Method for preparing free astaxanthin
A technology of astaxanthin and uniform stirring, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of high price, low conversion rate of enzymatic hydrolysis, and difficult separation of products, and achieve the goal of improving the conversion rate Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
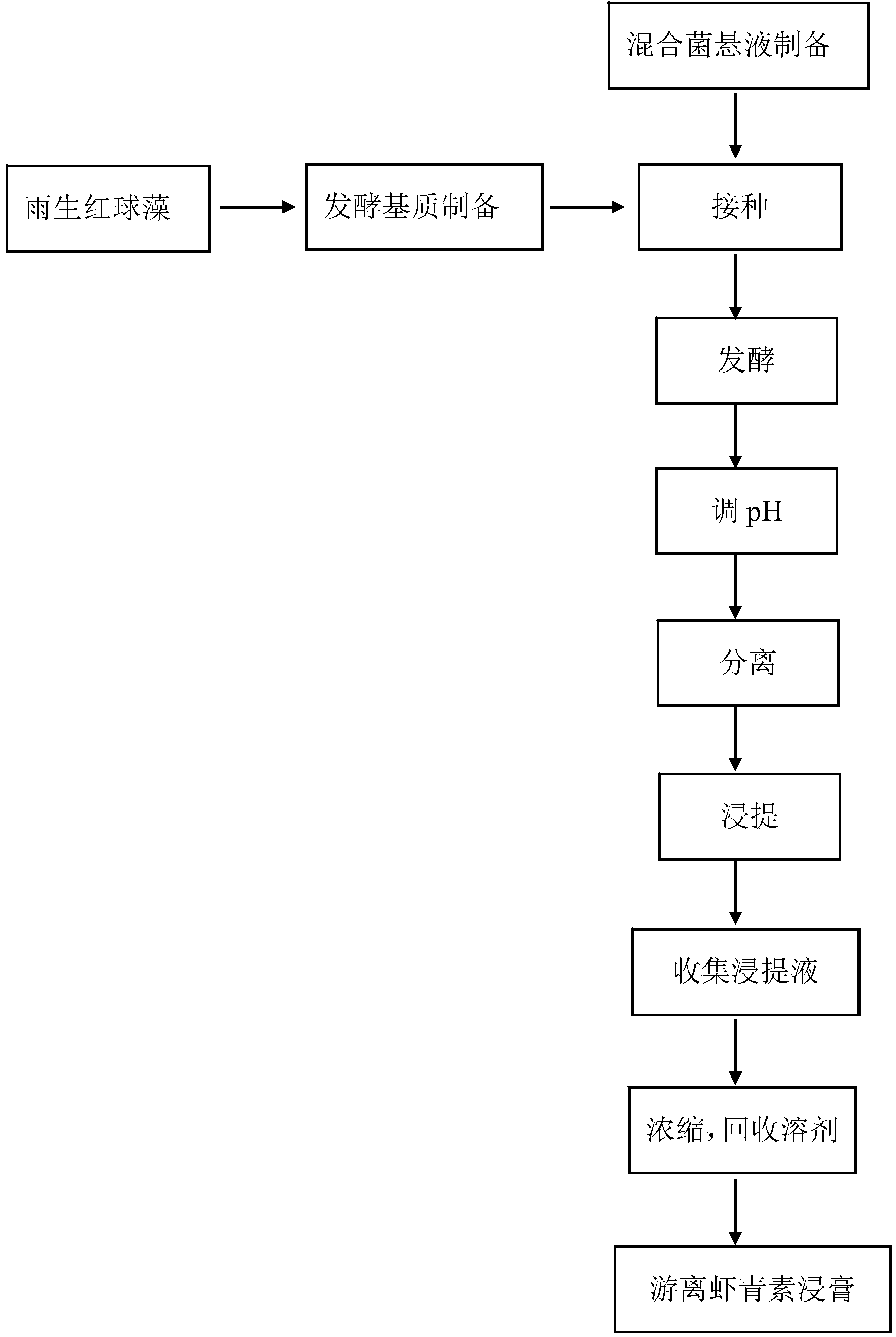
[0028] (1) Raw materials: 1Kg of Haematococcus pluvialis dry powder (Jingzhou Natural Astaxanthin Factory, 2.0% astaxanthin content) was added to 30kg of water and stirred evenly. The used Haematococcus pluvialis powder contains 38% carbohydrates, 24% fat, 24% protein, 2% ash, 1% minerals, 1% biotin, pigments (including: chlorophyll, carotenoids, etc.) 10 %.
