Light-emitting diode and manufacturing method thereof
A technology of light-emitting diodes and electrodes, applied in electrical components, circuits, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problems of high cost and large consumption of gold, and achieve the effect of reducing costs and reducing gold consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
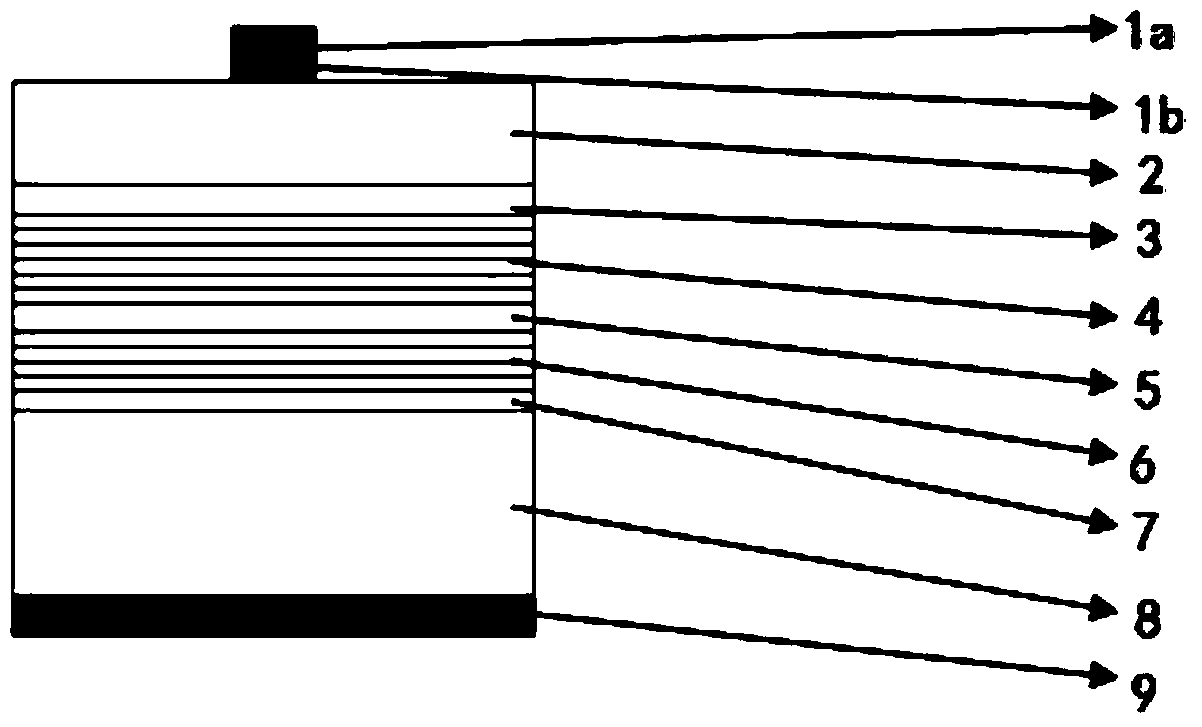
[0040] see figure 2 , an embodiment of the present invention provides a light emitting diode, including a substrate 11, a buffer layer 12, a distributed Bragg reflector 13, an n-type confinement layer 14, an active layer 15, a p-type confinement layer 16, and a GaP window layer stacked in sequence 17. P-type ohmic contact layer 18, an n-type ohmic contact electrode 10 is provided on the side of the substrate 11 opposite to the buffer layer 12, and a p-surface is provided on the side of the p-type ohmic contact layer 18 opposite to the GaP window layer 17 The bonding wire electrode 19, the C element heavily doped GaP layer 20 is laminated between the GaP window layer 17 and the p-type ohmic contact layer 18, the p-type ohmic contact layer 18 is an indium tin oxide film, and the p-side bonding wire electrode 19 is an Al electrode .
[0041] Specifically, in this embodiment, the substrate 11 can be a GaAs substrate, the buffer layer 12 can be GaAs, the distributed Bragg mirror ...
