Preparation method of cation-type waterborne polyurethane wool anti-felting emulsion
A water-based polyurethane and cationic technology, which is applied in the direction of animal fibers, can solve the problems of not obvious improvement of dry or wet rubbing fastness of fabrics, accelerated yellowing of polyester fabrics, and no explanation of the strength of wool fabrics, etc., to achieve storage stability Excellent performance, adjustable solid content, and the effect of improving bursting strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
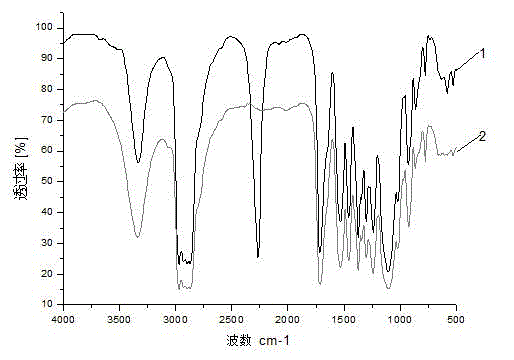
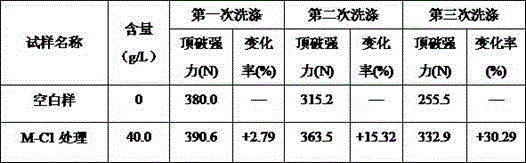
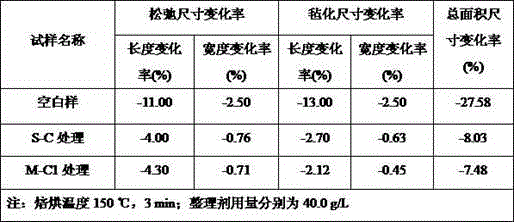
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Put 40.00 g of polypropylene glycol (PPG-2000) in a 500ml three-neck flask, raise the temperature to 110°C, and put it under vacuum (9.99×10 4 Pa) for 2 hours of dehydration, and lower the temperature to 70 °C. Add 20.00 g of isophorone diisocyanate (IPDI) into the reactor and raise the temperature to 80°C, and react for 2-3 hours (add 3-4 drops of catalyst diluted with acetone). When the system reacted for 2 h, the di-n-butylamine method was used to track the titration, and the reaction was stopped when -NCO reached the theoretical value of 8.70%. Cool down to about 50 °C and slowly add 7.00 g of N-methyldiethanolamine (MDEA) dropwise with a separatory funnel, and dilute with an appropriate amount of acetone depending on the viscosity of the system; after 1.5 h, cool down to 5 °C, add 7.00 g of sodium bisulfite ( SHS) reaction for 1.5 h, the capping rate was controlled above 95.0%; continue to heat up to 35 °C, add 4.00 g of glacial acetic acid for neutralization fo...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Put 30.00 g of PPG-2000 in a 500ml three-neck flask, raise the temperature to 110°C, 4 Pa) for 2 hours, then lower the temperature to 70°C. Add 11.00 g of IPDI into the reactor and raise the temperature to 80 °C, react for 2~3 h (drop 3~4 drops of catalyst diluted with acetone), and use the di-n-butylamine method to follow the titration when the system reacts for 2 h , stop this reaction when -NCO reaches the theoretical value of 6.52%. Cool down to about 50°C and slowly add 2.46g of MDEA dropwise with a separatory funnel, and add appropriate amount of acetone to dilute depending on the viscosity of the system. After 1.5 h, the temperature was lowered to 43 °C, and 2.50 g of methyl ethyl ketone oxime (MEKO) was added to react for 1.5 h, and the capping rate was controlled above 98.0%. Continue to add 1.90 g of glacial acetic acid for neutralization for 0.5 h, and then add 110 ml of deionized water to maintain the neutralization degree at 90~110%; use a rotation speed...
Embodiment 3
[0032] Put 45.00g of PPG-2000 in a 500ml three-neck flask, raise the temperature to 110°C, and under vacuum (9.99×10 4 Pa) for 2 hours, then lower the temperature to 70°C. Add 16.50 g of IPDI to the reactor and raise the temperature to 80 °C, react for 2~3 h (drop 3~4 drops of catalyst diluted with acetone), wherein, when the system reacts for 2 h, use the di-n-butylamine method to follow the titration , Stop this reaction when -NCO reaches the theoretical value of 6.63%. Cool down to about 50°C, slowly add 3.74 g of MDEA dropwise with a separatory funnel, and add appropriate amount of acetone to dilute depending on the viscosity of the system. After 1.5 h, the temperature was lowered to 43°C, and 4.00 g of MEKO was added to react for 1.5 h, and the capping rate was controlled above 98.0%. Then, 2.80 g of glacial acetic acid was added for neutralization for 0.5 h, and then 150 ml of deionized water was added to keep the neutralization degree at 90~110%; shear and emulsify...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com