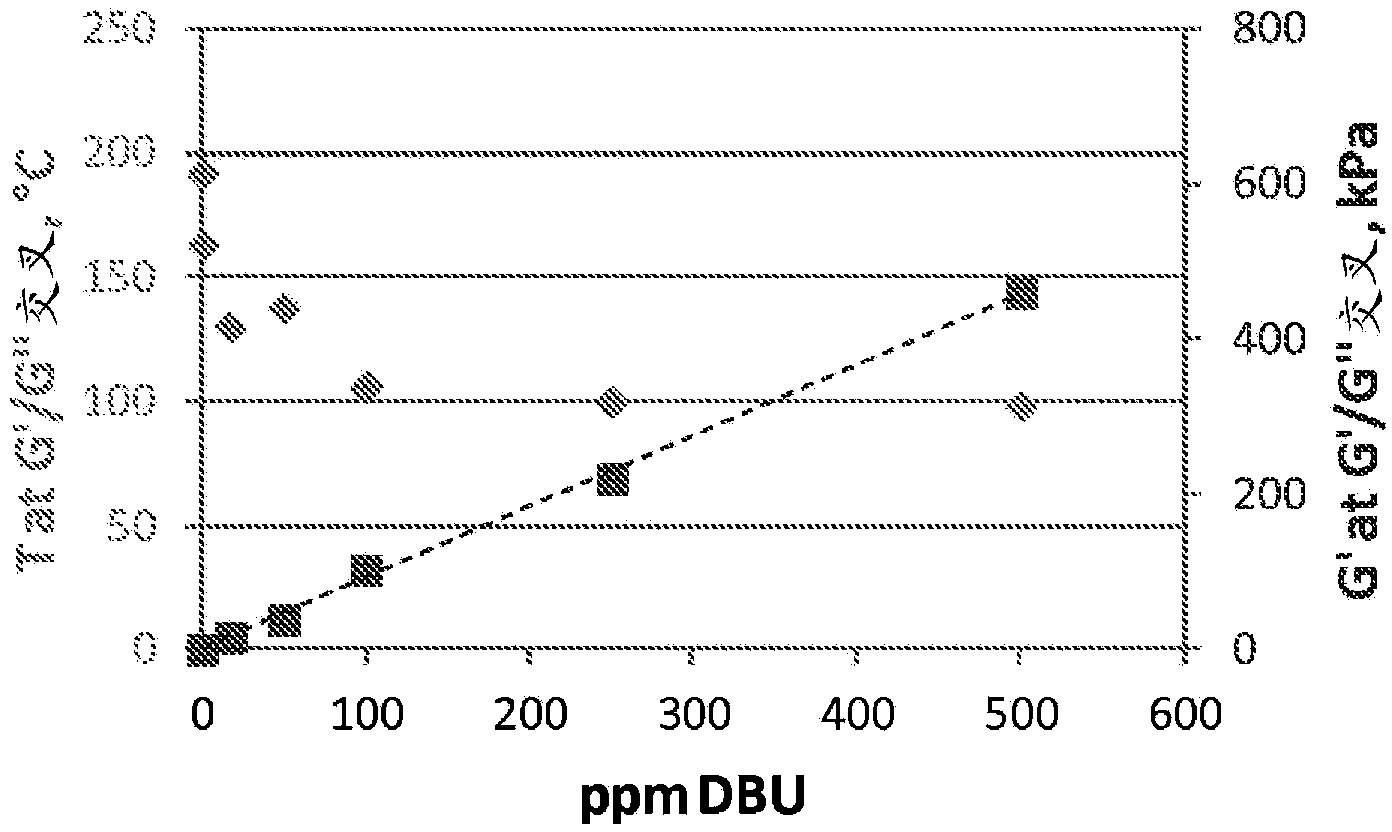
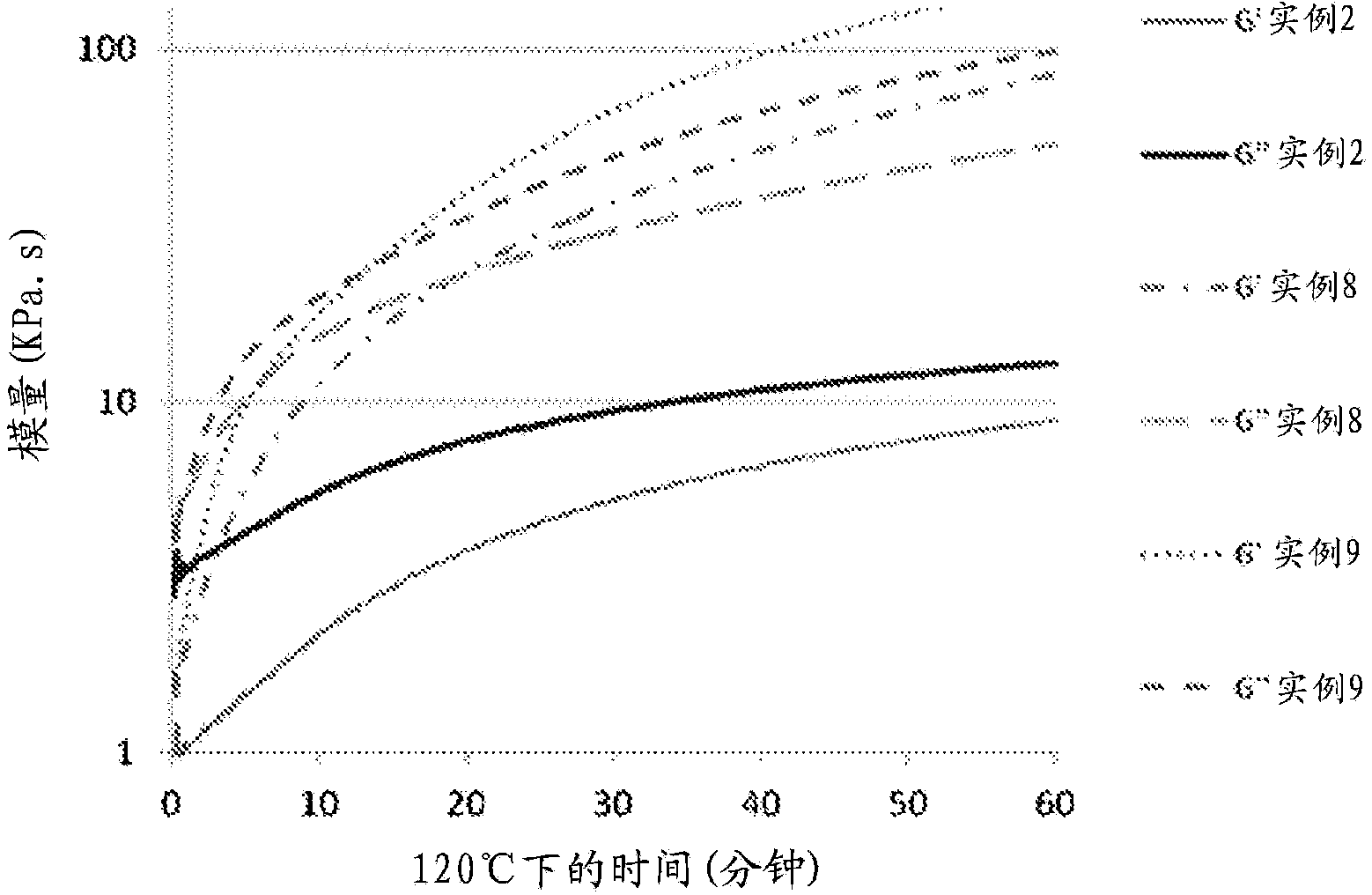
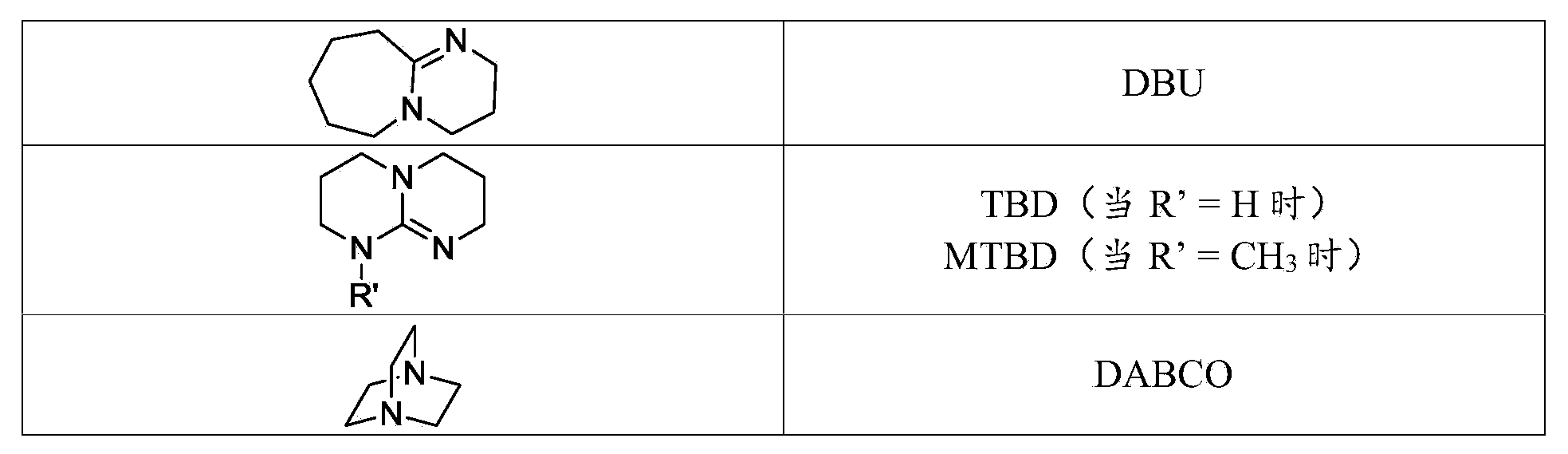
Curable compositions of resin-linear organosiloxane block copolymers
A curable composition, organosiloxane technology, applied in the direction of electrical solid devices, semiconductor/solid device components, coatings, etc., can solve problems such as difficult application, non-durability, lack of toughness of coatings, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0237] Containing at least 60 mole % of [R 2 SiO 3 / 2 ] Organosiloxane resins having siloxy units and methods for their preparation are known in the art. They are usually prepared by hydrolyzing organosilanes with three hydrolyzable groups (such as halogen or alkoxy groups) on the silicon atom in an organic solvent. Representative examples for preparing silsesquioxane resins can be found in US Patent No. 5,075,103. Additionally, many organosiloxane resins are commercially available and sold as solids (flakes or powders) or dissolved in organic solvents. Suitable non-limiting commercially available organosiloxane resins that can be used as component b) include: Dow 217Flake Resin (sheet resin), 233Flake, 220Flake, 249Flake, 255Flake, Z-6018Flake (Dow Corning Company, Midland, MI).
