Method for separating and recycling each component material in waste printed circuit boards by using near-critical water
A waste circuit board, near-critical water technology, applied in recycling technology, electronic waste recycling, solid waste removal, etc., can solve problems such as reducing fuel quality, corroding treatment equipment, polluting the environment, etc. Effect of carbonization rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
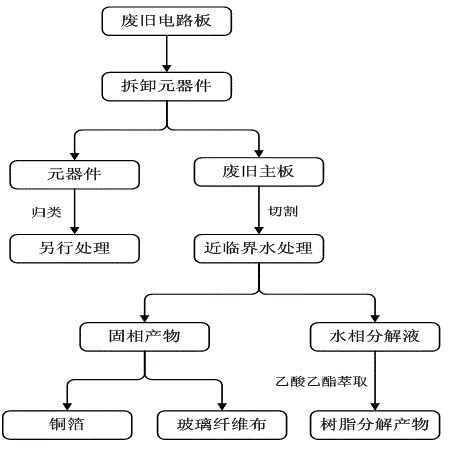
[0030] Such as figure 1 As shown, a method for separating and recycling components of waste circuit boards with near-critical water mainly includes four processes: pretreatment, near-critical water treatment, extraction of resin matrix decomposition products, and extraction of copper foil and fiber woven cloth. Separation, the specific steps are as follows:
[0031] (1) Pretreatment: Disassemble and separate the main board and components of the waste circuit board, and classify the disassembled components for further processing, and then cut the main board into cubes with a size of 1.0cm×1.0cm.
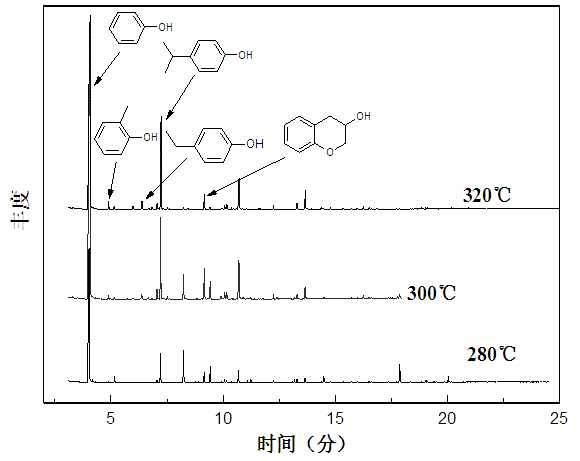
[0032](2) Near-critical water treatment: Add 1g of the cut waste circuit board main board and 5ml of water into the reactor according to the feed ratio of 1:5 (g / ml), and then add 0.02 g of hydrochloric acid (HCl) as a catalyst , seal the reaction kettle, turn on the power and start heating, the reaction temperature is 300°C, start timing after the temperature stabilizes, keep the re...
Embodiment 2
[0036] A method of using near-critical water to separate and recycle components of waste circuit boards, mainly comprising the following steps:
[0037] (1) Pretreatment: Disassemble and separate the main board and components of the waste circuit board, and classify the disassembled components for further processing, and then cut the main board into cubes with a size of 2cm×2cm.
[0038] (2) Near-critical water treatment: Add 1g of the cut waste circuit board main board and 15ml of water into the reactor according to the feed ratio of 1:15 (g / ml), and then add 0.02 g of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) , seal the reaction kettle, turn on the power and start heating, the reaction temperature is 320°C, start timing after the temperature stabilizes, and keep the reaction time for 150min. The pressure in the reactor is monitored by a pressure gauge connected to it, and the pressure in the reactor remains above 7.0MPa during the reaction.
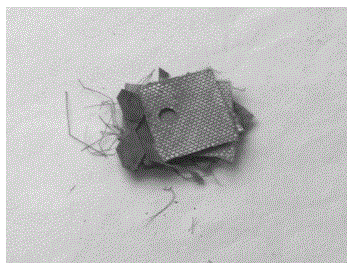
[0039] (3) Extraction of resin matrix decompositi...
Embodiment 3
[0042] A method of using near-critical water to separate and recycle components of waste circuit boards, mainly comprising the following steps:
[0043] (1) Pretreatment: Disassemble and separate the main board and components of the waste circuit board, and classify the disassembled components for further processing, and then cut the main board into cubes with a size of 0.5cm×0.5cm.
[0044] (2) Near-critical water treatment: Add 1g of the cut waste circuit board main board and 10ml of water into the reactor according to the feed ratio of 1:10 (g / ml), and then add 0.02 g of sodium carbonate (Na 2 CO 3 ) as a catalyst, seal the reactor, turn on the power and start heating, the reaction temperature is 280°C, start timing after the temperature stabilizes, and keep the reaction time for 150min. The pressure in the reactor is monitored by a pressure gauge connected to it, and the pressure in the reactor remains above 5.0 MPa during the reaction.
[0045] (3) Extraction of resin m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com