Method for transferring graphene on hard substrate with PDMS transition layer
A technology of hard substrate and transition layer, applied in chemical instruments and methods, inorganic chemistry, non-metallic elements, etc., can solve the problems of graphene damage and low transfer efficiency, and achieve the effect of stable process and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Transfer of graphene on copper foil to glass substrate with PDMS transition layer
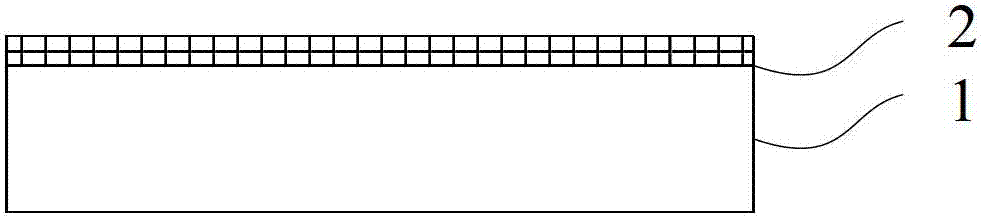
[0038] First, a high-quality graphene continuous film was grown on a 2 cm × 2 cm copper foil by the CVD method. Generally, after the CVD method, there are graphene 2 on the upper and lower sides of the copper foil 1, the lower side is particularly scattered, and the upper side is fine. The graphene film under the copper foil can be polished off or etched away by some means, such as oxygen plasma. In this embodiment, the graphene on the lower layer of the copper foil is removed. formed as Figure 1a structure shown.
[0039] Then use the following steps to transfer:
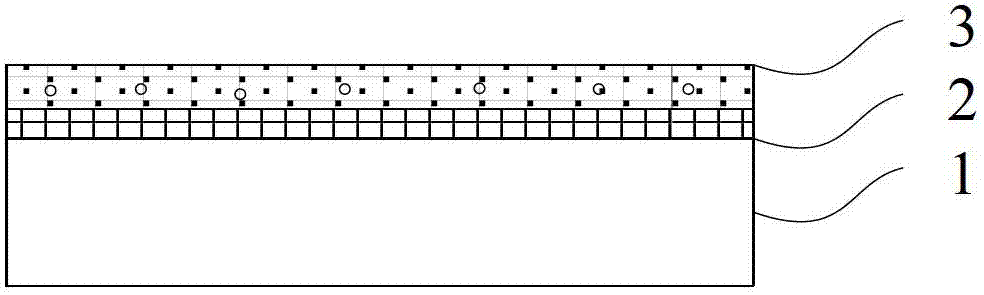
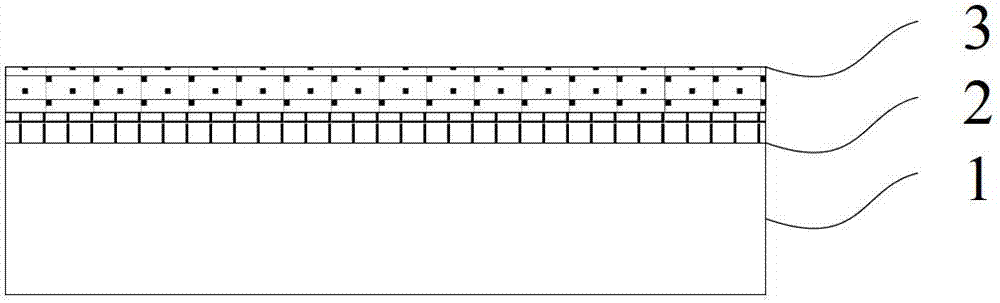
[0040] a) Spin-coat PDMS glue 3 with a thickness of 20 μm on the copper foil 1 after growing graphene 2; spin-coating is to disperse the PDMS glue evenly on the surface of the copper foil with a glue spreader, and the glue spreader can set the speed, generally About 4000 rpm;
[0041] PDMS (polydimethylsiloxane polydim...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Transfer of graphene grown on electroplated copper to Si / SiO with PDMS transition layer 2 Substrate
[0049] First, a copper film with a thickness of about 10 μm is electroplated on a silicon wafer with an oxide layer of about 300 nm; continuous graphene is grown on the copper film formed by the electroplating above by using a CVD process.
[0050] The graphene grown on electroplated copper was then transferred to Si / SiO with PDMS transition layer 2 The substrate process is as follows:
[0051] a) Manually apply a layer of PDMS glue on the above-mentioned electroplated copper, and do not exceed the edge of the above-mentioned copper film when applying PDMS glue;
[0052] b) Put the above-mentioned copper film coated with PDMS glue into a vacuum drying oven to evacuate and suck out the air bubbles in the PDMS glue;
[0053] c) Put the above copper film on a hot plate at 100°C and bake it for 50 minutes to cure the PDMS glue to form a PDMS transition layer on the copper ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com