An n×n Arrayed Waveguide Grating Optical Wavelength Router with Reduced Frequency Deviation
An arrayed waveguide grating and arrayed waveguide technology, which is applied in the directions of optical waveguides and light guides, can solve the problems of poor device performance, increased cost, complicated processes, etc., and achieves the effects of low cost, simple production, and simple working principle.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
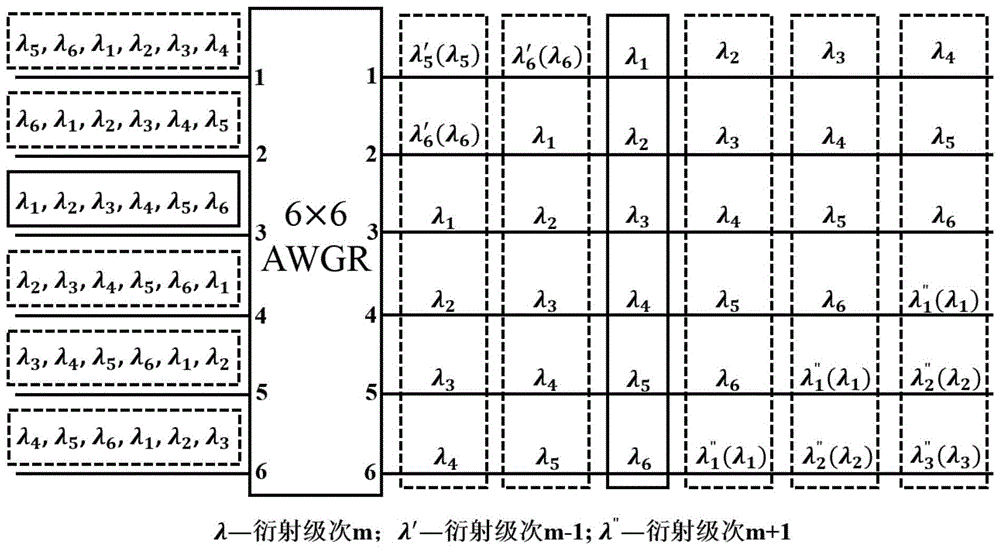
[0067] Design a 6×6 arrayed waveguide grating optical wavelength router (AWGR) with a channel spacing of 20nm, the center wavelength λ c is 1560nm, and the designed free spectral range FSR is 120nm. Table 1 shows the effective refractive index and group refractive index of the input / output slab waveguide region and the arrayed waveguide region at different wavelengths.
[0068] For the traditional arrayed waveguide grating optical wavelength router, the length difference ΔL between two adjacent waveguides in the arrayed waveguide area is obtained from formula (3) = 5.412 μm, and the diffraction order m = 6.12 is obtained by substituting into formula (2). Since the diffraction order m is an integer, take m=6, obtain the actual ΔL=5.310 μm through formula (2), and substitute ΔL=5.310 μm into formula (3) to obtain the actual free spectral range FSR=122.3nm, The actual free spectral range has a deviation of 2.3nm compared with the design value.
[0069] Image 6 For the spectru...
Embodiment 2
[0074] Design an 8×8 AWGR with a channel spacing of 10nm, and a central wavelength λ c is 1550nm, and the designed free spectral range FSR is 80nm.
[0075] For the traditional arrayed waveguide grating optical wavelength router, the length difference ΔL of two adjacent waveguides in the arrayed waveguide region is obtained from formula (3) = 8.02 μm, and the diffraction order m = 9.18 is obtained by substituting into formula (2). Since the diffraction order m is an integer, take m=9, obtain the actual ΔL=7.86 μm through the formula (2), and substitute ΔL=7.86 μm into the formula (3) to obtain the actual free spectral range FSR=81.7nm, The actual free spectral range has a deviation of 1.7nm compared with the design value.
[0076] Figure 9 Table 4 shows the output wavelength of each output channel of the AWGR for the spectrum diagram of the designed 8×8 traditional arrayed waveguide grating optical wavelength router.
[0077] The arrayed waveguide grating optical wavelengt...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com