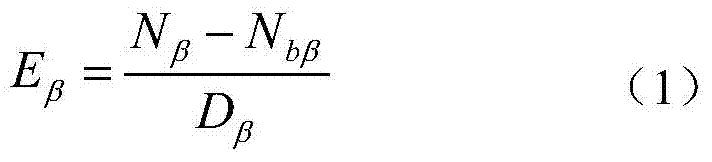A method for determining the activity concentration of potassium-removed total beta radionuclides in seawater
A technology of β radioactivity and nuclide activity, which is applied in the field of radioactive element detection, can solve the problem that the calibration source cannot be truly reflected, and achieve the effect of moderate quality and uniform precipitation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
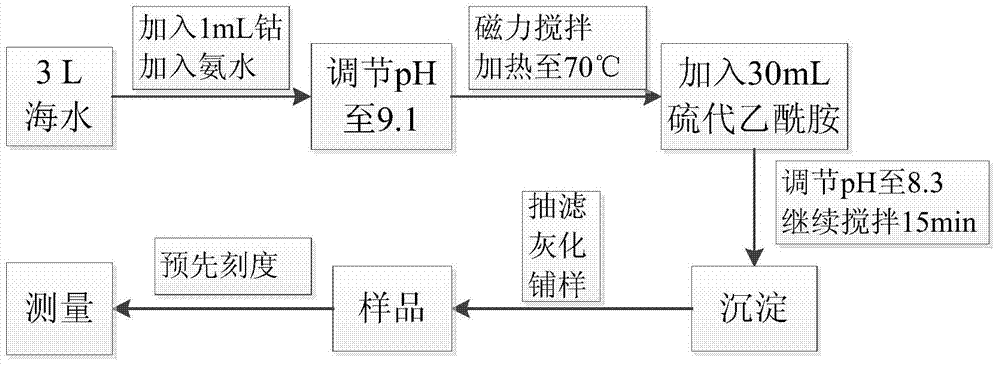
[0021] This embodiment provides a method for determining the activity concentration of total beta radionuclides in seawater, specifically:
[0022] Take 3.0L seawater, and add cobalt nitrate to it, add ammonia water to adjust the pH value of the solution to about 9.1; stir and heat to 70°C; add 30mL thioacetamide solution (40g / L), then add ammonia water to adjust the pH value of the solution Adjust to 8.3, continue to stir for 15min; place overnight (more than 10h), after the precipitation is coagulated, siphon off the supernatant, and filter the remaining part under vacuum with a filter membrane; put the cobalt sulfide precipitate and the filter membrane in a muffle furnace , burn at 700°C for 2 hours;
[0023] Weigh the cobalt sulfide precipitate, take out 110mg sample, grind it finely in a mortar, transfer it to a stainless steel measuring pan with constant weight, add ethanol dropwise, and spread the sample evenly;
[0024] If the gas flow proportional counter is used for...
experiment example 1
[0034] A certain amount of Co containing 2+ , Fe 3+ , Zn 2+ 、Ag + solution, the experiment adopts the precipitation method in Example 1 to process 1L, 2L and 3L seawater samples, and adopts an atomic absorption spectrophotometer to measure the Co 2+ , Fe 3+ , Zn 2+ 、Ag + content, the calculated enrichment efficiency is shown in Table 1. As can be seen from Table 1, the analysis method of co-precipitation of cobalt sulfide is very effective for Co 2+ , Fe 3+ , Zn 2+ 、Ag + The enrichment efficiencies were all higher than 95%. Therefore, the method of the present invention can be used to enrich the Co in seawater sample 2+ , Fe 3+ , Zn 2+ 、Ag + .
[0035] Table 1 Measurement results of metal ion enrichment efficiency in seawater samples
[0036]
[0037]
experiment example 2
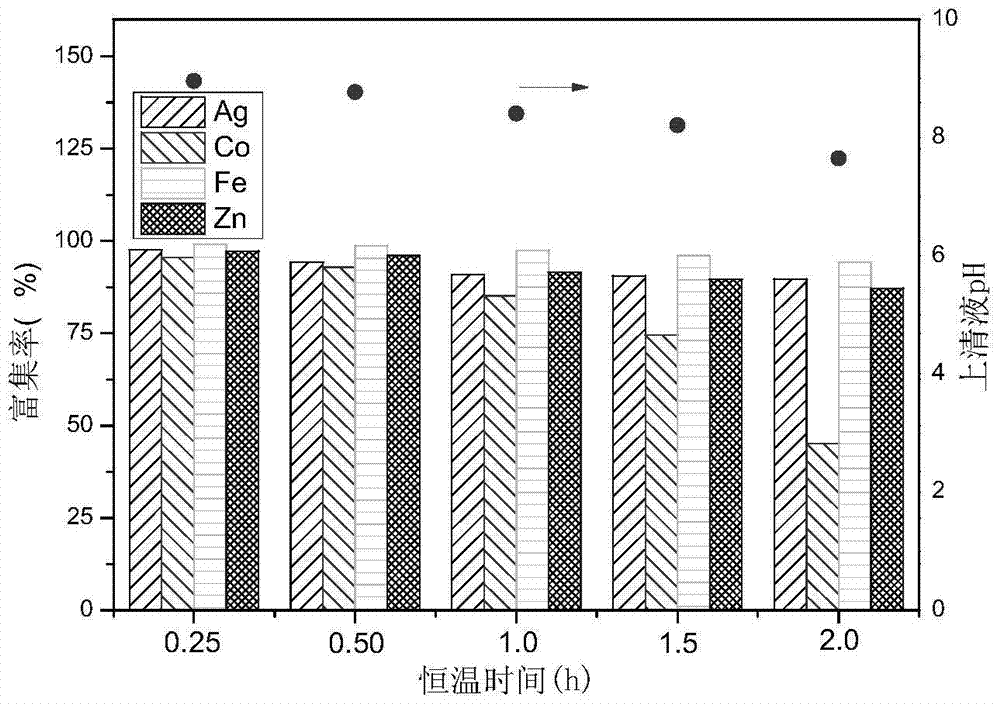
[0039] Example 1 After adding excess thioacetamide, adjust the pH of the cobalt ion solution to 8.3 with ammonia water, and then continue stirring at constant temperature for 15 minutes. In this experimental example, the constant temperature time was compared, specifically: take 5 parts of 1L seawater samples, add the same amount of Co 2+ , Fe 3+ , Zn 2+ 、Ag + The solution was treated by the precipitation method in Example 1, and the constant temperature time was set to 0.25h, 0.5h, 1.0h, 1.5h, and 2.0h, respectively. After the precipitation, the solution was placed overnight (more than 10 h), and the Co in the supernatant was measured by an atomic absorption spectrophotometer after the precipitation was coagulated. 2+ , Fe 3+ , Zn 2+ 、Ag + content, the calculated enrichment efficiency see figure 2 . From figure 2 It can be seen that the constant temperature of 0.25h has the best effect; as the reaction time prolongs, the pH of the solution decreases, making the Co ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com