Transcription factor SiARDP for conditioning resilience resistance of rice and encoding gene and application of transcription factor SiARDP
A transcription factor and gene technology, applied in the fields of application, genetic engineering, plant gene improvement, etc., can solve the problems of induction, etc., and achieve the effect of enhancing plant resistance to abiotic stress and benefiting agricultural production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Example 1 Cloning of the gene SiARDP induced by abiotic stress
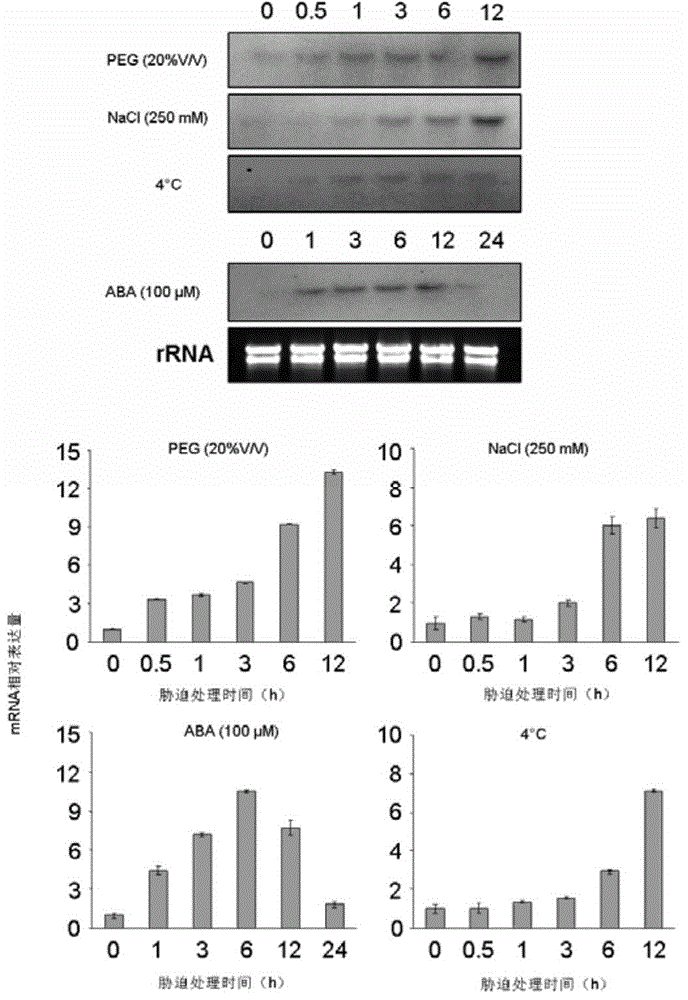
[0032] After mixing the millet materials subjected to drought, salt and low temperature stress, total RNA was extracted and a cDNA library was constructed. Using the DRE element sequence (ATACTACCGACATGAGC) in the promoter region of RD29A as bait, SiARDP was cloned from the abiotic stress cDNA library of millet by using the Clontech company yeast one-hybrid kit. The full-length sequence is shown in figure 1 . Northern and qRT-PCR analysis showed that the gene was induced by abiotic stresses such as ABA treatment and drought ( figure 2 ).
Embodiment 2
[0033] Example 2SiARDP has the function of transcription factor
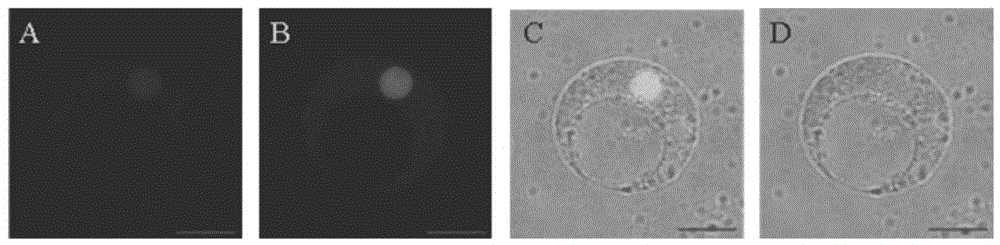
[0034] In order to study the localization of SiARDP in cells, the plasmid 35S:SiARDP-GFP with GFP tag was constructed. In addition, using the known nuclear localization of AHL22 as a positive control, a plasmid 35S:AHL22-RFP with an RFP tag was constructed. The two plasmids were co-transformed into protoplasts of etiolated millet seedlings, and the localization of SiARDP protein was observed under confocal laser microscope after culturing in the dark for 16 hours. The results showed that SiARDP was localized in the same position as AHL22 and located in the nucleus ( image 3 ), which is consistent with the predicted properties of SiARDP as a transcription factor. The transcriptional activity of SiARDP was analyzed using the yeast transcriptional activation system. SiARDP was constructed into pBD-GAL4 plasmid and transformed into yeast YRG-2. Dilute the transformed positive yeast with sterile water to OD 600...
Embodiment 3
[0035] Example 3 Obtaining of SiARDP heterologously expressed Arabidopsis plants
[0036] In order to study the function of SiARDP, a 35S promoter-driven SiARDP expression vector p35S:SiARDP was constructed, and p35S:SiARDP was transformed into wild-type Arabidopsis plants by Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. A total of 48 positive plants were obtained by hygromycin screening. After two generations of screening, 3 plants were selected from the homozygous single-copy plants obtained in the T3 generation as materials for further research, and they were named L4, L15 and L22 respectively. The total RNA of wild-type and transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana was extracted for PCR detection and RT-PCR detection. The primers were RT-SiARDPS and RT-SiARDPR. The transgenic plants all had SiARDP inserted and expressed ( Figure 5 ).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com