Embodiment 2
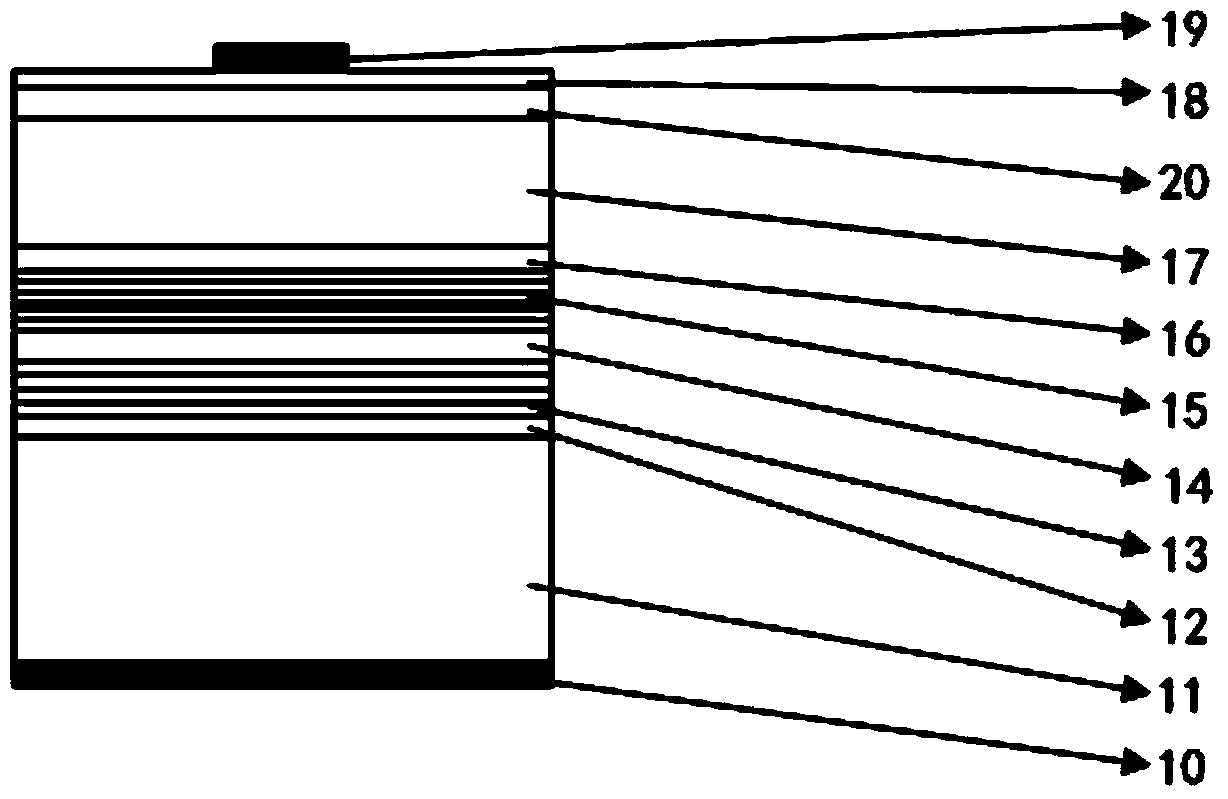
[0052] see Figure 5 , the embodiment of the present invention provides a method for manufacturing a light-emitting diode, which can be used to prepare the light-emitting diode (especially the red and yellow light-emitting diode) provided in Example 1. The method includes:
[0053] S10: providing a substrate;
[0054] In this embodiment, the substrate of the light emitting diode is a GaAs substrate.
[0055] S11: sequentially forming a buffer layer, a distributed Bragg reflector, an n-type confinement layer, an active layer, a p-type confinement layer, a GaP window layer, and a surface C heavily doped layer on the substrate;
[0056] Among them, the doping concentration of C element is greater than 1x10 19 cm -3 , the C element heavily doped the GaP layer 20 to a degree of 400-1000nm.
[0057] S12: Evaporate a layer of indium tin oxide film on the C element heavily doped GaP layer to form a p-type ohmic contact layer;
[0058] In this embodiment, an electron beam is used ...
