Bi-directional light control thyratron transistor chip, optical triggering coupler and solid-state relay
A thyristor, bidirectional light technology, applied in semiconductor devices, circuits, electrical components, etc., can solve the problem of increasing the chip area, achieve the effect of improving the rectification characteristics and suppressing the increase of the chip area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
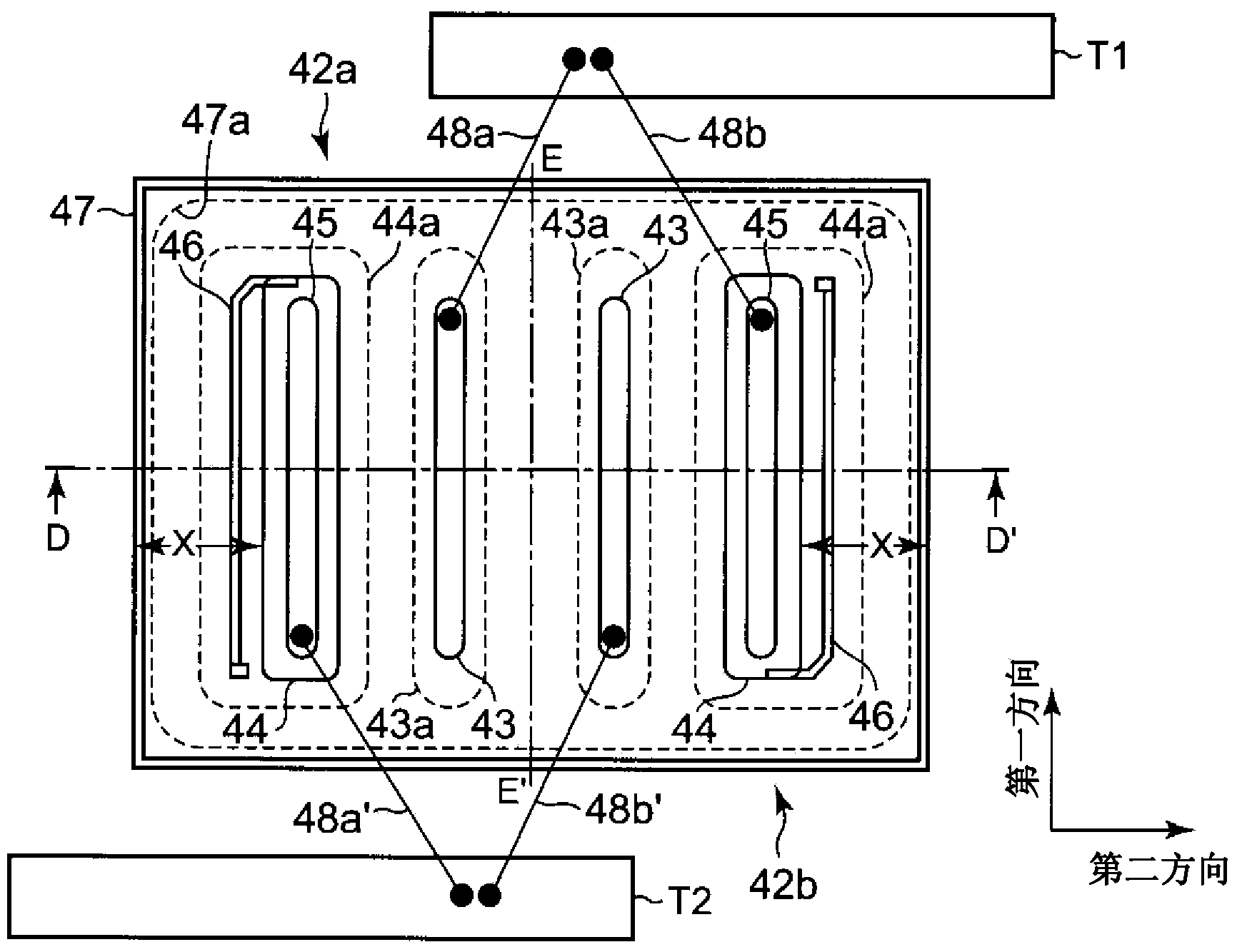
[0109] figure 1 A schematic pattern layout of the bidirectional phototriac thyristor chip of the present embodiment is shown, figure 2 yes figure 1 The schematic diagram of the D-D' cross-section.
[0110] The bidirectional light-controlled thyristor chip of this embodiment, such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, it includes: the first photothyristor 42a of CH1 and the second photothyristor 42b of CH2 formed separately on the surface of the N-type silicon substrate 41 constituting the chip.
