Method for recovering rare earth from rare earth fluoride fused salt electrolysis waste with effects of environmental protection and low cost
A rare earth fluoride, molten salt electrolysis technology, applied in the fields of rare earth metal compounds, chemical instruments and methods, inorganic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of high energy consumption required for equipment, very large environmental impact, difficult waste gas collection and treatment, etc., to achieve production The effect of low cost, low requirement for reaction equipment and high rare earth yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
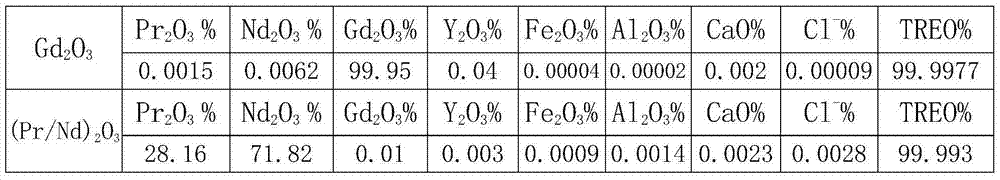
[0024] Take 1000Kg gadolinium electrolytic waste as an example, the sample content and distribution are as follows:
[0025] Gd 2 o 3 %
F%
Y 2 o 3 %
Nd 2 o 3 %
Fe 2 o 3 %
al 2 o 3 %
CaO%
TiO 2 %
MoO 3 %
NaCl%
TREO%
54.42
30.91
0.02
0.12
12.47
0.14
0.45
0.11
0.21
1.14
54.57
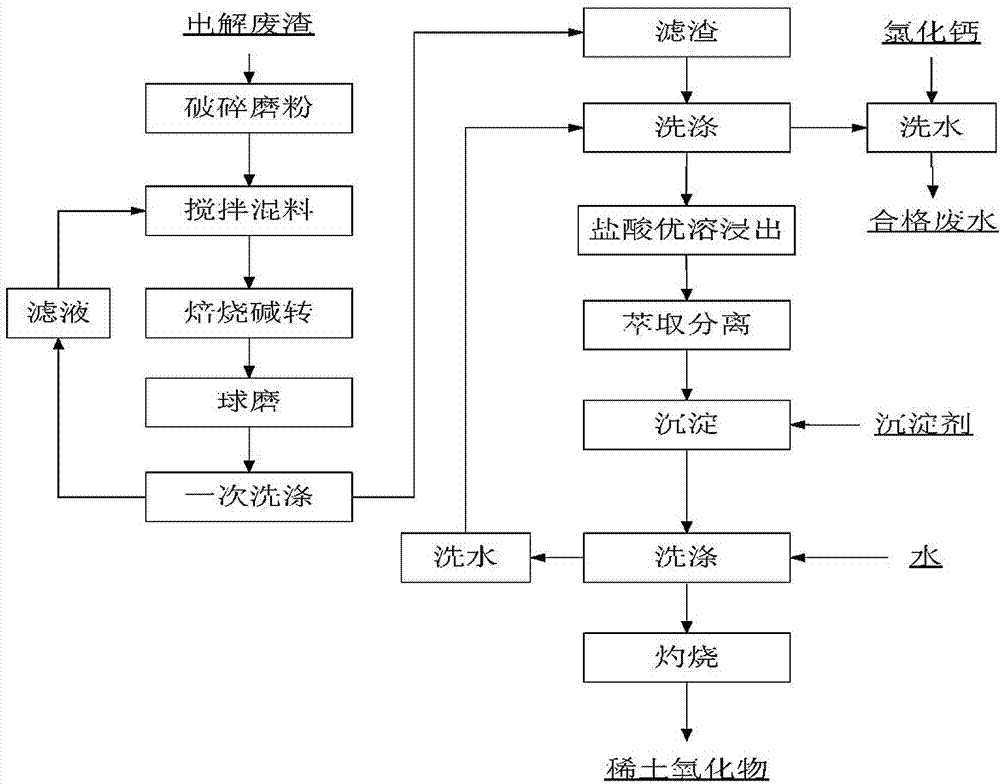
[0026] Step A. Crushing and milling: the raw materials are coarsely broken by a crusher, and the waste molten salt after primary crushing is about 10-20 mesh; then it is ground by a ball mill to more than 200 mesh.
[0027] Step B. stirring and mixing: the raw materials of step A and 620Kg sodium hydroxide are batched and fully mixed.
[0028] Step C. Roasting conversion: put the material in step B into a roasting iron bowl, and enter the tunnel kiln for roasting at 350°C for 4 hours.
[0029] Step D. Ball milling: Put the material in step C into a ball mill and grind it to 200 me...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Taking 1000Kg electrolytic waste as an example, the sample content and distribution are as follows:
[0040] Gd2O 3 %
F%
Y 2 o 3 %
PR 4 o 11 %
Nd 2 o 3 %
Fe 2 o 3 %
al 2 o 3 %
CaO%
TiO 2 %
MoO 3 %
Li 2 O%
Cl%
TREO%
7.78
31.24
0.01
11.7
29.87
2.99
0.46
0.89
0.08
0.36
12.31
2.31
49.36
[0041] Step A. Crushing and milling: the raw materials are coarsely broken by a crusher, and the waste molten salt after primary crushing is about 10-20 mesh; then it is ground by a ball mill to more than 200 mesh.
[0042] Step B. stirring and mixing: the raw material 500Kg of step A is mixed with 220Kg sodium hydroxide and 74.1Kg sodium carbonate batching, fully mixed.
[0043] Step C. Roasting conversion: put the material in step B into a roasting iron bowl, enter the tunnel kiln at 400°C and roast for 6 hours.
[0044] Step D. Ball milling:...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com