Deep treatment method and device of coking wastewater
A technology for advanced treatment and coking wastewater, applied in the direction of oxidized water/sewage treatment, natural water treatment, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of high cost of advanced treatment, failure to achieve COD of effluent, poor biodegradability of wastewater, etc., to avoid Effects of unsafe factors and potential health hazards, reasonable process and device system design, and strong engineering application value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
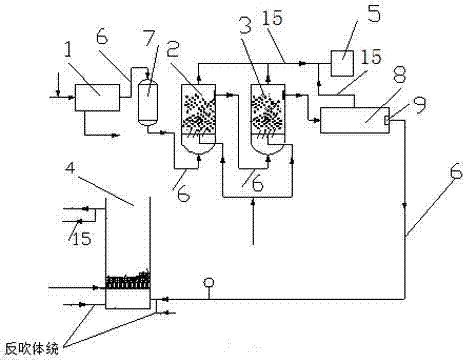
[0033] The method for advanced treatment of coking wastewater, its steps:
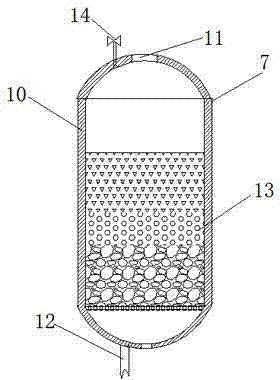
[0034] 1) Adjust the pH value of the wastewater after conventional biochemical and coagulation treatment to 7, and then enter the multimedia filter 7 for filtration;
[0035] 2) The wastewater filtered by the multimedia filter 7 enters the first-level ozone reaction tower 2, and ozone is added to the wastewater at a rate of 50 mg / L, stirred and the hydraulic retention time is 21 minutes, so that the wastewater and ozone can fully react;
[0036] 3) The wastewater from the first-level ozone reaction tower 2 enters the second-level ozone reaction tower 3, and without adding ozone, stir and make the hydraulic retention time 19 minutes, so that the wastewater and ozone can fully react again;
[0037] 4) The wastewater treated by the secondary ozone reaction tower 3 enters the corridor-shaped closed intermediate pool 8 for ozonolysis, and the hydraulic retention time of the wastewater in it is 35 minutes; ...
Embodiment 2
[0042] The method for advanced treatment of coking wastewater, its steps:
[0043] 1) Adjust the pH value of the wastewater after conventional biochemical and coagulation treatment to 8, and then enter the multimedia filter 7 for filtration;
[0044] 2) The wastewater filtered by the multimedia filter 7 enters the first-level ozone reaction tower 2, and ozone is added to the wastewater at a rate of 60 mg / L, stirred and the hydraulic retention time is 26 minutes, so that the wastewater and ozone can fully react;
[0045] 3) The wastewater from the first-level ozone reaction tower 2 enters the second-level ozone reaction tower 3, and ozone is added to the wastewater at a rate of 10 mg / L, stirred and the hydraulic retention time is 15 minutes, so that the wastewater and ozone can fully react again;
[0046] 4) The wastewater treated by the secondary ozone reaction tower 3 enters the corridor-shaped closed intermediate pool 8 for ozone decomposition, and the hydraulic retention t...
Embodiment 3
[0051] The method for advanced treatment of coking wastewater, its steps:
[0052] 1) Adjust the pH value of the wastewater after conventional biochemical and coagulation treatment to 8.5, and enter the multimedia filter 7 for filtration;
[0053] 2) The wastewater filtered by the multimedia filter 7 enters the first-level ozone reaction tower 2, and ozone is added to the wastewater at a rate of 70 mg / L, stirred and the hydraulic retention time is 30 minutes, so that the wastewater and ozone can fully react;
[0054] 3) The waste water from the first-level ozone reaction tower 2 enters the second-level ozone reaction tower 3, and ozone is added according to 20 mg / L of waste water, stirred and the hydraulic retention time is 21 minutes, so that the waste water and ozone can fully react again;
[0055] 4) The wastewater treated by the secondary ozone reaction tower 3 enters the corridor-shaped closed intermediate pool 8 for ozonolysis, and the hydraulic retention time of the wa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com