Method for knocking out two mir-505 alleles
A biallelic, gene technology, applied in DNA/RNA fragments, introduction of foreign genetic material using vectors, recombinant DNA technology, etc., can solve problems such as unclear specific methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] (1) Construction of neo-EGFP-Xho I-Nru I vector (with EGFP targeting vector)
[0040] A. Obtaining of EGFP Fragment
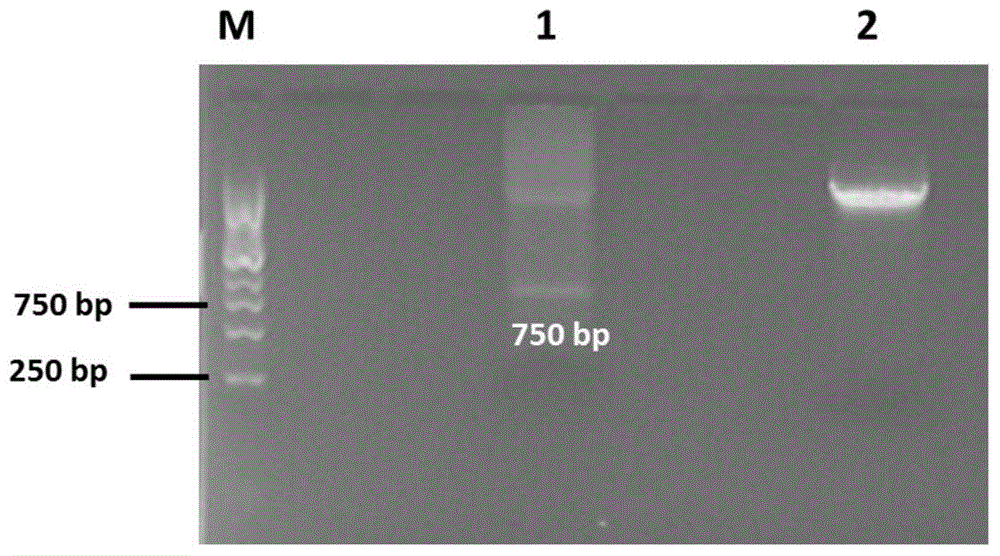
[0041] Using the pEGFP-C1 vector as a donor, the EGFP fragment was obtained by enzyme digestion. First digest the pEGFP-C1 vector with Nhe I, and use Klenow enzyme to blunt the sticky end to become a blunt end. On this basis, use Bgl II to perform a single enzyme digestion to obtain a blunt end at one end and a blunt end at the other end. EGFP fragment with cohesive ends. After digestion products were subjected to 1% agarose gel electrophoresis, as figure 1 As shown, a small fragment of 750 bp was indeed excised from the pEGFP-C1 vector, which is the EGFP fragment required for the experiment, and then the EGFP fragment was obtained by the method of rubber tapping and recovery.
[0042] B. Construction of neo-EGFP vector
[0043] After the pIRES-neo2 vector is linearized by EcoR V and BamH I, a linearized vector with a blunt end and a cohesive end is...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com