, defects caused by application of the magnetic beads are overcome, and the detection sensitivity to the protein is also improved greatly.
Owner:HANGZHOU JINXI BIOLOGICAL TECH
Electronic mediator type enzymatic electrochemical immunodetection method of p53 protein
InactiveCN104483489AHigh sensitivityHigh selectivityBiological material analysisBiological testingElectricityElectrospinning
The invention discloses an electronic mediator type enzymatic electrochemical immunodetection method of p53 protein. The electronic mediator type enzymatic electrochemical immunodetection method specifically comprises the following steps: preparing an immune molecule immobilized active interface; constructing and optimizing an electronic mediator type enzymatic electrochemical immunoassay system; and performing quantitative detection on p53 protein. The method specifically comprises the following steps: performing electrostatic spinning and performing electropolymerization on thionine to obtain a PA6-MWCNTs-PTH immune molecule immobilized active interface, constructing the electronic mediator type enzymatic electrochemical immunoassay system on the PA6-MWCNTs-PTH interface by virtue of sandwich immunoreaction, performing relevant parameter optimization, and performing quantitative detection on p53 protein by using the constructed immunoassay system. The detection method disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of high sensitivity, high selectivity, high stability, regeneration performance, wide linear range, low detection limit and the like.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
P53 fusion proteins and methods of making and using thereof
Owner:PROTEOMTECH
Medicine for treating or preventing human cervical cancer as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN112870185ANovel mechanism of actionNon-addictiveInorganic non-active ingredientsEther/acetal active ingredientsMechanism of actionCervical ca
The invention discloses a medicine for treating or preventing human cervical cancer as well as a preparation method and application thereof, belongs to the technical field of medicines, and particularly relates to a medicine for treating or preventing human cervical cancer based on an MDM2-p53 protein and protein interaction signal channel and a target mechanism as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The invention finds that the action mechanism of the compound 1, 5, 6-trimethoxy-2, 7-dihydroxyphenanthrene is a new mechanism based on an MDM2-p53 protein and protein interaction