Method for degrading patulin by using enzymes
A technology of patulin and degradation temperature, applied in the field of enzyme preparations, to achieve the effects of wide sources, easy cultivation, and easy acquisition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
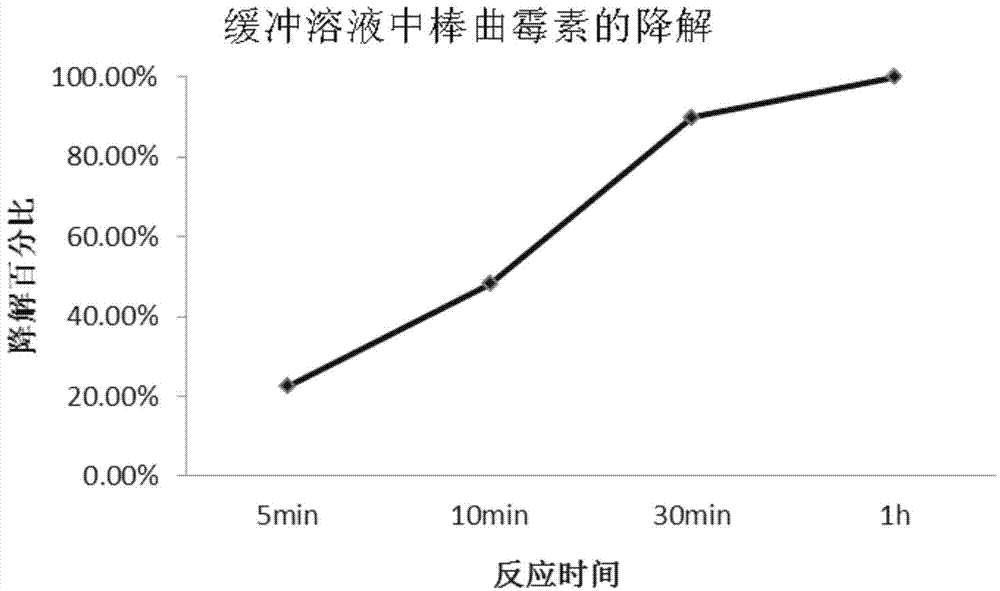
[0067] Example 1. The crude enzyme preparation degrades patulin in Britton-Robinson buffer solution (pH=7.0), and the following steps are carried out in sequence:
[0068] 1), the preparation of crude enzyme preparation:
[0069] First prepare sterile NYDB containing patulin:
[0070] Add patulin to 1L of sterile NYDB culture solution to make the final concentration 1ppm; obtain NYDB culture solution containing patulin;
[0071] A single colony of Rhodosporidium paludigenum Fell&Tallman was picked and inoculated into 50 mL of the above-mentioned NYDB culture solution containing patulin, and cultured in a shaker at 25° C. and 200 rpm for 36 hours. After the cultivation, centrifuge at 3000rpm for 10min, discard the supernatant, wash the precipitate with sterile water (about 30ml), repeat this process twice (that is, repeat the above centrifugation again, discard the supernatant, wash with sterile water precipitation), and finally centrifuged again (3000rpm for 10min), discarde...
Embodiment 2
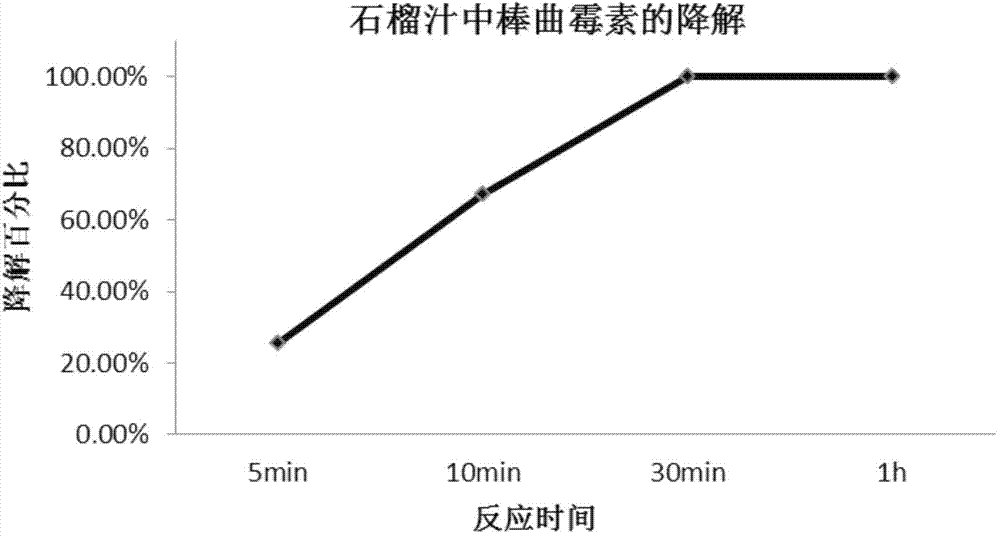
[0081] Example 2, the crude enzyme preparation degrades patulin in pomegranate juice (pH 4.6), the following steps are carried out in sequence:
[0082] 1), the preparation of crude enzyme preparation:
[0083] With the preparation of the crude enzyme preparation in embodiment 1.
[0084] 2) Degradation of patulin in pomegranate juice:
[0085] Add 20 mL of commercially available pomegranate juice into a 50 mL centrifuge tube. It has been previously measured that the pomegranate juice contains 95 μg / L of patulin (that is, there is a total of 1.9 μg of patulin in the tube). Add 100 μL of crude enzyme preparation and mix well. Placed in a 40°C incubator to react; the detection time points were 5 minutes, 10 minutes, 30 minutes, and 1 hour; thereby realizing the degradation of patulin.
[0086] All the other contents are equal to embodiment 1.
[0087] The result is as figure 2 shown. During the 1h degradation process, the content of patulin in the treatment group decreased ...
Embodiment 3
[0089] Embodiment 3, with respect to embodiment 1, make the following changes:
[0090] Add 336 μL of Britton-Robinson buffer solution (pH=7.0), 64 μL of patulin solution, and 100 μL of crude enzyme preparation into a 2 mL centrifuge tube, mix well, that is, a total of 16 μg of patulin is contained. The treatment without crude enzyme preparation was used as the blank control. Three parallels were set up for each treatment and blank control. Placed in a 40°C incubator for reaction; the detection time points were 5 minutes, 10 minutes, 30 minutes, and 1 hour.
[0091] The results were: in the 1h degradation process, the content of patulin in the treatment group decreased continuously with time. In just 5 minutes, 25% of the patulin was degraded; after 10 minutes, 55% of the patulin was degraded; in 30 minutes, 95% of the patulin was degraded; 1h At that time, the presence of patulin could not be detected.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com