Complex insecticide of tung tree leaf extractive and Metarhizium anisopliae and preparation method thereof
A technology of Metarhizium anisopliae and its extract, applied in botany equipment and methods, insecticides, biocides, etc., can solve problems such as unused, discarded, and leaf shedding, and achieve poor quick-acting, waste reduction, and The effect of small environmental impact
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] The compound insecticide in this example is prepared from the following raw materials in mass percentage: 60% of tung tree leaf extract; 10% of spore powder of Metarhizium anisopliae; 10% of diatomite; 15% of polyoxypropylene ether; -400 5%.
[0028] The tung leaf extract is prepared according to the following method:
[0029] (1) Dry the tung tree leaves, crush them with a pulverizer, pass through a 200-mesh sieve, add methanol and acetone mixed extract (the volume ratio of methanol and acetone is 2:1), heat to 70°C and reflux for three times, The volume (ml) of the mixed extract of methanol and acetone added each time: the mass of tung tree leaf powder (g)=6:1, the extraction time of each reflux is 3 hours, after combining the extracts each time, use a rotary evaporator Carry out vacuum distillation to remove methanol and acetone until methanol and acetone are all volatilized to obtain tung tree leaf methanol and acetone mixture extract extract; volatilized methanol ...
Embodiment 2
[0048] The difference between this embodiment and Example 1 is that the mass ratio of each raw material component is: 50% of the tung leaf extract, 50% of the tung chafer metarhizium anisopliae ( Metarhizium anisopliae ) spore powder (the concentration of live spores is 10 10 pcs / g) 20%, talc powder 10%, sodium lauryl sulfate 10%, dispersant Z 10%.
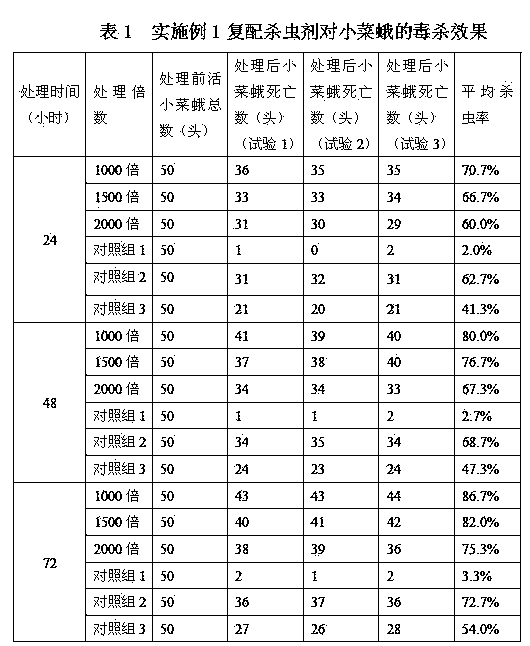
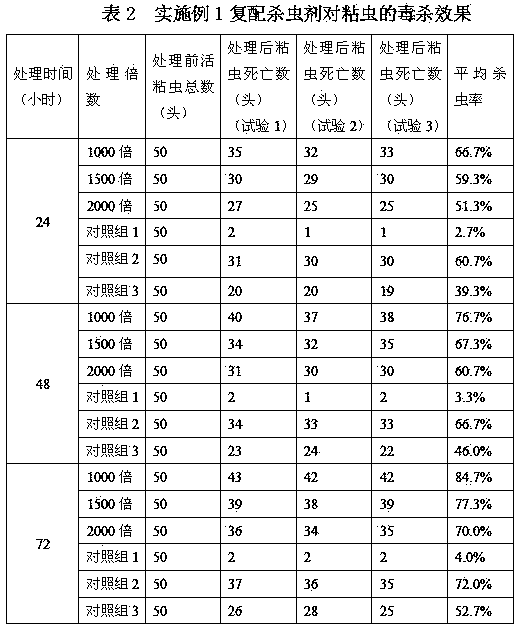
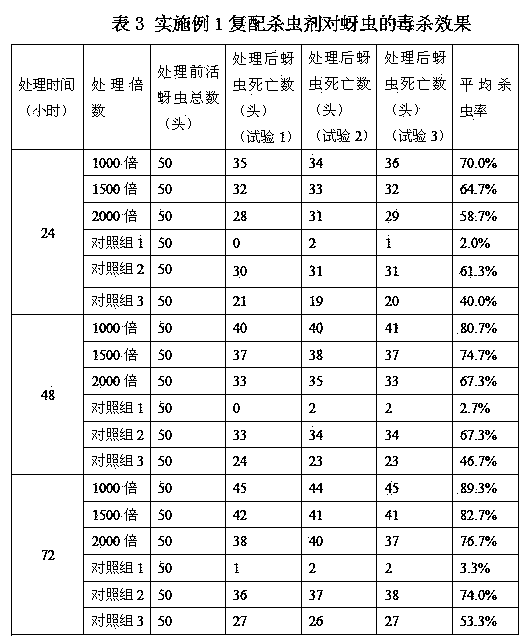
[0049] The efficacy of compounded insecticides in this example is shown in Tables 4-6.
[0050] (1) Toxic effect on diamondback moth
[0051] After diluting the compound insecticide of Example 2 with water in different times (1000 times, 1500 times, 2000 times), spray it onto the surface of cabbage leaves, and then raise live diamondback moths on the cabbage leaves to carry out the insecticidal efficacy test. Repeat three times, and set up 3 groups of control groups in addition: Control group 1: do not spray the composite insecticide of embodiment 2; Control group 2: spray the tung tree leaf extract insecticide diluted 1000 time...
Embodiment 3
[0063] The difference between the present embodiment and Example 1 is: the proportion of each raw material quality component is: 30% of the sieved material of the tung tree leaf extract passing through a 100 mesh sieve, Beauveria bassiana ( Beauveria bassiana ) spore powder (the concentration of live spores is 10 12 per g) 30%, kaolin 15%, sorbitol polyoxyethylene ether 10%, calcium lignosulfonate 15%.
[0064] The insecticidal effects of the compound insecticides in this example are shown in Tables 7-9.
[0065] (1) Toxic effect on diamondback moth
[0066]The compound insecticide of Example 3 was diluted with water in different times (1000 times, 1500 times, 2000 times), sprayed onto the surface of cabbage leaves, and then the live diamondback moth was raised on the cabbage leaves to carry out the insecticidal efficacy test. Repeat three times, set up 3 groups of control groups in addition: Control group 1: do not spray the composite insecticide of embodiment 3; Control g...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com