A kind of zirconium alloy and preparation method thereof
A technology of zirconium alloy and master alloy, applied in the field of zirconium alloy and its preparation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0047] The present invention also provides a preparation method of the above-mentioned zirconium alloy, which includes the following steps: a) mixing Bi, Mo, Cr, Fe and Zr, and melting to obtain a zirconium alloy; wherein the content of Bi is 0.05-0.8wt%, and the content of Mo The content of Cr is 0.05~1.0wt%, the content of Cr is 0.4~1.2wt%, the content of Fe is 0.1~0.5wt%, and the balance is Zr.
[0048] Wherein, according to the present invention, the Bi, Mo, Cr, Fe and Zr elements are the same as those mentioned above, and will not be repeated here.
[0049] Step a) described in the present invention is specifically: a1) mixing Zr and Bi, melting, to obtain Zr-Bi master alloy; a2) mixing said Zr-Bi master alloy, Zr, Fe, Cr and Mo, melting, A zirconium alloy is obtained.
[0050] The smelting method in the step a1) can be a method well-known to those skilled in the art, and there is no special limitation, and the conditions of the smelting can also be a method well-known t...
Embodiment 1
[0056] 1.1 Mix and melt 100g Zr and 110gBi to obtain a Zr-Bi master alloy, and through chemical analysis, the specific content of Bi element is 50wt%.
[0057] 1.2 Pulverize 0.2g of the Zr-Bi master alloy obtained in 1.1 and add it to the mixture of 48.9gZr, 0.2gFe, 0.5gCr and 0.2gMo, and then use a non-consumable vacuum electric arc furnace at a vacuum degree of 5×10 -3 Pa, 0.5atm under the protection of argon smelting 5 times to obtain a zirconium alloy, wherein the content of Bi is 0.2wt%, the content of Mo is 0.4wt%, the content of Cr is 1.0wt%, and the content of Fe is 0.4wt%. , The content of Zr is 98wt%.
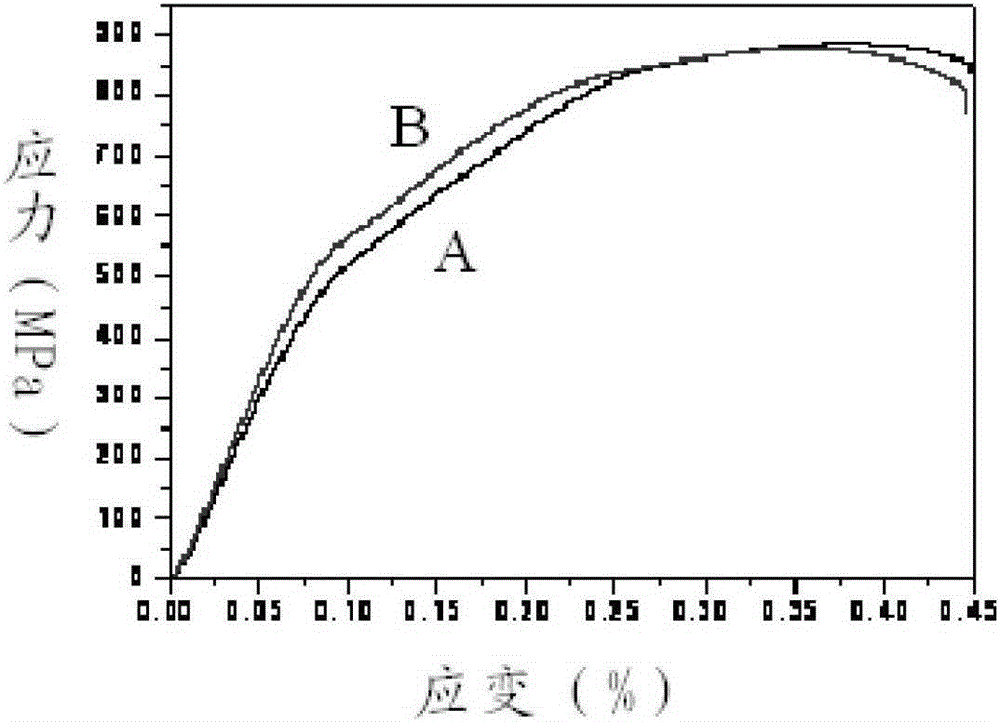
[0058] The mechanical properties of the zirconium alloy obtained in 1.2 were tested to obtain its tensile strength, yield strength and elongation. As shown in Table 1, the zirconium alloy was hot-rolled and annealed, and then the mechanical properties were tested at room temperature to obtain Its tensile stress-strain curve, such as figure 1 , where A is the stress-...
