Method for manufacturing micro/nano composite structure based on 4D printing and nanoimprint lithography
A micro-nano composite structure and nano-imprinting technology, which is applied in the photoengraving process, instruments, optics and other directions of the pattern surface, can solve the impact, it is difficult to meet the requirements of industrial production and application, and restrict the wide commercial application of the micro-nano composite structure. and other problems, to achieve the effect of wide application range, good controllability and repeatability, and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
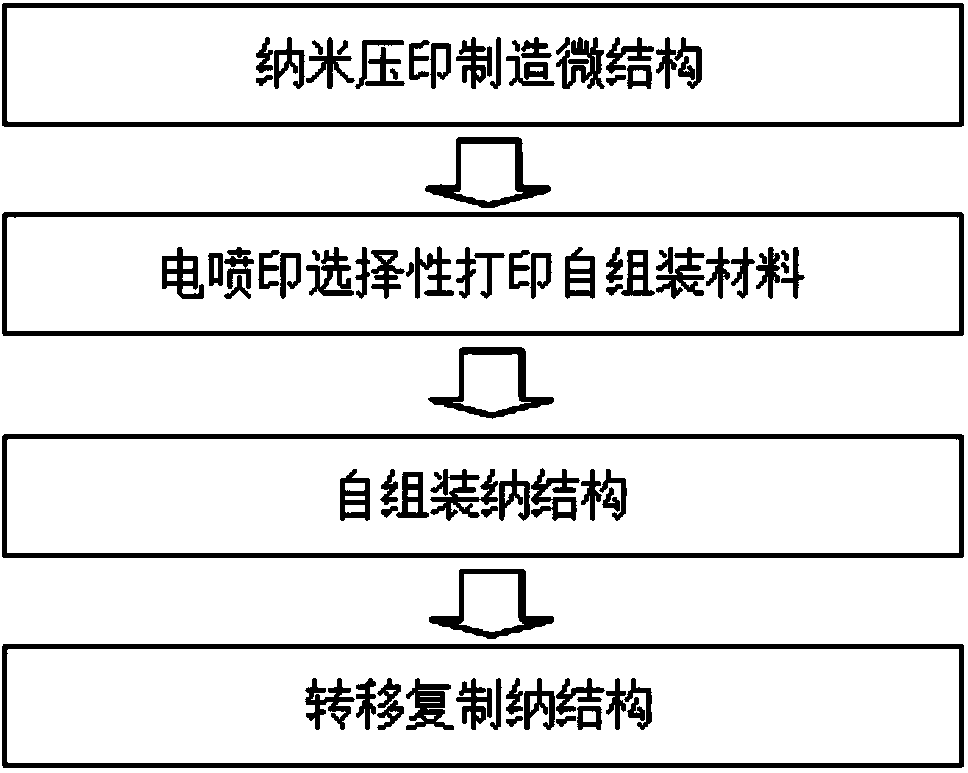
[0079] In this embodiment, glass is used as the substrate 1, and the micro-nano composite structure to be manufactured is a micro-nano composite structure imitating a lotus leaf. The microstructure 3 is a cylindrical array (mastoid structure) with a diameter of 6 microns, and the period is 10 microns. The height of the cylinder is 4 microns, and the nanostructure 8 is a nanowire (like a hair-like structure) with a diameter of 120 nanometers. The specific manufacturing process steps are as follows:
[0080] (1) Fabrication of microstructures using nanoimprinting 3
[0081] ① Spread a 4.5 micron thick UV-cured and conductive liquid polymer imprinting material 2 on the glass substrate 1, such as Figure 2a shown;
[0082] ②Using soft UV nanoimprinting process, the microstructure imprinting on the soft mold is copied to the polymer imprinting material 2;
[0083] ③ Reactive plasma etching is used to remove the residual layer, and a microscale cylinder array is formed on the imp...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com