[0111] The above-mentioned first photo-controlled thyristor 42a and the second photo-controlled thyristor 42b each have: a P-type anode diffusion region 43; a P-type gate diffusion region 44 opposite to the anode diffusion region 43; An N-type cathode diffusion region 45 is formed in the electrode diffusion region 44 to face the anode diffusion region 43 . In this way, a PNPN portion is formed from the anode diffusion region 43 to the cathode diffusion region 45 . In addition,...
no. 2 approach
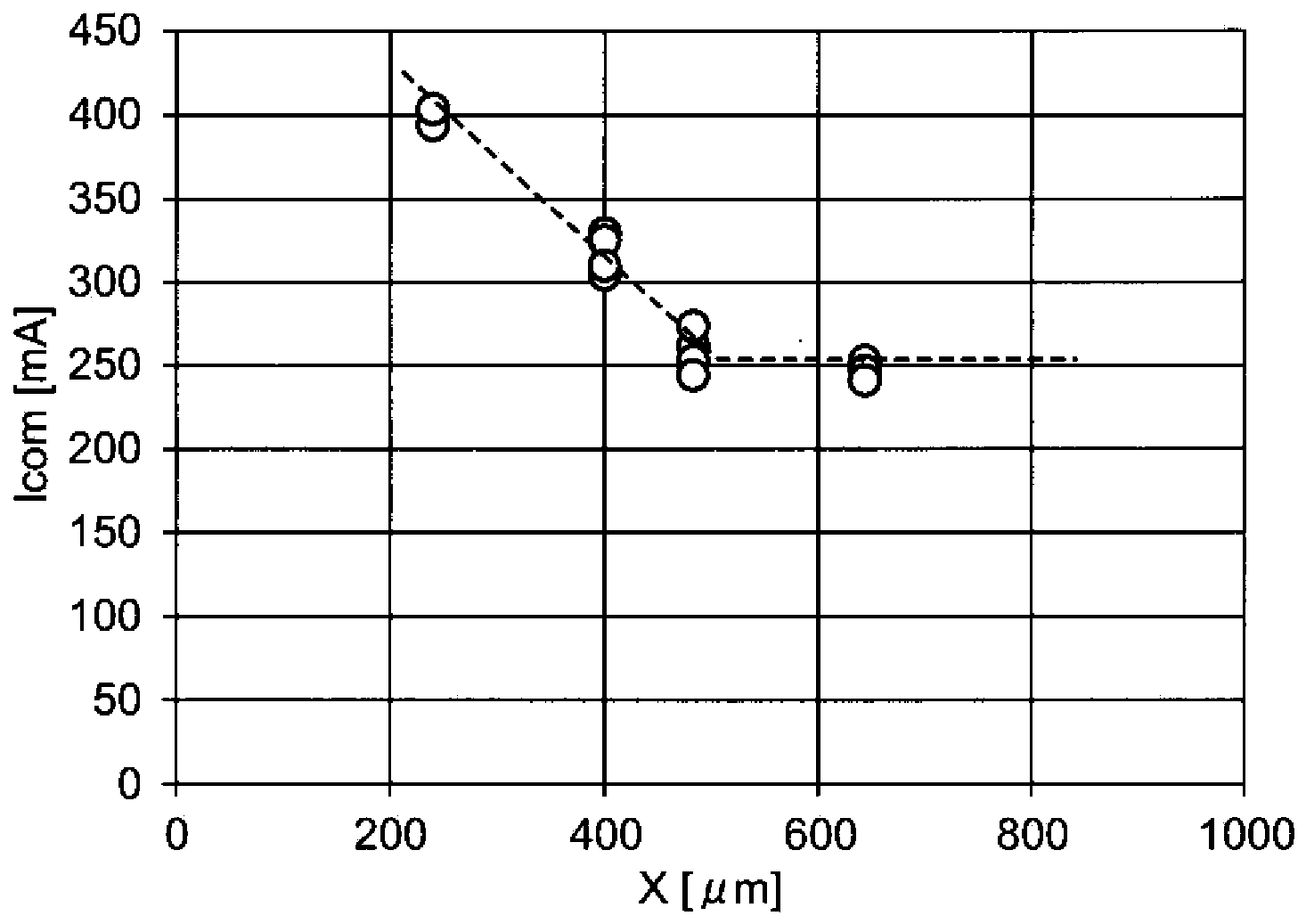
[0134] This embodiment relates to the "critical turn-off voltage rise rate dV / dt (hereinafter referred to simply as dV / dt characteristic)" and the "rectification characteristic Icom" and " Photosensitivity IFT".
[0135] Here, the aforementioned dV / dt characteristics and photosensitivity IFT will be described.
[0136] The above-mentioned "dV / dt characteristic" is determined by the minimum rising edge (=dV / dt) of the false conduction of the bidirectional phototronic thyristor when a pulse voltage with a steep rising edge is applied to the bidirectional phototronic thyristor. definition. This dV / dt characteristic represents noise tolerance. Therefore, it can be said that the larger the dV / dt characteristic is, the better it is in terms of high noise tolerance.