Embodiment 2
[0060] 2.1 Mix and melt 100g Zr and 110gBi to obtain a Zr-Bi master alloy, and through chemical analysis, the specific content of Bi element is 50wt%.
[0061] 2.2 Pulverize 0.4g of the Zr-Bi master alloy obtained in 2.1 and add it to the mixture of 48.7gZr, 0.2gFe, 0.5gCr and 0.2gMo, and then use a non-consumable vacuum electric arc furnace at a vacuum degree of 5×10 -3 Pa, 0.5atm under the protection of argon smelting 5 times to obtain a zirconium alloy, wherein the content of Bi is 0.4wt%, the content of Mo is 0.4wt%, the content of Cr is 1.0wt%, and the content of Fe is 0.4wt%. , The content of Zr is 97.8wt%.
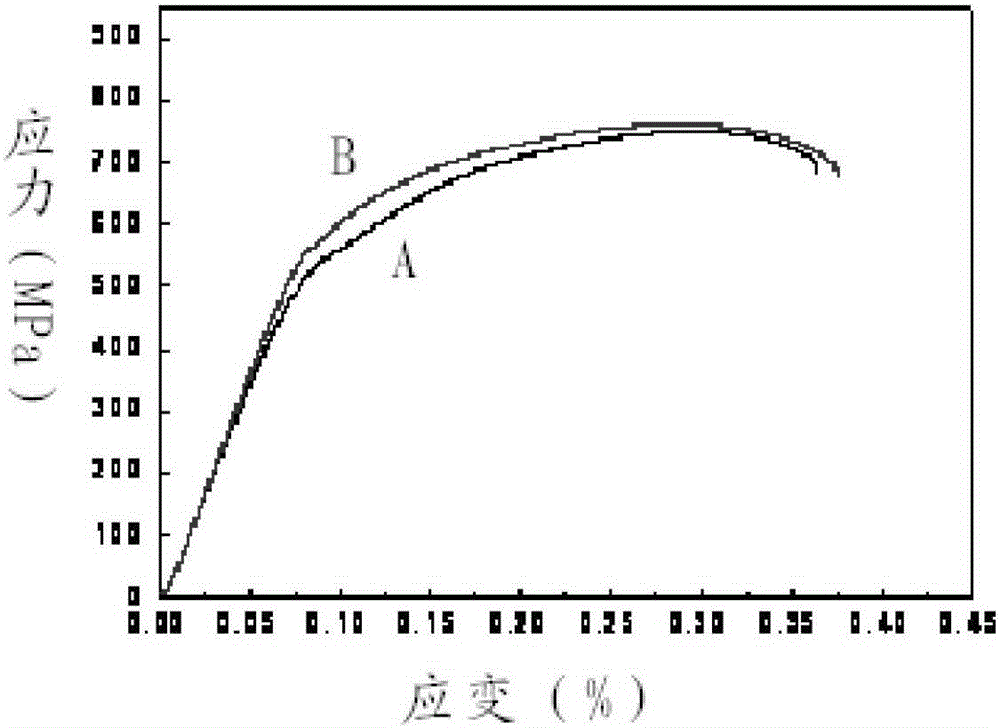
[0062] The zirconium alloy obtained in 2.2 is hot-rolled and annealed, and then the mechanical properties are tested at room temperature to obtain its tensile stress-strain curve, such as figure 2 , where A is the stress-strain curve of tensile sample 1, and B is the stress-strain curve of tensile sample 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com