Embodiment 3
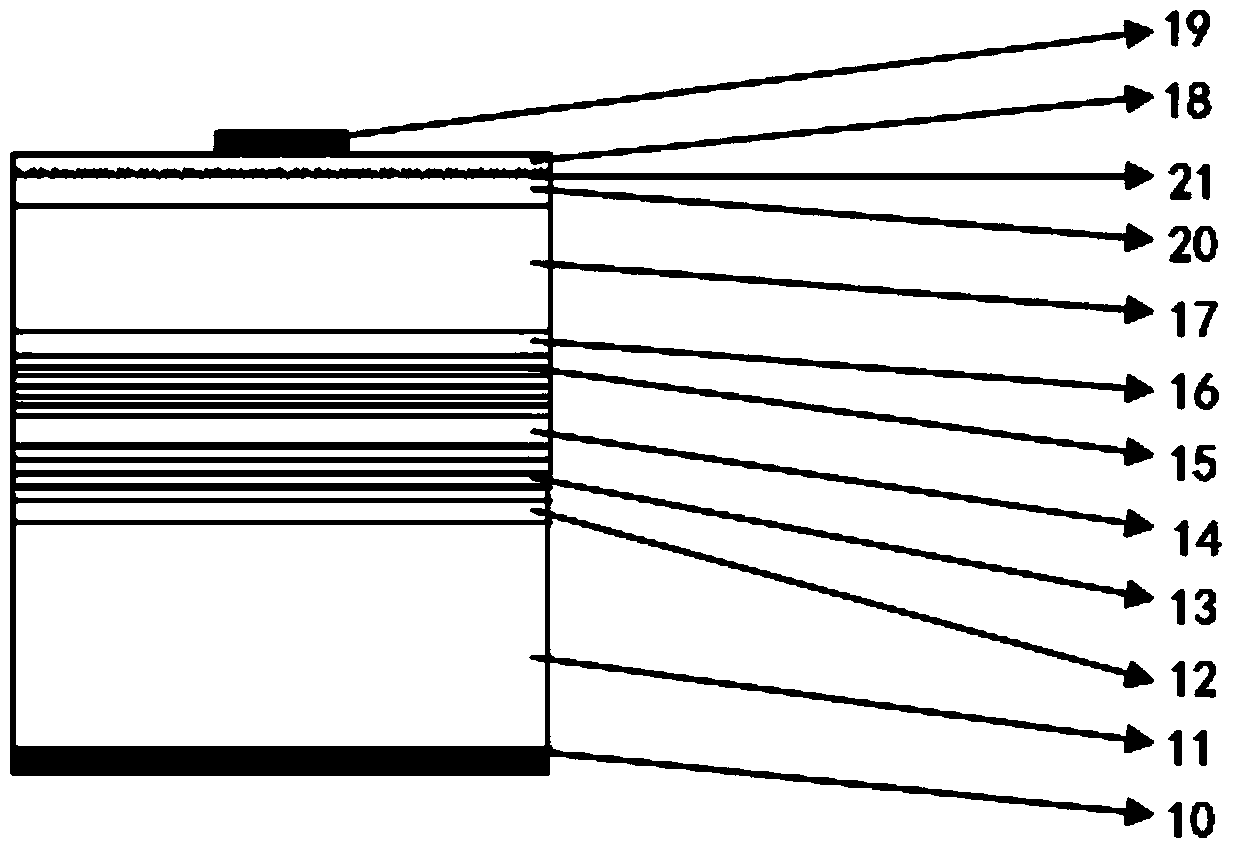
[0069] see Figure 6 , the embodiment of the present invention provides a method for manufacturing a light-emitting diode, which can be used to prepare the light-emitting diode (especially the red and yellow light-emitting diode) provided in Example 1. The difference from the method for manufacturing the diode in Example 2 is that A surface roughening layer is formed, the method comprising:
[0070] S20: providing a substrate;
[0071] In this embodiment, the substrate of the light emitting diode is a GaAs substrate.
[0072] S21: sequentially forming a buffer layer, a distributed Bragg reflector, an n-type confinement layer, an active layer, a p-type confinement layer, a GaP window layer, and a surface C heavily doped layer on the substrate;
[0073] Among them, the doping concentration of C element is greater than 1x10 19 cm -3 , the C element heavily doped the GaP layer 20 to a degree of 400-1000nm.
[0074] S22: performing surface roughening on the C element heavily d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com