[0238] Those skilled in the art also recognize that containing such high amounts of [R 2SiO 3 / 2 ]Organosiloxane resins with siloxy units and silanol content can also retain water molecules, es...
example
[0263] The following examples are included to illustrate specific embodiments of the invention. However, those of skill in the art should, in light of the present invention, appreciate that many changes can be made in the specific embodiments which are disclosed and still obtain a similar or equivalent result without departing from the spirit and scope of the invention. All percentages are % by weight. All measurements are at 23°C unless otherwise indicated.
[0264] Characterization technology
[0265] 29 Si and 13 C NMR spectrum
[0266] By mixing approximately 3 g of solvent-free resin-linear copolymer (prepared by drying the sample at room temperature overnight), 1 g of CDCl 3 and 4 grams of 0.04M Cr(acac) 3 CDCl 3 The solution was weighed into a vial and mixed thoroughly to prepare an NMR sample of the resinous linear product. Samples were then transferred into silicon-free NMR tubes. Spectra were acquired with a Varian Mercury 400MHz NMR. by diluting ...
example 1
[0277] Example 1 (reference)
[0278] Preparation of PhMe resin linear products using 47dp diacetoxy-terminated PhMe siloxane
[0279] Composition: (PhMeSiO 2 / 2 ) 0.52 (PhSiO 3 / 2 ) 0.41 (45% by weight phenyl-T)
[0280] A 500 mL 4 neck round bottom flask was charged with Dow Corning 217 Flake (45.0 g, 0.329 mol Si) and toluene (Fisher Scientific, 70.38 g). The flask was equipped with a thermometer, a Teflon stirring impeller and a Dean Stark apparatus attached to a water-cooled condenser. A nitrogen blanket was applied, the Dean Stark apparatus was preloaded with toluene, and an oil bath was used for heating. The reaction mixture was heated at reflux for 30 minutes. After cooling the reaction mixture to 108°C, a solution of the diacetoxy terminated PhMe siloxane was added rapidly. By adding 50 / 50 wt% methyltriacetoxysilane (MTA) / ethyl triacetoxysilane (MTA) to a solution of 47dp silanol terminated PhMe siloxane (55.0g, 0.403mol Si) dissolved in tolu...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com