A method for knocking out the fgf5 gene in animals using the CRISPR-Cas9 system
A technology for knocking out animals and genes, which is applied in the field of animal genetic engineering and genetic modification, can solve the problems of complicated operation, complicated design and production of ZFNs, and high cost, and achieve the effects of improving transfection efficiency, wide applicability, and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1 Construction of the CRISPR-Cas9 expression system for the FGF5 gene
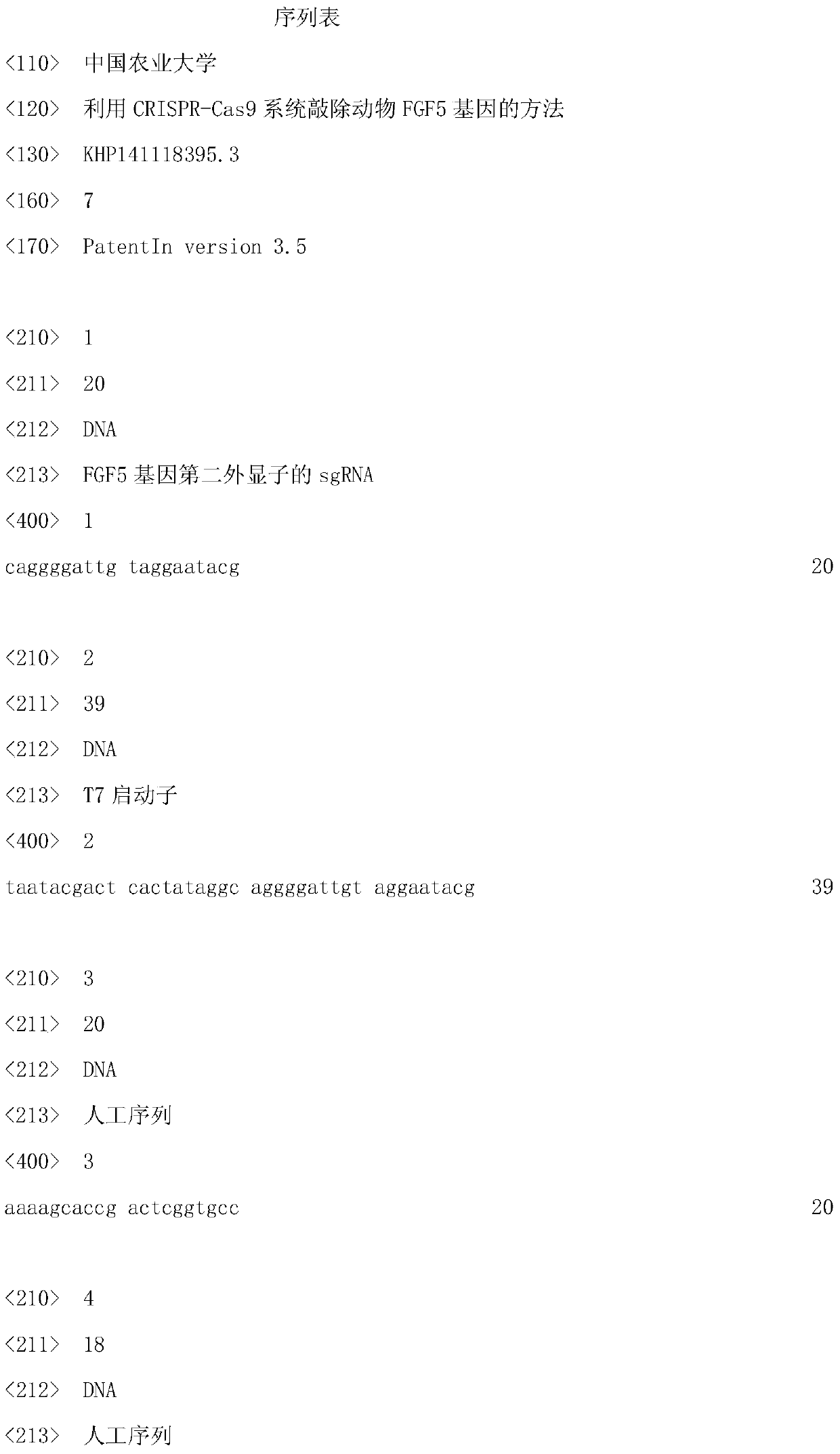
[0035] 1. Compared the FGF5 gene sequences of different species (human, mouse, pig, cow, sheep, goat), found a relatively conserved region, designed sgRNA in these two regions and obtained a sgRNA sequence information. The DNA sequence of the sgRNA specifically targeting the second exon of the FGF5 gene is shown in SEQ ID NO.1.
[0036] 2. Construction of pX330-F2: (1) Design and synthesize the DNA sequence of the sgRNA recognition region that recognizes the second exon of FGF5, as shown in SEQ ID NO.1; (2) Gradient after phosphorylation of the synthesized sgRNA sequence Cooling and annealing, the specific steps are to mix the synthesized oligoDNA with 10X T4Ligation Buffer and T4PNK at a ratio of 2:2:1, then add 3 times the volume of water to make up the system, then incubate at 37°C for 30min, then denature at 95°C for 5min, Afterwards, the temperature was lowered to 25°C at a rate of 5°...