[0137] On the other hand, photosensitivity is used for example in Figure 22 In the light trigger coupler 3 shown, the minimum forward current value IFT when the forward current IF flows through the light emitting e...
no. 3 approach
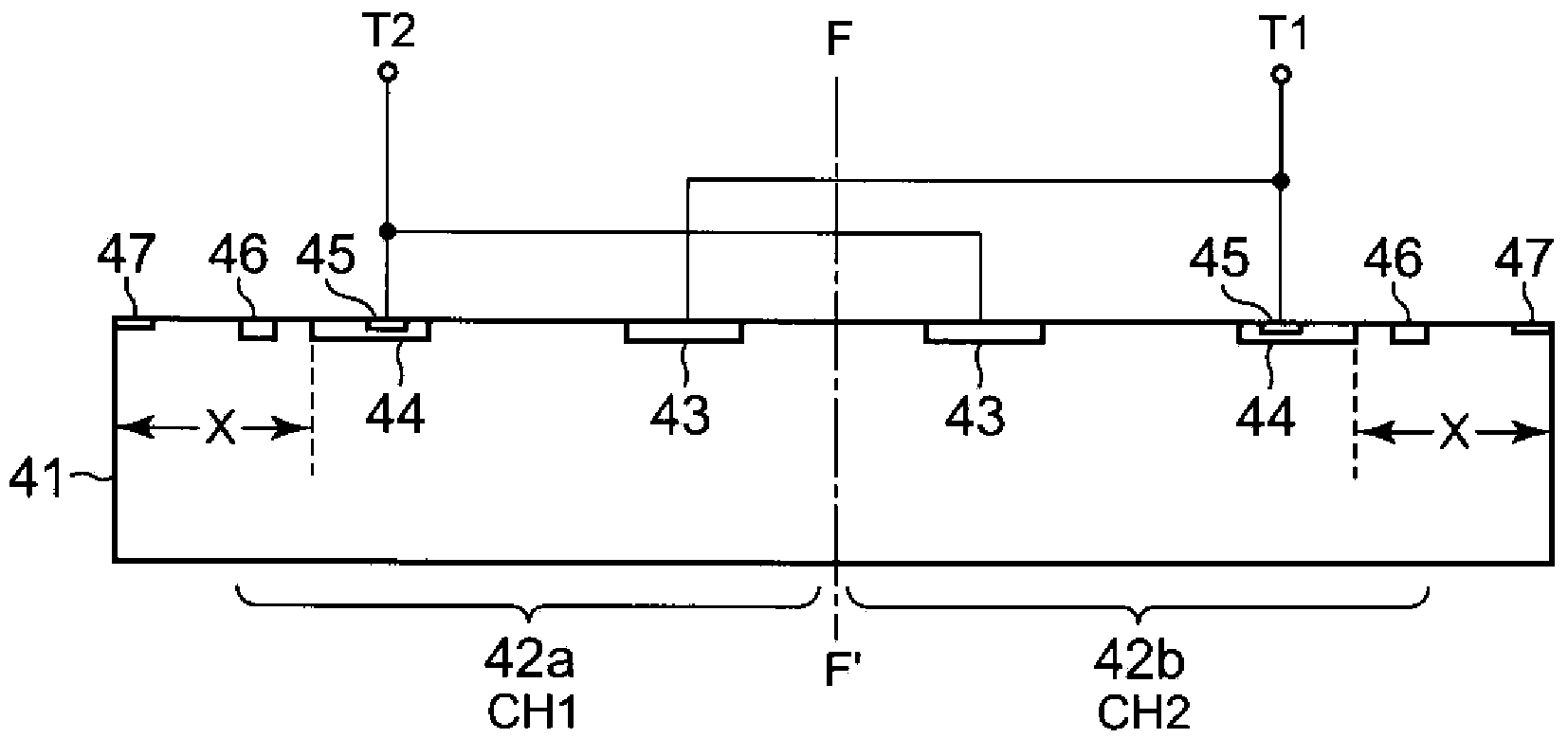
[0170] The present embodiment relates to the gap Z1 between the high-concentration P-type diffusion region constituting the short diode as the channel separation region and the anode diffusion region.
[0171] Figure 14 It is a schematic cross-sectional view of the bidirectional phototriac thyristor chip of this embodiment. The basic structure of the bidirectional photo-controlled thyristor chip of this embodiment is the same as figure 1 and figure 2 The diac chip shown is the same. Figure 14 with the first embodiment described above figure 2 correspond. Thus, in Figure 14 In the bidirectional photo-controlled thyristor chip shown, in order to facilitate understanding, the figure 1 and figure 2 The components that are the same as those shown in the bidirectional photo-controlled thyristor chips are marked with the same symbols, and detailed descriptions are omitted.
[0172] In this embodiment, in addition to the structure of the bidirectional photothyristor ch...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com