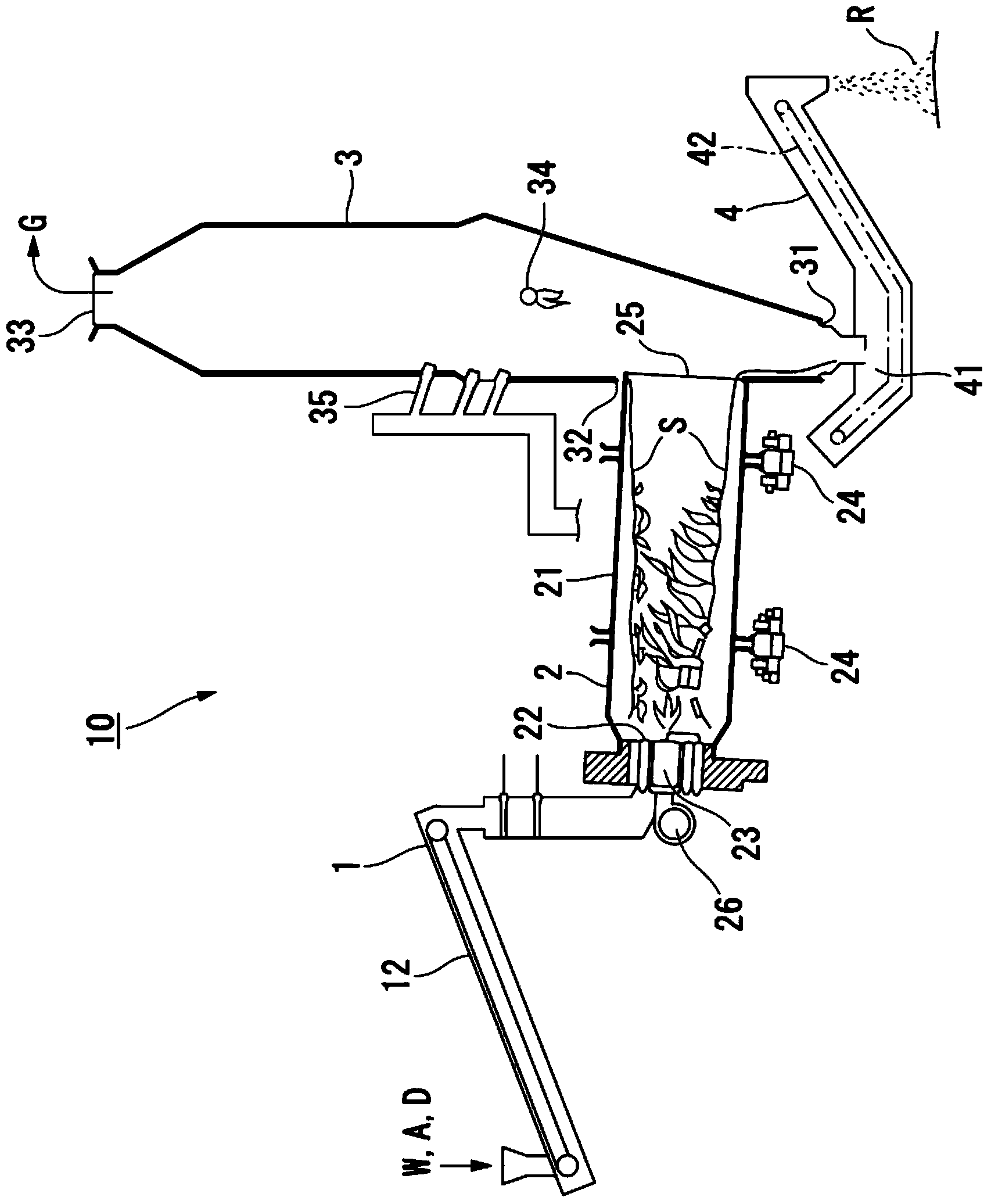
Method for processing starting materials for recycling
A treatment method and reuse technology, applied in the direction of combustion method, chemical instrument and method, process efficiency improvement, etc., can solve the problems of treatment cost (increased cost of crushing, easy loss of bricks, loss of bricks, etc.), and achieve Reduced fuel costs, suppressed local loss, and stabilized treatment efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0107] Hereinafter, the present invention will be specifically described by way of examples. However, the present invention is not limited to this Example.
[0108] Using the rotary kiln 2 described in the foregoing embodiment, the treatment tests A to C were performed under the following conditions.
[0109] Specifically, a furnace having an inner diameter of 5 m and a length (length along the axial direction) of 14 m was used as the rotary kiln 2 . In addition, in the treatment tests A and B, Al was used as a refractory material on the inner wall of the rotary kiln 2. 2 o 3 -Cr 2 o 3 Alumina-chromia bricks with a content of 70% or more. In detail, the Al in the brick (refractory) 2 o 3 -Cr 2 o 3 The content rate is 70%, as the Al 2 o 3 -Cr 2 o 3 Components other than ZrO 2 The content rate is about 20%, SiO 2 The content rate is about 10%, and the balance is ZrSiO 4 .
[0110] [Processing Test A]
[0111] The amount of substrates containing valuable metals ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com