Embodiment 2
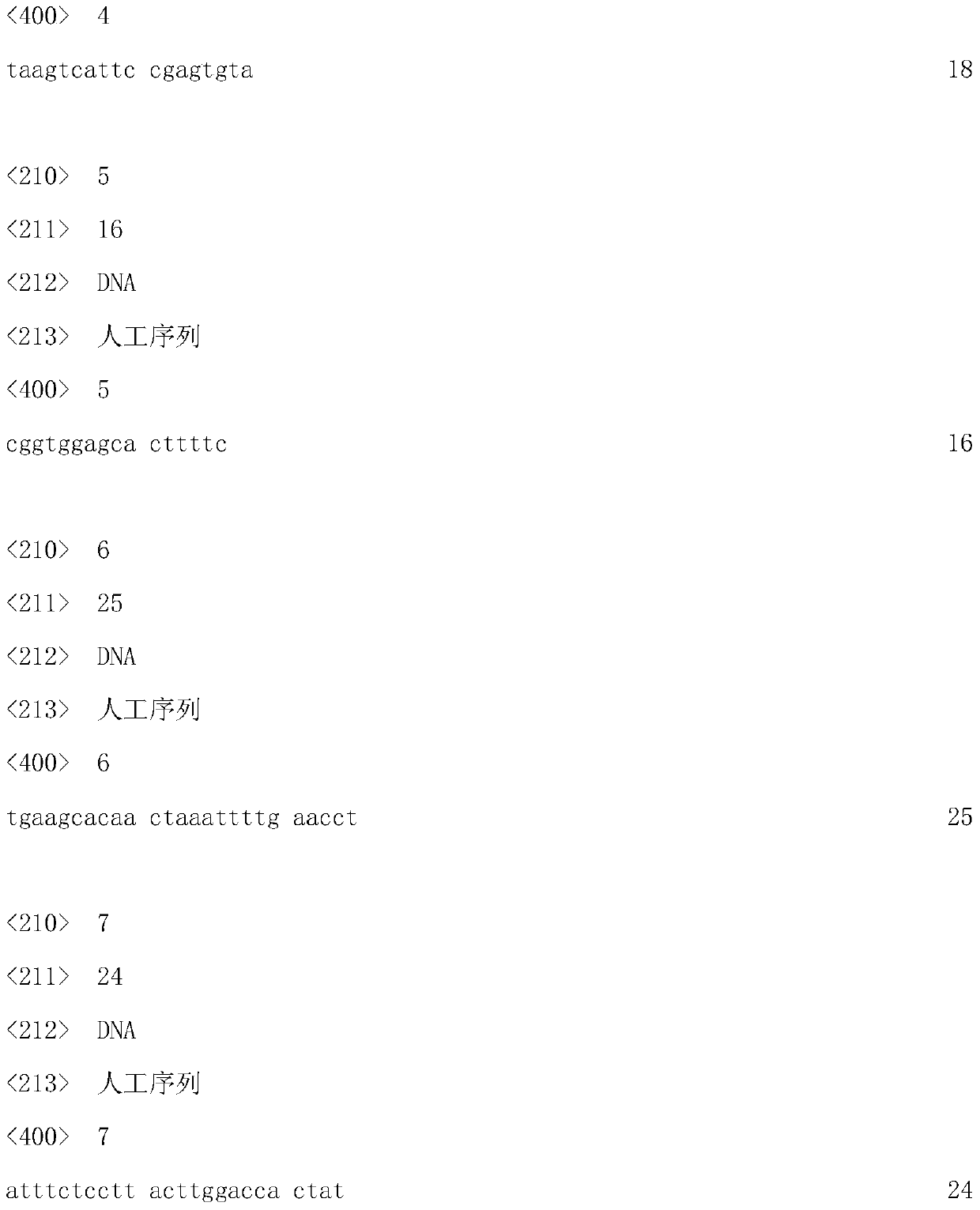
[0040] Example 2 In vitro transcription
[0041] Use the constructed in vitro transcription vectors pIVT-F2-T and pCas9-puro3 to perform in vitro transcription mediated by the T7 promoter, that is, use the T7 promoter as the promoter for in vitro transcription, and use RNA polymerase to realize the conversion from DNA to mRNA in vitro For the transcription process, the specific method is: use SalI and NotI to linearize the vectors pIVT-M2-T and pCas9-puro3 respectively, then use the linearized in vitro transcription vector as a template, add T7 transcriptase, buffer and rNTPs, and incubate at 37°C for 6h. Then add DNase at 37°C for 15 minutes to digest and remove the template DNA, then use phenolform extraction to remove protein impurities, ethanol precipitation to obtain the transcribed mRNA, and purify the transcribed mRNA with an adsorption column. The specific method is: add 3.5 Double the volume of binding buffer and 2.5 times the volume of absolute ethanol, mix well and ...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Example 3 Production of gene-targeted mice using the CRISPR-Cas9 system mRNA targeting the FGF5 gene
[0043] 1. Pronuclear injection and embryo transfer
[0044] The pronuclear fertilized eggs of B6D2F1 mice were taken, and the premixed Cas9mRNA / sgRNA mixture (the final concentration of Cas9mRNA was 150ng / μl, and the final concentration of sgRNA was 20ng / μl) was injected into the cytoplasm or in the nucleus. After the injection, the fertilized eggs are transferred to the culture medium for short-term culture, and then transplanted into the oviduct of recipient mother mice to produce gene-targeted mice.
[0045] 2. Identification of gene targeting mice
[0046] After the birth of the surrogate mother mouse, cut off about 1 cm of mouse tail when the offspring grow to 2 weeks old, digest with proteinase K at 55°C, and extract the mouse tail genome by phenolform extraction. Using the mouse tail genome as a template, design primers targeting the second exon of FGF5, ampl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com