High-voltage cable
A high-voltage cable and cable core technology, applied in the direction of insulated cables, cables, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of burning the cable, affecting the transmission efficiency of the cable, easily causing leakage current, etc., and achieving the effect of excellent flame retardant performance and excellent mechanical and physical properties.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
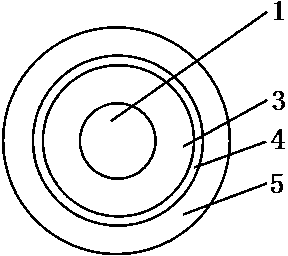
[0043] please see figure 1 , a high-voltage cable, which includes a conductor 1, an insulating layer 3 that is extruded and coated on the conductor, a shielding layer 4 that is coated on the insulating layer, and a sheath layer 5 that is extruded and coated on the outside of the shielding layer. , it is characterized in that described sheath layer is calculated by weight, is made up of following raw material: Medium-density polyethylene or high-density polyethylene for commercially available electric wire and cable: 85~100 parts;
[0044] Ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer: 10-20 parts;
[0045] Titanium dioxide with fineness less than 400 mesh: 5-8 parts;
[0046] Carbon black with a fineness of less than 400 mesh: 2 to 4 parts;
[0047] Aluminum hydroxide: 5-10 parts;
[0048] Titanium trioxide: 2 to 6 parts;
[0049] Antioxidant for cable sheathing material of commercially available model 1010 or 1076: 1 to 3 parts;
[0050] Polyethylene wax: 2 to 4 parts;
[0051] Fine...
Embodiment 2
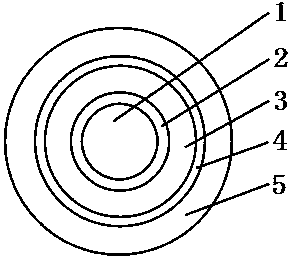
[0053] please see figure 2 , a high-voltage cable, which includes a conductor 1, an inner shielding layer 2 coated outside the conductor, an insulating layer 3 coated outside the inner shielding layer by extrusion molding, a shielding layer 4 wrapped outside the insulating layer, and an extrusion molding It is composed of a sheath layer 5 coated outside the shielding layer, and is characterized in that the sheath layer is composed of the following raw materials in parts by weight: commercially available medium-density polyethylene or high-density polyethylene for wire and cable: 85-100 share;
[0054] Ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer: 10-20 parts;
[0055] Titanium dioxide with fineness less than 400 mesh: 5-8 parts;
[0056] Carbon black with a fineness of less than 400 mesh: 2 to 4 parts;
[0057] Aluminum hydroxide: 5-10 parts;
[0058] Titanium trioxide: 2 to 6 parts;
[0059] Antioxidant for cable sheathing material of commercially available model 1010 or 1076: 1 to...
Embodiment 3
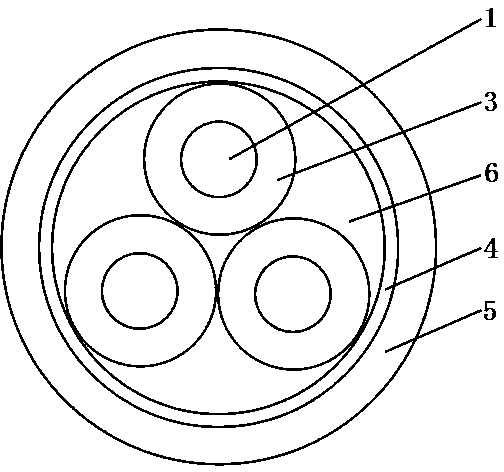
[0064] please see image 3 , a high-voltage cable, including a cable core formed by placing three insulated conductors in a triangular cross section, a shielding layer 4 wrapped outside the cable core, and a sheath layer 5 coated outside the shielding layer by extrusion molding. The core gap is filled with fillers 6 that prevent the positions of the three insulated conductors from moving, and each insulated conductor includes a conductor 1 and an insulating layer 3 coated outside the conductor; it is characterized in that the sheath layer is calculated by weight and consists of the following Raw material composition:
[0065] Commercially available medium-density polyethylene or high-density polyethylene for wire and cable: 85 to 100 parts;
[0066] Ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer: 10-20 parts;
[0067] Titanium dioxide with fineness less than 400 mesh: 5-8 parts;
[0068] Carbon black with a fineness of less than 400 mesh: 2 to 4 parts;
[0069] Aluminum hydroxide: 5-10 pa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com