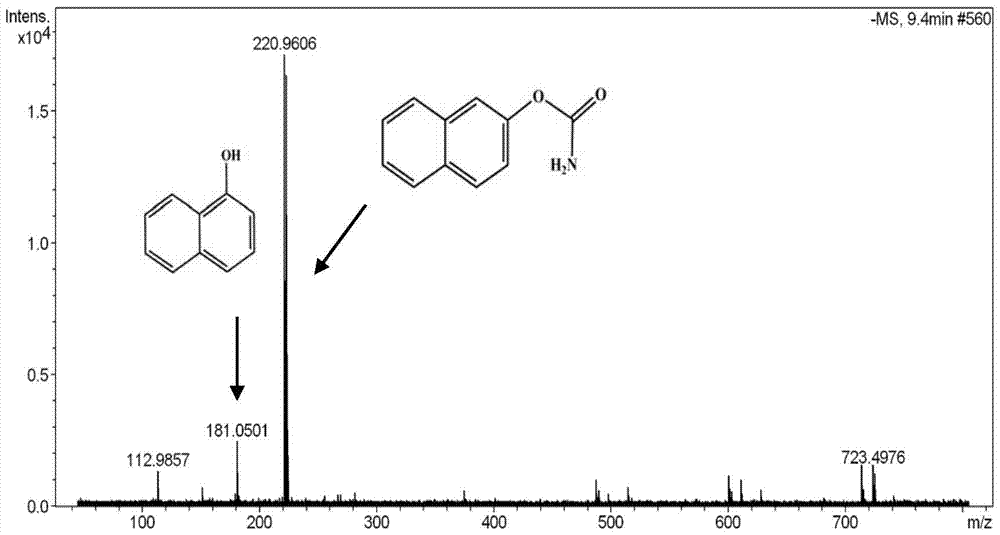
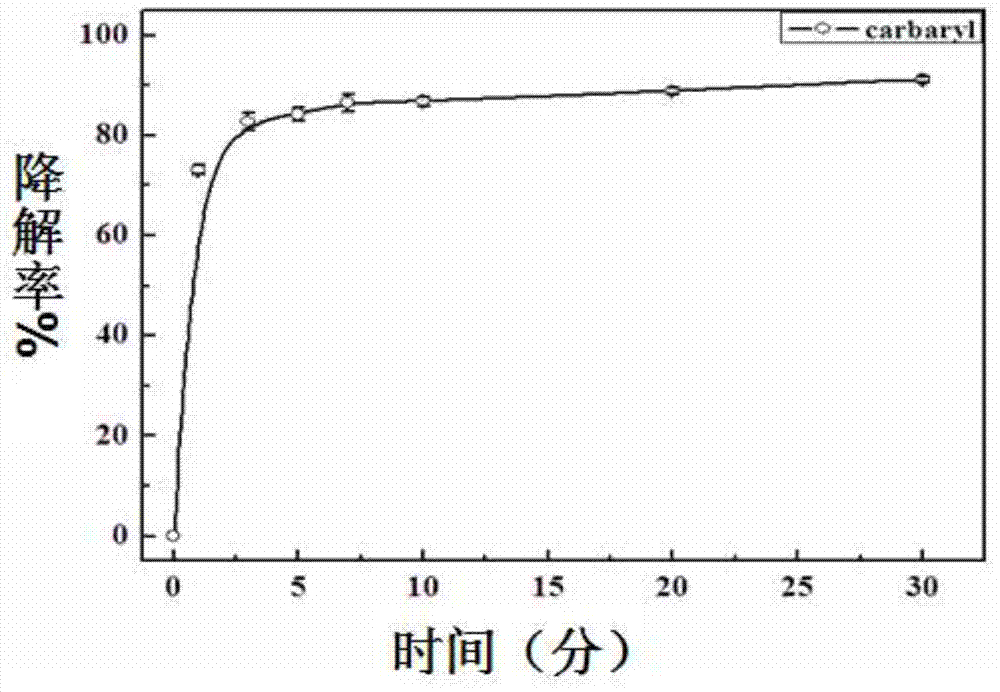
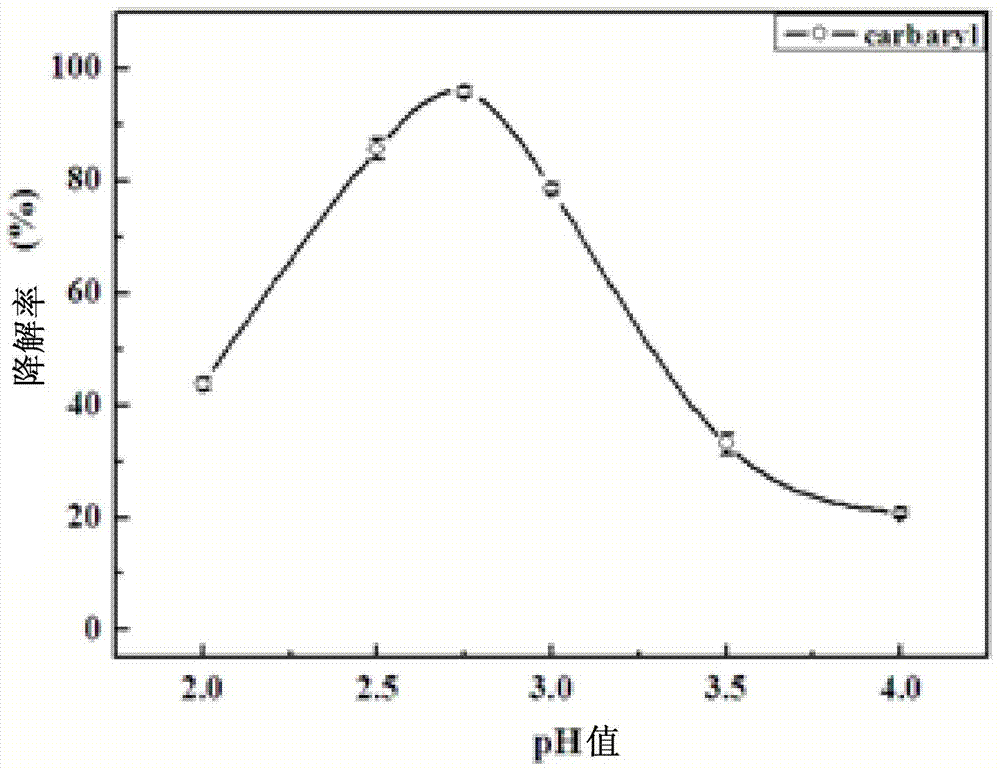
A method for regulating biological enzymes and its degradation of environmental hormone carbaryl by ionic liquid, and a method for determining the degradation rate
A technology of ionic liquids and environmental hormones, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, enzyme stabilization, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of expensive membrane modules, high cost of chemical methods, incomplete treatment, etc., and achieve fast degradation rate , high catalytic efficiency, and the effect of improving the effective utilization rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] (1) Take the pH value as 5.8 and the concentration as 0.1mol L -1 KH 2 PO 4 -K 2 HPO 4 solution, adjusted to a pH 2.75 phosphate buffer solution with hydrochloric acid.
[0034] (2) According to carbaryl and H 2 o 2 The molar ratio of the substance is 1: (9~12), and the initial concentration of 500 μL is 100 μmol L -1 Carbaryl solution, 5 μL initial concentration is 4.8 μmol L -1 Chloroperoxidase solution, 36 μL with an initial concentration of 10mol L -1 Tetramethylammonium bromide solution, and 45-60 μL with an initial concentration of 10 mmol L -1 H 2 o 2 The solution was added to the phosphate buffer solution respectively, and the volume was adjusted to 3mL by the phosphate buffer solution, and mixed evenly to form a reaction system. In the reaction system, the concentration of each substance was as follows: the concentration of chloroperoxidase was 0.008 μmol L -1 , the concentration of tetramethylammonium bromide is 0.12mol L -1 , H 2 o 2 The concent...
Embodiment 2
[0047] (1) Take the pH value as 5.8 and the concentration as 0.1mol L -1 KH 2 PO 4 -K 2 HPO 4 solution, adjusted to a pH value of 2 phosphate buffer solution with hydrochloric acid.