signal pathway and a target spot. The medicine disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of novel action mechanism, no addiction and small dosage, and has the effect of inhibiting the growth of Hela cells. The IC50 on Hela cells for 48 hours is 0.42 [mu]M. And cell apoptosis can be caused by acting on an MDM2-p53 pathway, and meanwhile, mitochondrial apoptosis is caused.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
Methods and Compositions for Preventing Metastasis and for Improving the Survival Time
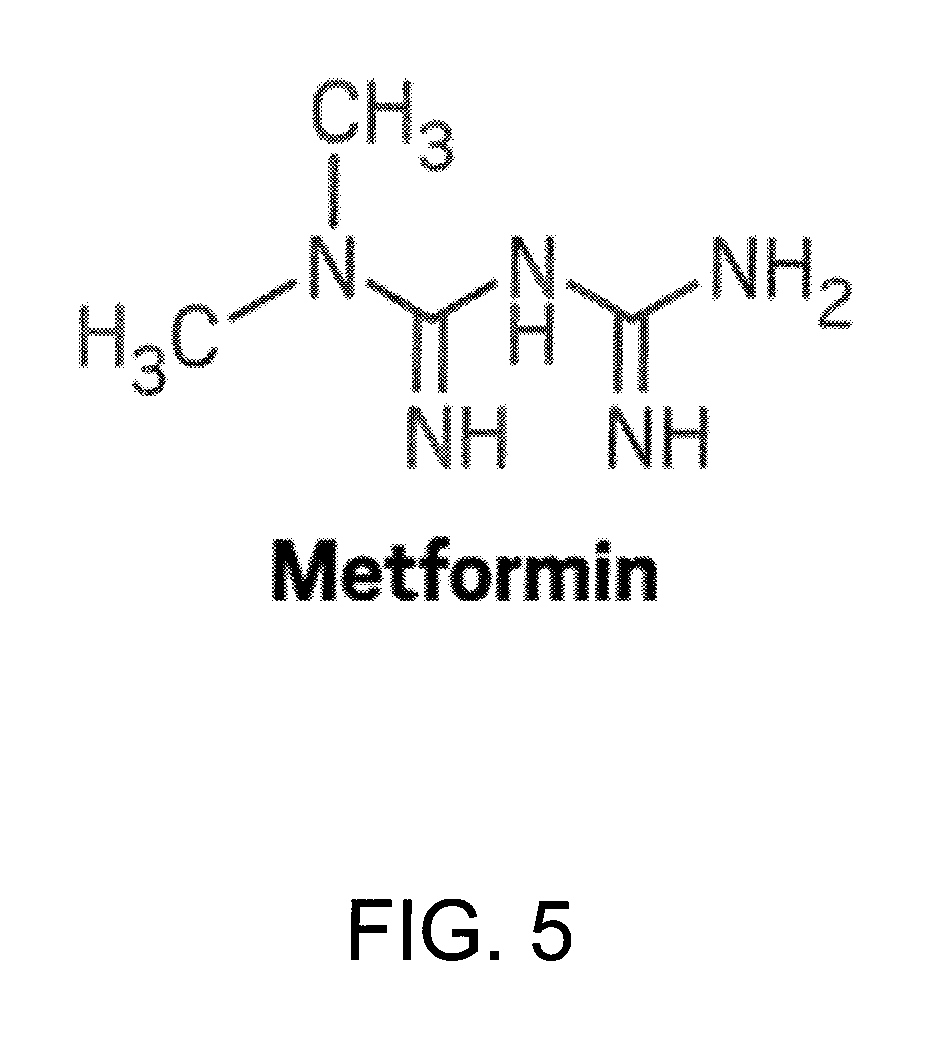
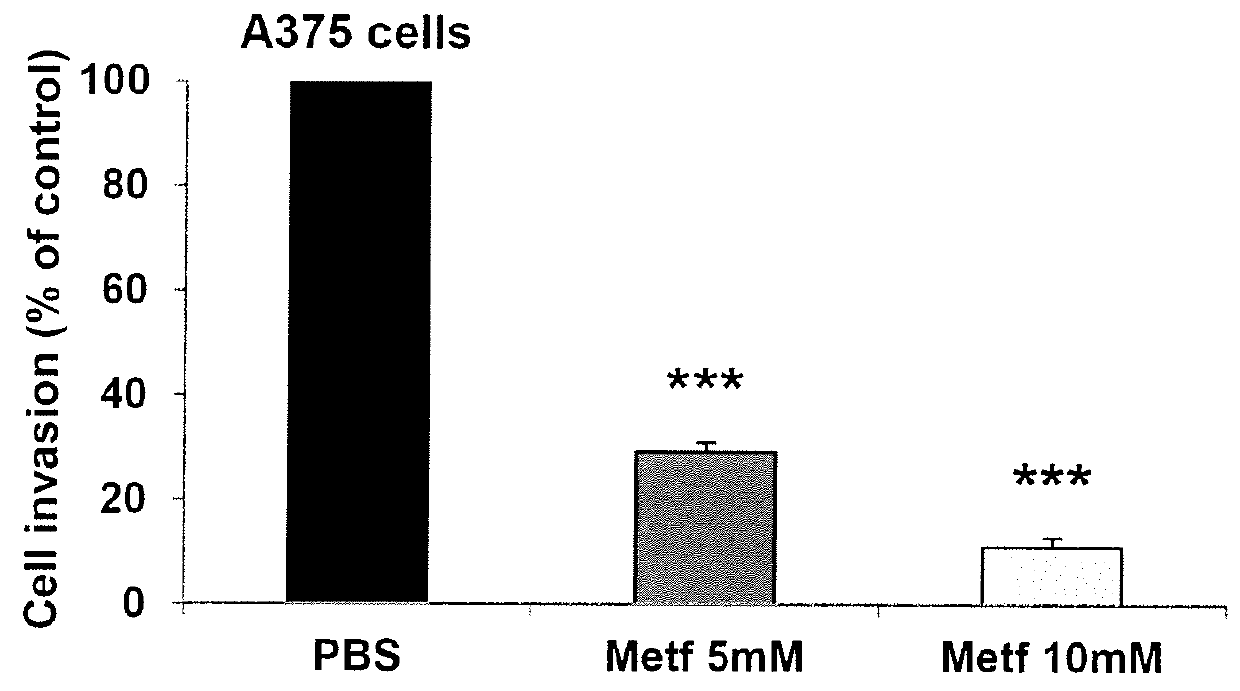
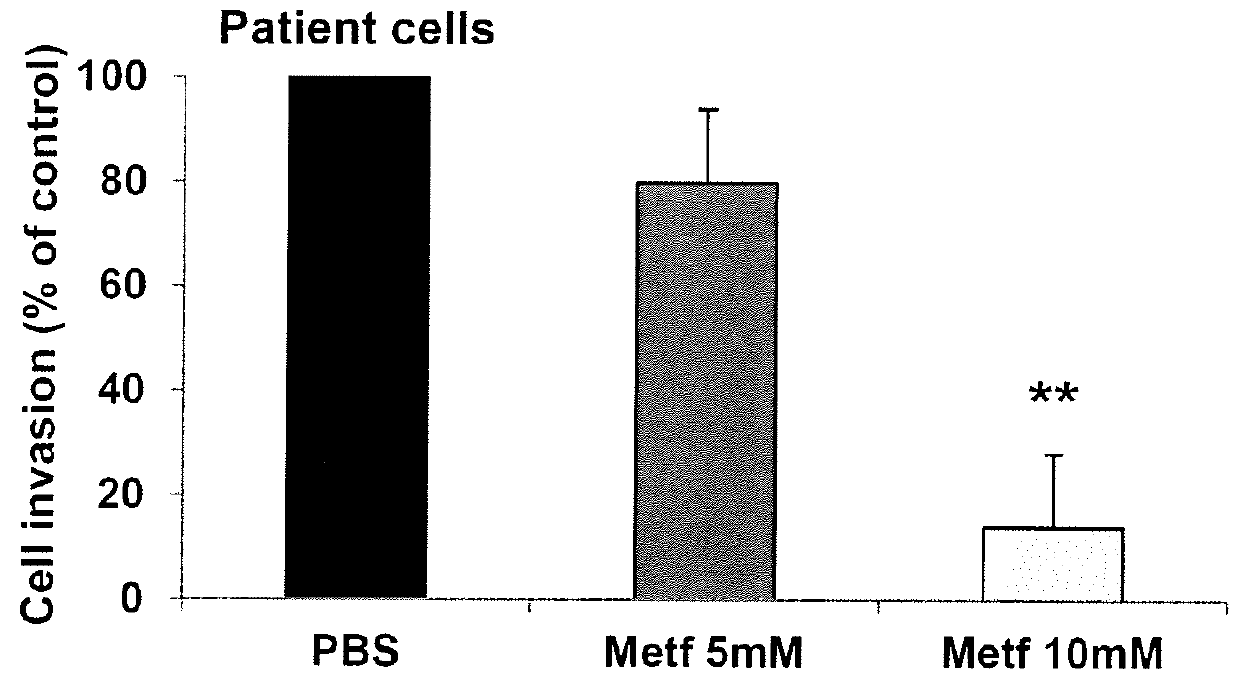
InactiveUS20160030367A1Prolong survival timeShort hybridization timeBiocideOrganic active ingredientsP53 proteinOncology
The invention relates to an AMPK activator (such as for instance metformin) for use in preventing metastasis in a patient suffering from a cancer, wherein said patient has a non-mutated p53 gene or lacks a mutant form of the p53 protein. The invention also relates to an AMPK activator for use in improving the survival time of a patient suffering from a cancer, wherein said patient has a non-mutated p53 gene or lacks a mutant form of the p53 protein.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com