Rare-earth permanent magnet and preparation method thereof
A technology of rare earth permanent magnets and permanent magnets, which is applied in the direction of magnetic objects, permanent magnets, inductors/transformers/magnets, etc., and can solve the problems of magnet corrosion resistance decline
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
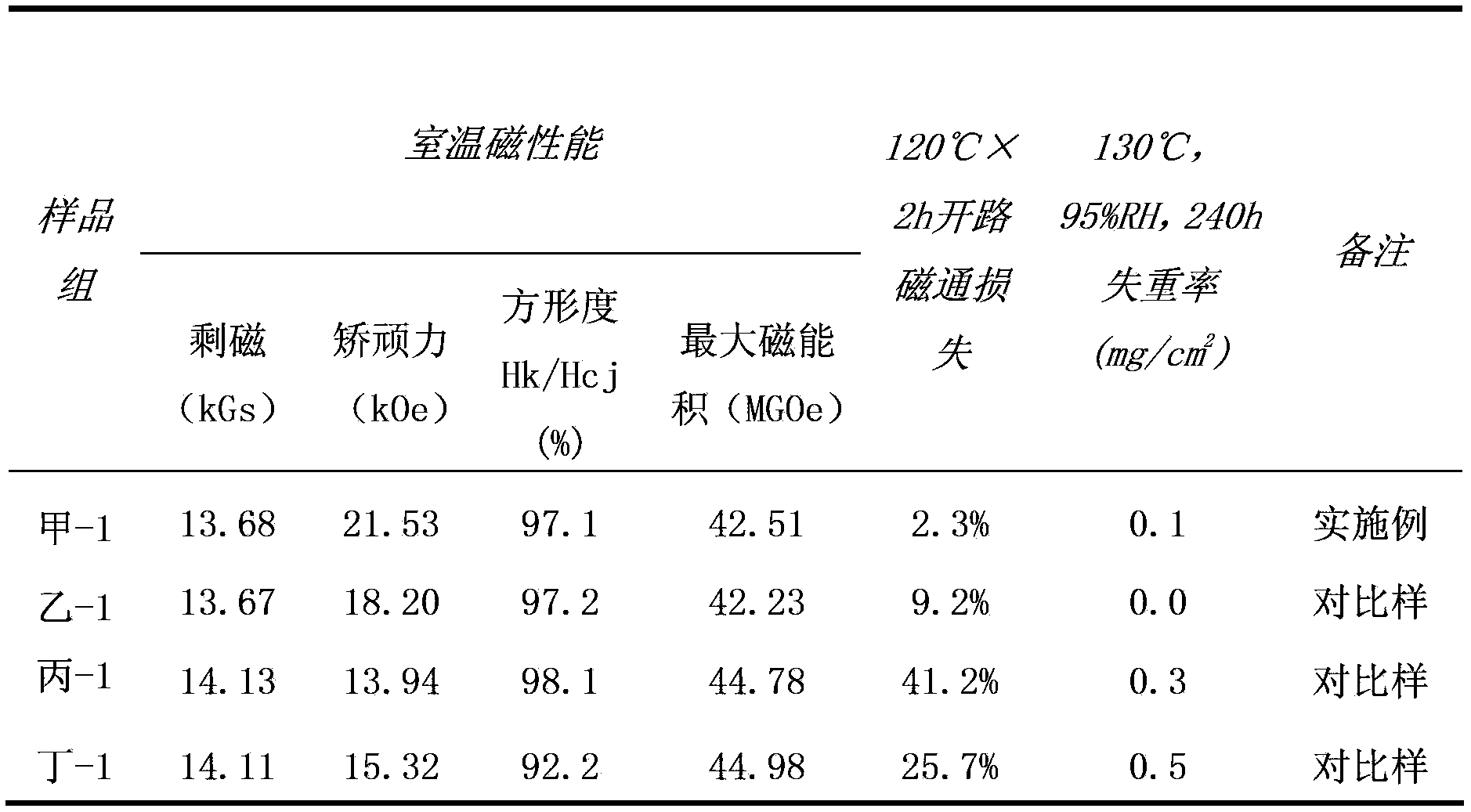
[0046] Smelt the alloy to get (Nd,Pr) 10 (Fe,Co) 81 B 7 (Nb,V) 2 The main phase alloy strips and (Nd, Dy) 40 Fe 30 (Cu,Al) 30 Auxiliary alloy ingot blocks, the flakes are subjected to mechanical coarse crushing, hydrogen crushing, and jet milling, and the ingot blocks are subjected to mechanical coarse crushing, hydrogen crushing, and ball milling to obtain a main phase alloy powder with a D50 of 7.5 μm and a D90 / D10 The D50 of the auxiliary alloy powder is 2 μm; then the above two powders are fully mixed at a mass percentage of 85:15, and then subjected to 2.0T orientation magnetic field orientation pressing, 180MPa isostatic pressing, and the green body is sintered at 1050°C for 2.5h. To obtain a rough magnet, the surface of the sintered rough magnet was ground to remove scale, and the surface was cleaned with lye. The obtained Φ10.1mm×10.1mm magnet samples were divided into two groups, A-1 and B-1.
[0047] The samples in group B-1 are comparative samples without any ...
