Nanofiber bone cartilage repairing stent for tissue engineering and preparation method thereof
A nanofiber and tissue engineering technology, applied in the field of tissue engineering nanofiber osteochondral repair scaffold and its preparation, can solve the problems affecting the repair of cartilage layer and subchondral bone layer, easy to migrate and grow into each other, so as to improve the overall physical and chemical properties, The production cost is low and the effect of promoting regeneration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
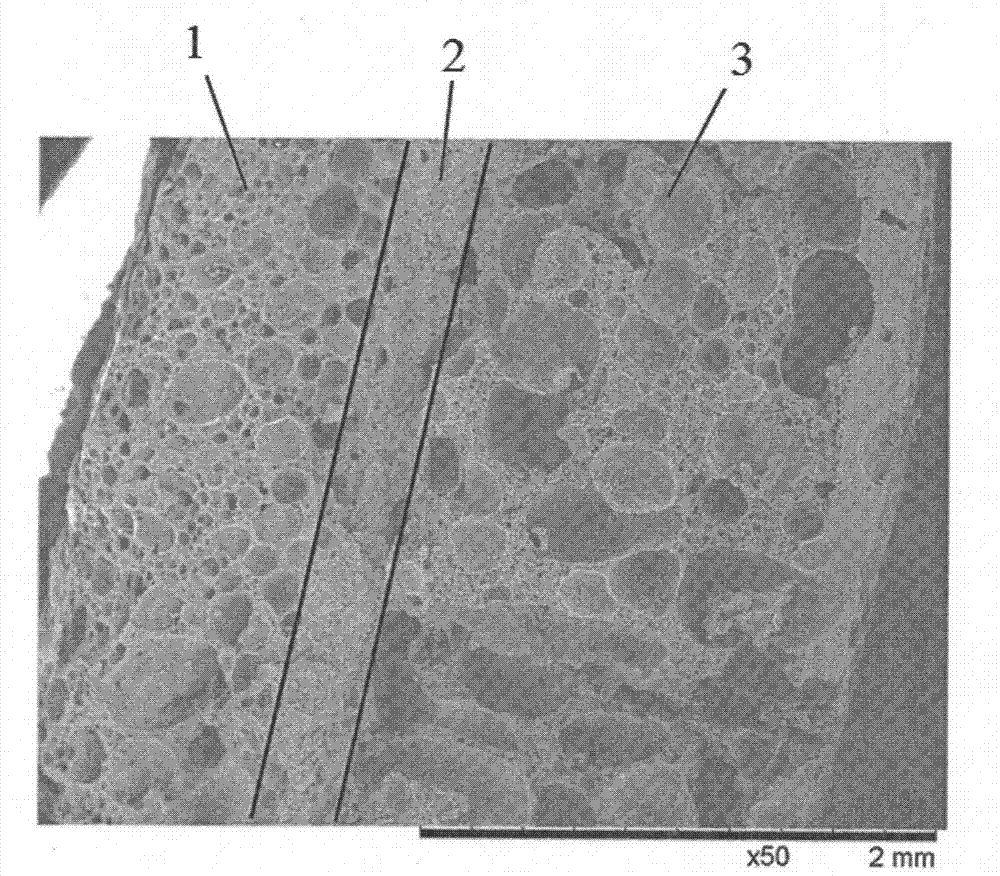
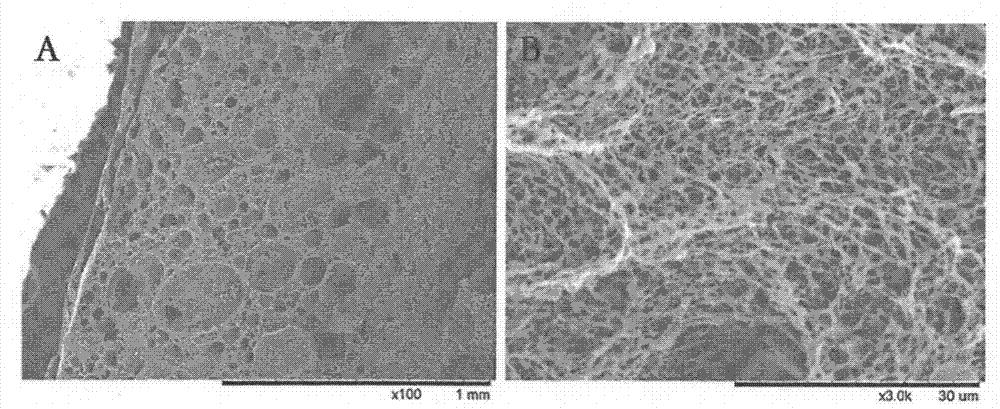
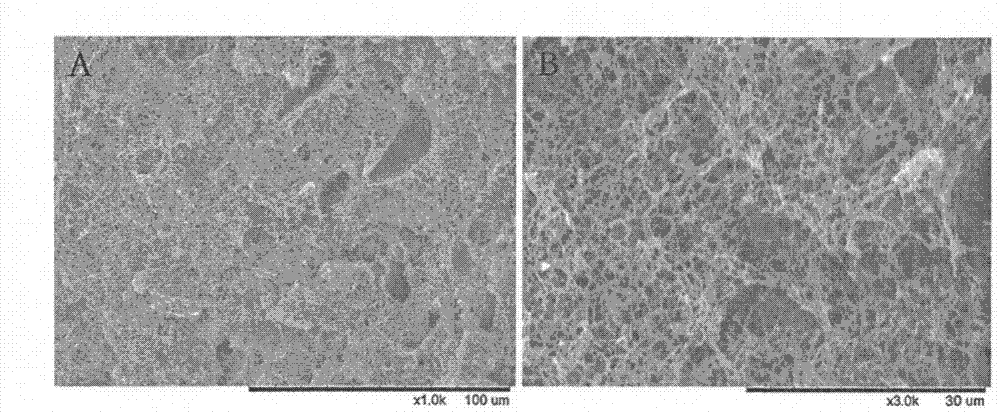
[0025] like figure 1 As shown, the tissue engineering nanofibrous osteochondral repair scaffold of the present invention is composed of a porous cartilage layer 1, a porous subchondral bone layer 3 and a connecting layer 2 arranged between the porous cartilage layer 1 and the porous subchondral bone layer 3. The porous cartilage layer 1 includes a PLLA-based composite degradable polymer material, which is a porous nanofiber structure, with a pore size of 20 to 60 μm and a thickness of 1 mm; the connecting layer 2 includes a PLLA-based composite degradable polymer material, which is a porous nanofiber structure. , the pore diameter is less than 5 μm, and the thickness is 0.4 mm; the porous subchondral bone layer 3 includes a PLLA-based composite degradable polymer material containing 20% nano-hydroxyapatite, which is a porous nanofiber structure with a pore diameter of 60-400 μm and a thickness of 1.8 mm.
[0026] The preparation method of the tissue engineering nanofiber os...
Embodiment 2
