Primer group using vtaA9 gene as target spot and application of primer group to identification and diagnosis of haemophilus parasuis
A technology of Haemophilus parasuis and primer set, applied in the field of specific primer set, reagent, primer set for identification and diagnosis of Haemophilus parasuis, which can solve the problems of inability to distinguish similar strains, enhanced specificity, and decreased sensitivity And other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
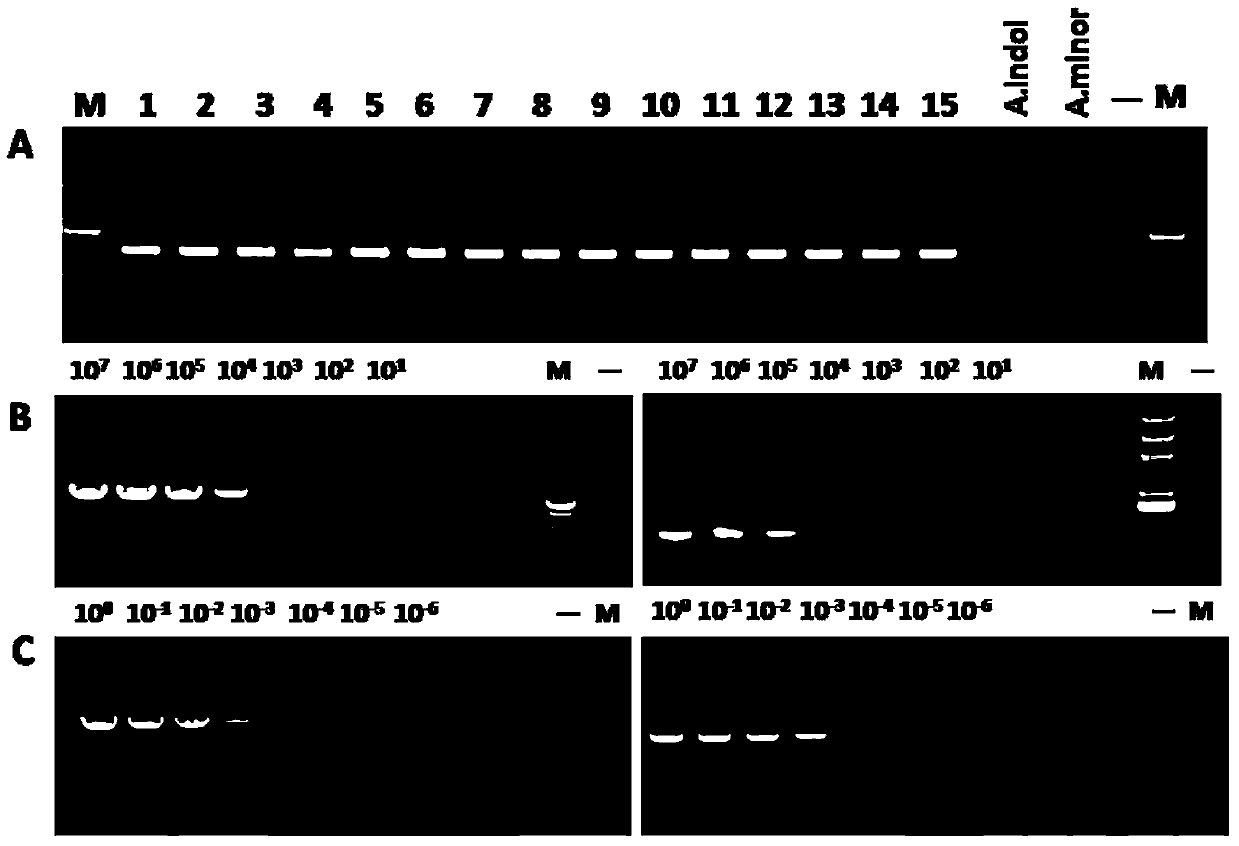
[0027] Example 1 The establishment of a PCR method for the identification and diagnosis of Haemophilus parasuis with the vtaA9 gene as the target and the sensitivity and specificity analysis
[0028] 1. Sample material
[0029] The samples of the present invention include 15 H.parasuis reference strains, see Table 1, 24 non-H.parasuis strains, and purified genomic DNA of 10 related strains, see Table 2. At the same time, 1.0 g sample was added to 500 μl PBS buffer solution from the clinically suspected H. parasuis infection material for grinding, and then the strains were directly separated and detected by PCR.
[0030] Table 1. H.parasuis reference strains used in the present invention
[0031]
[0032] Table 2 is applied to non-H.parasuis bacterial strains in the present invention
[0033]
[0034] H.parasuis isolated from disease materials were grown in solid TSA (Trypticase Soy Agar) and liquid TSB (Trypticase Soy Broth) medium, supplemented with NAD (10 μg / ml) and...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Example 2 Application of the PCR method with vtaA9 as the target in the identification and diagnosis of Haemophilus parasuis
[0059] In order to further describe the reliability of detecting Haemophilus parasuis clinical samples with vtaA9 as the target of the present invention. The present invention collects 121 clinical samples of 53 pigs infected with Haemophilus parasuis (H.parasuis) from 2008 to 2011. Samples were collected from different tissues and organs, including joint fluid, nasal swabs, heart, lung, and pleural effusion, and the disease materials were immediately sent to the laboratory for bacterial isolation and culture. At the same time, 1.0 g of the sample was added to 500 μl of PBS buffer solution for grinding, and then PCR detection was performed directly.
[0060] 90 and 88 of the 121 samples were positive by vtaA9PCR and 16S rRNA PCR respectively, the positive ratios were 74.4% and 72%, respectively, and 83 of the 121 samples were positive for bacte...
Embodiment 3
[0064] Example 3 Identification and typing of clinical isolates obtained by vtaA9 gene isolation
[0065]In Example 2, the vtaA9PCR method was used to detect and isolate 90 H.parasuis clinical isolates. They had typical H.parasuis characteristics. The biochemical reaction revealed that 90 clinical isolates were NAD-dependent and had no hemolysis. The use of urease is negative, and the positive of catalase is consistent with the results of Kielstein et al. (2001). The 90 H.parasuis clinical isolates showed different isolation sites and different isolation rates, the isolation rate of lung (n=34; 37.8%), the isolation rate of pleural effusion (n=14; 15.6%), the isolation rate of heart (n =13;14.4%), joint fluid separation rate (n=10;11.1%), tracheal separation rate (n=8,8.9%), brain separation rate (n=6;6.7%), nasal separation rate (n =4; 4.4%), tonsil separation rate (n=1; 1.1%). Similar to the results of Nedbalcova (2006), the success rate of separation and culture of pleura...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com