Method for accelerating permeation of Dy/Tb adhesive layer on surface of sintered neodymium-iron-boron magnet
A technology of NdFeB and adhesion layer, which is applied in the field of accelerating the diffusion of Dy/Tb adhesion layer on the surface of sintered NdFeB magnets, which can solve the problems of resources, energy waste, adverse effects on the structure and performance of sintered NdFeB matrix, and unfavorable efficiency. , to achieve the effects of improving efficiency, facilitating industrial production, and inhibiting growth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
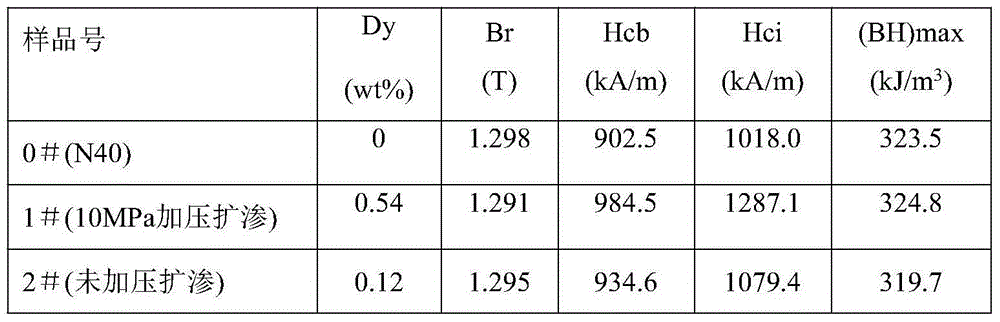
[0024] Example 1: The surface of a 4mm thick N40 magnet is coated with Dy 2 o 3 After 10MPa / 700℃ / 0.5h heat treatment
[0025] Select an N40 magnet with a size of 20mm×20mm×4mm and mark it as 0# sample. The N40 magnet was degreased with 5% trisodium phosphate, washed with distilled water, washed with 5% nitric acid for 15-30s, ultrasonically cleaned with distilled water, and dried; Dy with a particle size of 2 μm 2 o 3 Mix the solution with ethanol at a weight ratio of 2:1, put the magnetic sheet into the solution, mix it with ultrasonic waves for 1-3 minutes, take it out and dry it; put the sample in the furnace, and vacuum to (3-5)×10 -3Pa, start rapid heating to 700°C, fill it with argon to apply an isostatic pressure of 10MPa, keep it warm for 0.5h, and then perform heat treatment at 500°C / 2h, this sample is marked as 1# sample. Except that no pressure is applied, the other process parameters are consistent with the 1# sample, which is marked as the 2# sample. The Dy c...
Embodiment 2
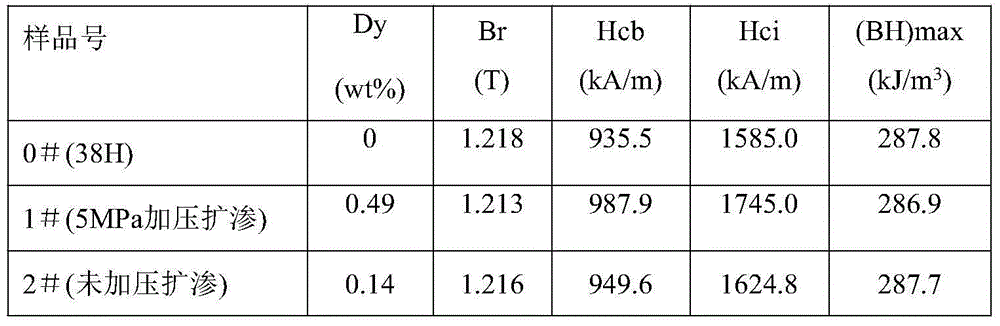
[0028] Example 2: The surface of a 7mm thick 38H magnet is coated with DyF 3 After heat treatment at 6MPa / 740℃ / 1h
[0029] Select a 38H magnet with a size of 20mm×20mm×7mm and mark it as 0# sample. The 38H magnet is degreased by 5% trisodium phosphate, washed with distilled water, washed with 5% nitric acid for 15-30s, ultrasonically cleaned with distilled water, and dried; DyF with a particle size of 2 μm 3 Mix the solution with ethanol at a weight ratio of 2:1, put the magnetic sheet into the solution, mix it with ultrasonic waves for 1-3 minutes, take it out and dry it; put the sample in the furnace, and vacuum to (3-5)×10 -3 Pa, start rapid heating to 740°C, fill it with argon to apply an isostatic pressure of 5MPa, keep it warm for 1h, and then perform heat treatment at 500°C / 2h, this sample is marked as 1# sample. Except that no pressure was applied, the other process parameters were consistent with the 1# sample, which was labeled as 2# sample. The Dy content and magn...
Embodiment 3
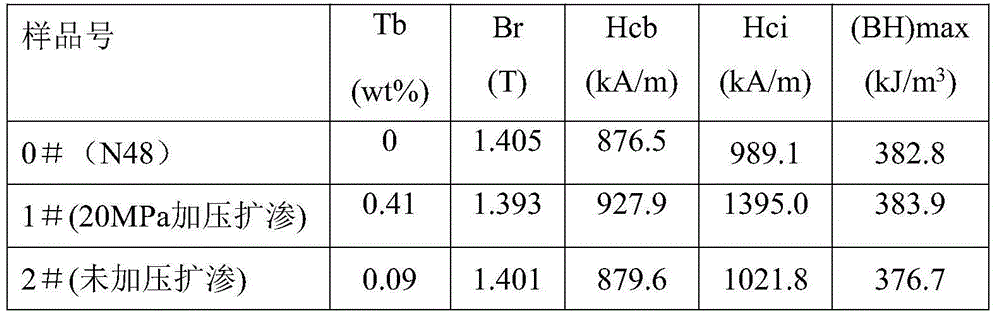
[0032] Example 3: 20MPa / 720°C / 1h heat treatment after sputtering Tb metal layer on the surface of 10mm thick N48 magnet
[0033] Select an N48 magnet with a size of φ15mm×10mm and mark it as 0# sample. The N48 magnet is degreased with 5% trisodium phosphate, cleaned with distilled water, washed with 5% nitric acid for 15-30s, ultrasonically cleaned with distilled water, and dried; the sintered NdFeB that has been cleaned on the surface is used as the substrate, and sputtered on its surface Attach a layer of Tb metal layer; place the sample in the furnace and vacuumize to (3-5)×10 -3 Pa, start rapid heating to 720°C, fill it with argon to apply an isostatic pressure of 20MPa, keep it warm for 1h, and then perform heat treatment at 500°C / 2h, this sample is marked as 1# sample. Except that no pressure was applied, the other process parameters were consistent with the 1# sample, which was labeled as 2# sample, and the Tb content and magnetic property parameters are shown in Table...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com