A kind of lightweight ceramsite assisted sintering on the surface of sodium sulfate and preparation method thereof
A surface-assisted sintering, lightweight ceramsite technology, applied in the field of new building materials, can solve the problems of reducing the heat insulation and sound insulation effect of ceramsite, reducing the sintering temperature of ceramsite, and low strength of ceramsite, and achieving low cost and strength of ceramsite. High, easy-to-control effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
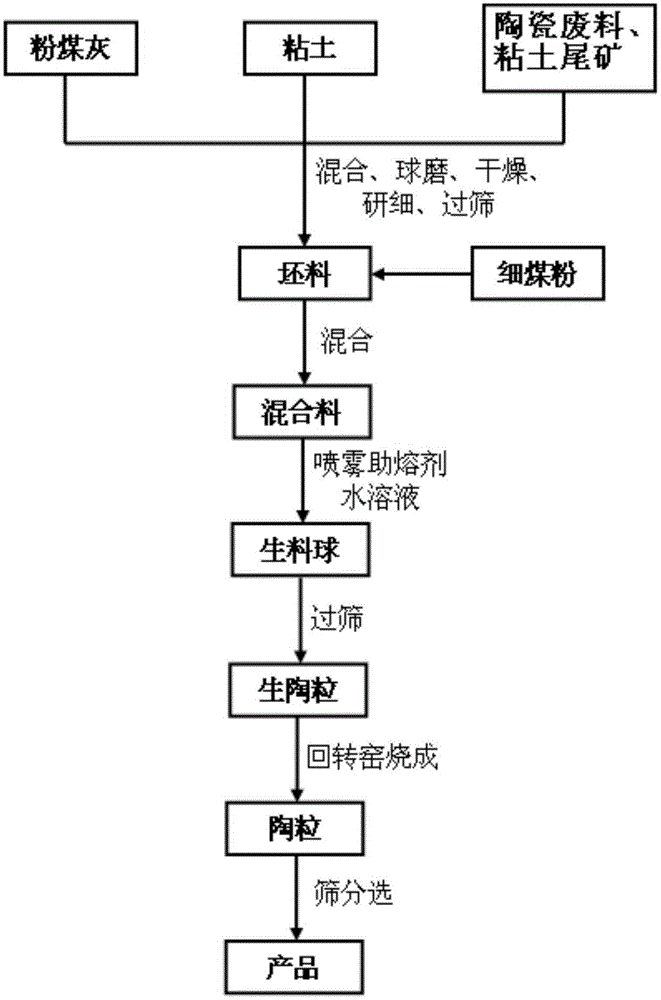
[0021] see figure 1 and 2 A method for preparing light-weight ceramsite assisted by sintering on the surface of sodium sulfate comprises the following steps:
[0022] 1) Take the raw materials in terms of mass percentage: 0%-65% of fly ash, 35%-95% of clay, 0-65% of ceramic waste and 0-65% of clay tailings; mix the raw materials and perform ball milling , dry and finely grind the blanks for later use; wherein the blanks with a particle size of less than 65 μm account for more than 90% of the total mass of the blanks;
[0023] 2) Mixing the blank prepared in step 1) and a pore-forming agent with a particle size of less than 0.125mm at a mass ratio of 100:(5-20) to obtain a mixture;
[0024] 3) Put the mixed material prepared in step 2) into the sugar coating machine for balling treatment to obtain raw meal balls. During the balling process, add the mixed material intermittently according to the balling situation, and in the balling process, add the mixed material with a conce...
Embodiment 1
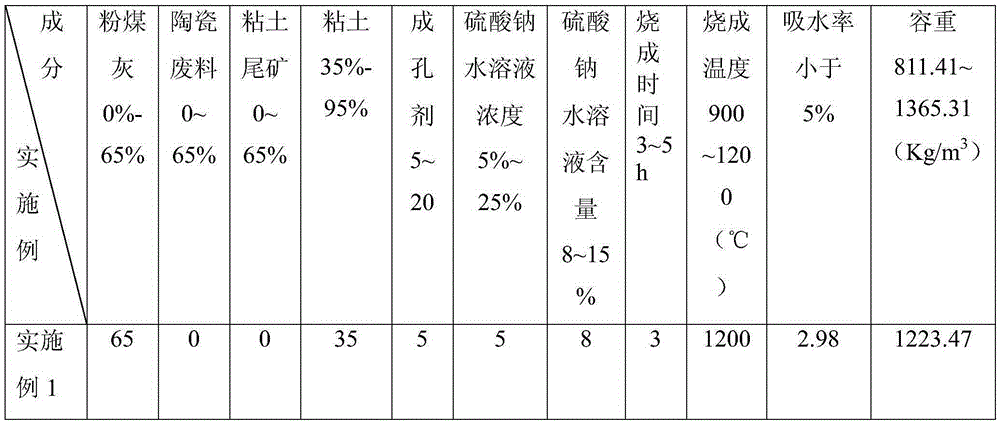
[0034] 1) Take the raw materials in terms of mass percentage: 65% of fly ash and 35% of clay; after mixing the raw materials, carry out ball milling, drying and grinding to obtain a billet for subsequent use; wherein the billet with a particle size less than 65 μm accounts for 10% of the total mass of the billet more than 90 percent;
[0035] 2) mixing the blank prepared in step 1) with a pore-forming agent with a particle size of less than 0.125 mm at a mass ratio of 100:5 to obtain a mixture;
[0036] 3) Put the mixed material prepared in step 2) into the sugar coating machine for balling treatment to obtain raw meal balls. During the balling process, add the mixed material intermittently according to the balling situation, and in the balling process, add the mixed material with a concentration of 5 % sodium sulfate aqueous solution intermittently sprayed onto the mixture, the content of sodium sulfate aqueous solution in the obtained raw meal balls accounts for 8% of the to...
Embodiment 2
[0041] 1) Take the raw materials in terms of mass percentage: a mixture of 35% clay and 65% ceramic waste; after mixing the raw materials, perform ball milling, drying and grinding to obtain a blank for later use; wherein the blank with a particle size of less than 65 μm accounts for the total mass of the blank More than 90% of;
[0042] 2) mixing the blank prepared in step 1) with a pore-forming agent with a particle size of less than 0.125mm at a mass ratio of 100:6 to obtain a mixture;
[0043] 3) Put the mixed material prepared in step 2) into the sugar coating machine for balling treatment to obtain raw meal balls. During the balling process, add the mixed material intermittently according to the balling situation, and in the balling process, add the mixed material with a concentration of 8 % of sodium sulfate aqueous solution intermittently sprayed onto the mixture, the content of sodium sulfate aqueous solution in the obtained raw meal balls accounts for 9% of the total...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com