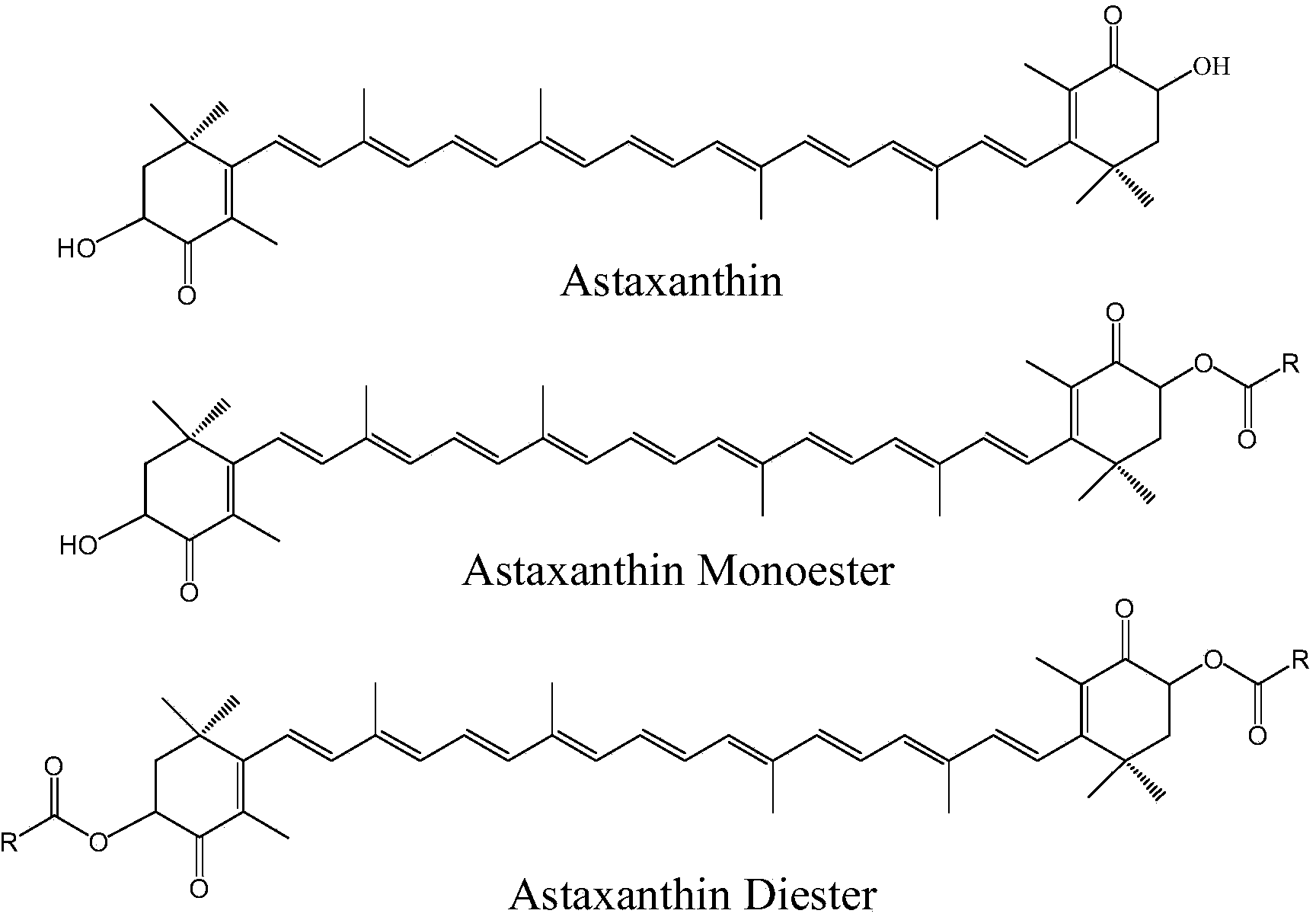
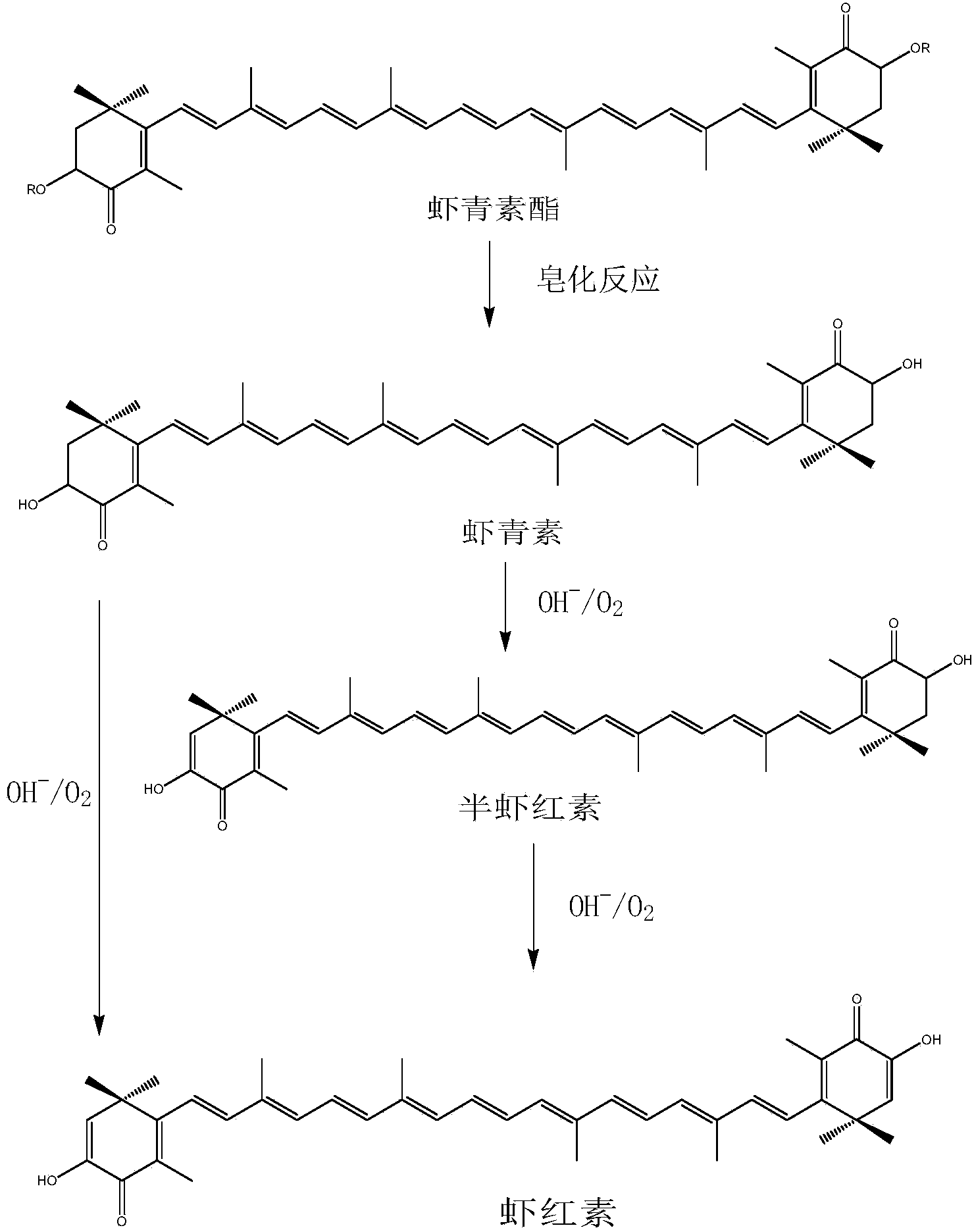
[0029] The astaxanthin in the raw material of Haematococcus pluvialis is analyzed by HPLC-DAD method, and the obtained results are as follows Figure 4 shown, from Figure 4 It can be seen from the figure that the main form of astaxanthin in Haematococcus pluvialis is astaxanthin ester, and astaxanthin monoester is the majority in astaxanthin ester, calculated by the integrated peak area, The relative percentages of free astaxanthin, astaxanthin monoester and astaxanthin diester in Haematococcus were 4.2%, 75.6%, and 20.2%, respectively.
[0030] (2) Ingredients: adding glucose with a mass fraction of 5% to the unifor...
Embodiment 2
[0040] (1) Raw materials: 1Kg of Haematococcus pluvialis (Jingzhou City Natural Astaxanthin Factory, astaxanthin content 2.0%), add water 10 times the weight (W / V) of Haematococcus pluvialls, and stir evenly.
[0041] (2) Ingredients: adding glucose with a mass fraction of 10% to the uniformly stirred mixing system in step (1), stirring uniformly and then sterilizing to obtain the fermentation base material.
[0042] (3) Fermentation: mix the bacterial suspensions of the activated Aspergillus niger and Candida two kinds of bacteria according to the volume ratio of 2:1 to make a mixed bacterial liquid, and then mix the bacterial suspension with 12% The amount of inoculum is inoculated into the sterilized fermentation base material, and then fermented at 40°C for 12 hours, with continuous or intermittent stirring during the process.
[0043] (4) Separation: After the fermentation, adjust the fermented liquid to pH 2.0, rest for 0.5h, centrifuge at 8000r / min, and collect the prec...
Embodiment 3
[0047] (1) Raw material: 10Kg of Haematococcus pluvialis (Jingzhou Natural Astaxanthin Factory, astaxanthin content 2.0%), add 20 times the weight (W / V) of Haematococcus pluvialis, and stir evenly.
[0048] (2) Ingredients: adding glucose with a mass fraction of 8% to the uniformly stirred mixing system in step (1), stirring uniformly, and then sterilizing to obtain a fermentation base material.
[0049] (3) Fermentation: Mix the bacterial suspensions of the activated rhizopus and candida in a volume ratio of 1:1 to make a mixed bacterial suspension, and then inoculate the bacterial suspension with 15% amount, inoculated into the sterilized fermentation base material, and then fermented at 38°C for 20h, with continuous or intermittent stirring during the process.
[0050] (4) Separation: After the fermentation, adjust the fermented liquid to pH 3.0, let it rest for 2 hours, filter, and collect the precipitate.
[0051] (5) Leaching: add the ethanol solution that mass volume r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com