[0032] The tissue engineering nanofibrous osteochondral repair scaffold of the present invention is composed of a porous cartilage layer, a porous subchondral bone layer, and a connecting layer arranged between the porous cartilage layer and the porous subchondral bone layer, and the porous cartilage layer includes PLLA-based The composite degradable polymer material is a porous nanofiber structure with a pore size of 20-60 μm and a thickness of 1.5 mm; the connecting layer includes a PLLA-based composite degradable polymer material with a porous nanofiber structure with a pore size of <5 μm and a thickness of 0.5 mm The porous subchondral bone layer includes PLLA-based composite degradable polymer materials containing 30% nano-hydroxyapatite, which is a porous nanofiber structure with a pore size of 60-500 μm and a thickness of 2.5 mm.
[0033] The preparation method of the tissue engineering nanofiber osteochondral repair scaffold is as follows:
[0034] (1) Dissolve PLLA an...
Embodiment 3
[0039] The tissue engineering nanofibrous osteochondral repair scaffold of the present invention is composed of a porous cartilage layer, a porous subchondral bone layer, and a connecting layer arranged between the porous cartilage layer and the porous subchondral bone layer, and the porous cartilage layer includes PLLA-based The composite degradable polymer material is a porous nanofiber structure with a pore size of 20-60 μm and a thickness of 2 mm; the connecting layer includes a PLLA-based composite degradable polymer material with a porous nanofiber structure with a pore size of <5 μm and a thickness of 0.5 mm; The porous subchondral bone layer includes PLLA-based composite degradable polymer material containing 40% nano-hydroxyapatite, which is a porous nanofiber structure with a pore diameter of 60-400 μm and a thickness of 2.5 mm.
[0040] The preparation method of the tissue engineering nanofiber osteochondral repair scaffold is as follows:
[0041] (1) Dissolve PLLA ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com