Embodiment 2
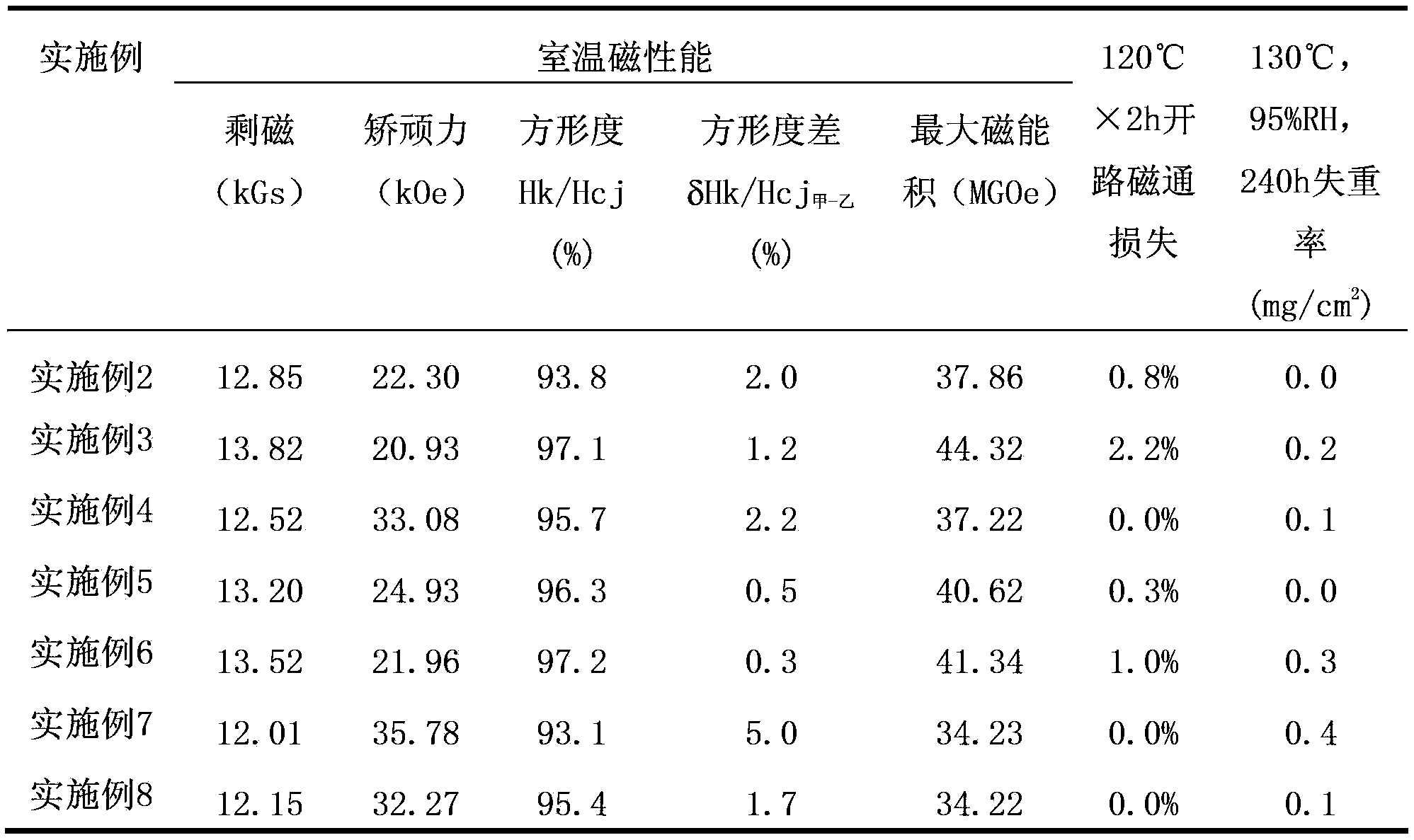
[0060] Smelt the alloy to get (Nd,Pr) 8 (Fe,Co) 81.1 B 7.4 (Nb, Zr) 3.5 The main phase alloy flakes and Nd 60 (Fe,Co) 25.5 B 5.1 (Cu,Ga) 9.4 Auxiliary alloy ingot blocks, the flakes are subjected to mechanical coarse crushing, hydrogen crushing, and jet milling, and the ingot blocks are subjected to mechanical coarse crushing, hydrogen crushing, and ball milling to obtain a main phase alloy powder with a D50 of 3.0 μm and a D90 / D10 15.0, D50 of the auxiliary alloy powder is 0.3 μm; then the above two powders are fully mixed with a mass percentage of 70:30, and then subjected to 2.0T orientation magnetic field orientation pressing, 180MPa isostatic pressing, and the green body is sintered at 1100°C for 0.2h , to obtain a rough magnet, grind the surface of the sintered rough magnet, wash the surface with lye, and obtain a Φ20mm×5mm rough magnet.
[0061] The obtained rough magnet sample surface layout DyF 3 , Dy 2 o 3 and DyOF three powders, their mass percentages are ...
Embodiment 3
[0068] Smelt the alloy to get (Nd,Pr) 15.2 (Fe,Co) 75.8 B 5.8 (Nb,Zr,V) 3.2 The main phase alloy flakes and Nd 60 (Al,Zn) 40 Auxiliary alloy ingot blocks, the flakes are subjected to mechanical coarse crushing, hydrogen crushing, and jet milling, and the ingot blocks are subjected to mechanical coarse crushing, hydrogen crushing, and ball milling to obtain a main phase alloy powder with a D50 of 10.0 μm and a D90 / D10 The D50 of the auxiliary alloy powder is 8.0 μm; then the above two powders are fully mixed at a mass percentage of 99:1, and then subjected to 2.0T orientation magnetic field orientation pressing, 180MPa isostatic pressing, and the green body is sintered at 1060°C for 3h. A rough magnet is obtained, the surface of the sintered rough magnet is ground, and the surface is cleaned with lye to obtain a Φ15mm×15mm rough magnet.
[0069] The obtained rough magnet sample surface layout DyF 3 Powder, the average particle size is 40μm, the solution is prepared accord...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com