[0048] (2) According to carbaryl and H 2 o 2 The molar ratio of the substance is 1:6, take 500 μL of the initial concentration of 100 μmol L -1 Carbaryl solution, 5 μL with an initial concentration of 30 μmol L -1 Chloroperoxidase solution, 60 μL with an initial concentration of 10mol L -1 Tetramethylammonium bromide solution, and 30 μL with an initial concentration of 10 mmol L -1 H 2 o 2 The solution was added to phosphate buffer solution respectively, and the volume was adjusted to 3mL by phosphate buffer solution, and mixed evenly to form a reaction system. In the reaction system, the concentration of each substance was as follows: the concentration of chloroperoxidase was 0.05 μmol L -1 , the concentration of tetramethylammonium bromide is 0.20mol L -1 , H 2 o 2 The concentrati...
Embodiment 3
[0052] (1) Take the pH value as 5.8 and the concentration as 0.1mol L -1 KH 2 PO 4 -K 2 HPO 4 solution, adjusted with hydrochloric acid to a phosphate buffered solution with a pH of 2.5.
[0053] (2) According to carbaryl and H 2 o 2 The molar ratio of the substance is 1:3, take 500 μL of the initial concentration of 100 μmol L -1 Carbaryl solution, 5 μL initial concentration is 6 μmol L -1 Chloroperoxidase solution, 18 μL with an initial concentration of 10mol L -1 Tetraethylammonium bromide solution, and 15 μL for an initial concentration of 10 mmol L -1 H 2 o 2 The solution was added to the phosphate buffer solution respectively, and the volume was adjusted to 3mL by the phosphate buffer solution, and mixed evenly to form a reaction system. In the reaction system, the concentration of each substance was as follows: the concentration of chloroperoxidase was 0.01 μmol L -1 , the concentration of tetraethylammonium bromide is 0.06mol L -1 , H 2 o 2 The concentrat...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com