Method for removing aflatoxin out of peanut oil
A technology of aflatoxin and peanut oil, applied in the field of biochemistry, can solve the problems of harsh enzyme action conditions, achieve mild reaction conditions, avoid large oil consumption, and have broad application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] A method for removing aflatoxin in peanut oil, comprising
[0031] A material selection process:
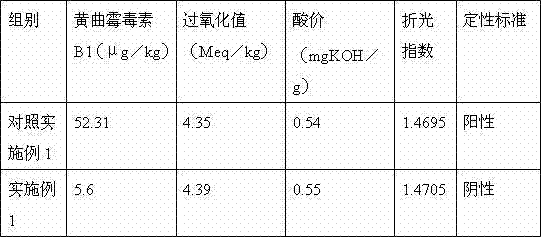
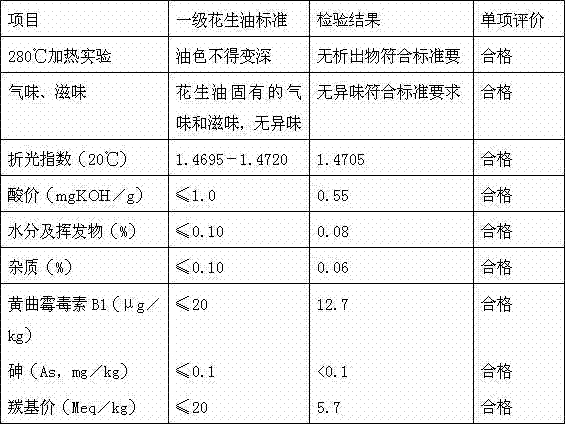
[0032] First, distinguish the origin of raw materials, select high-quality peanuts in batches of 200 tons, and conduct sampling inspections before shelling and rice transformation, such as: water impurities, aspergillus flavus, acid value, peroxidant, oil content and other indicators for laboratory testing , make a record; after passing the test, receive it into the warehouse.
[0033] Use the specific gravity destoner to separate and wash out the dust, soil, stones, metals, impurities, etc. in the fruit; use the sheller to grade and shell the large and small fruits according to the specific gravity level, so as to reduce the damage of peanuts. The damage rate is guaranteed to be around 5%, and the improved semi-finished peanuts are packaged into the warehouse.
[0034] B Peanut Grading Screening:
[0035] Firstly, check the bag opening, arrange the raw material bags in...
Embodiment 2
[0046] A method for removing aflatoxin in peanut oil, comprising
[0047] A material selection process:
[0048] First, distinguish the origin of raw materials, select high-quality peanuts in batches of 200 tons, and conduct sampling inspections before shelling and rice transformation, such as: water impurities, aspergillus flavus, acid value, peroxidant, oil content and other indicators for laboratory testing , make a record; after passing the test, receive it into the warehouse.
[0049] Use the specific gravity destoner to separate and wash out the dust, soil, stones, metals, impurities, etc. in the fruit; use the sheller to grade and shell the large and small fruits according to the specific gravity level, so as to reduce the damage of peanuts. The damage rate is guaranteed to be around 5%, and the improved semi-finished peanuts are packaged into the warehouse.
[0050] B Peanut Grading Screening:
[0051] Firstly, check the bag opening, arrange the raw material bags in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com