Microbiological method for detecting heavy-metal cadmium in water body
A water body and wild-type technology, applied to the construction of Escherichia coli, established in the field of detection of heavy metal cadmium in the water environment, can solve the problems of engineering strains without literature reports, achieve reliable results, reduce background values, good repeatability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
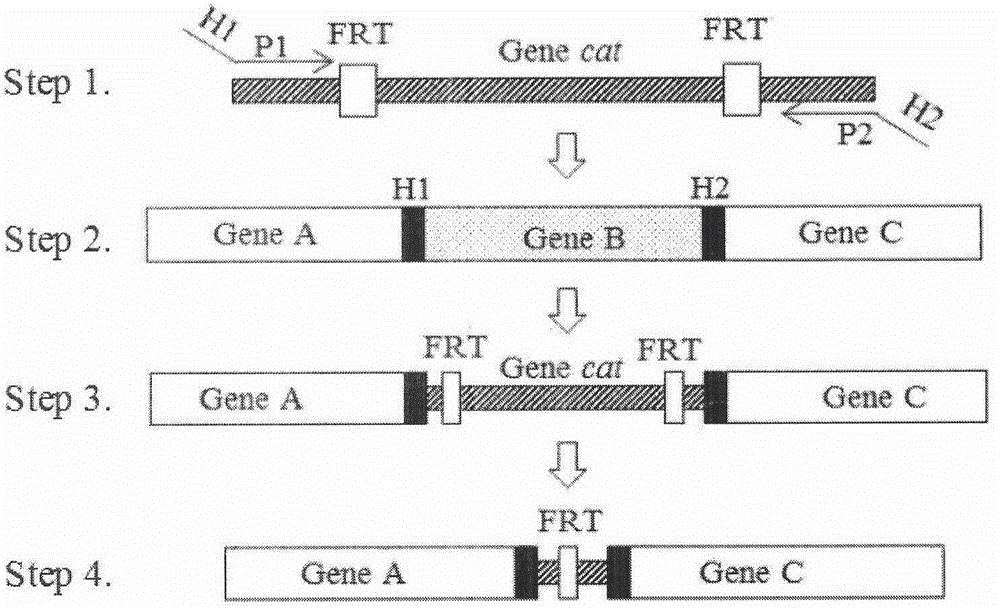
[0067] Embodiment 1. Preparation of mutant bacteria
[0068] 1. Primer information and synthesis
[0069] Gene knockout primers: According to the gene knockout primer sequence provided by http: / / ecogene.org / , Primer5.0 and DNAMAN software, design homologous recombination primers, see Table 1, the 5' end is the homology on both sides of the cat gene For the arm, see the ununderlined part in Table 1, and the 3' end is used to amplify the chloramphenicol resistance gene, see the underlined part in Table 1. Upstream homology arm primer zntA-Nf, sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.6 and zntR-Nf, sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.8; downstream homology arm primer zntA-Cr, sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.7 Shown and zntR-Cr, the sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.9.
[0070] Gene knockout identification primers: use a pair spanning the gene to be knocked out provided by Harvard Molecular Technology Group & Lipper Center for Computational Genetics website http: / / arep.med.harvard.edu / labgc / adnan / ...
Embodiment 2
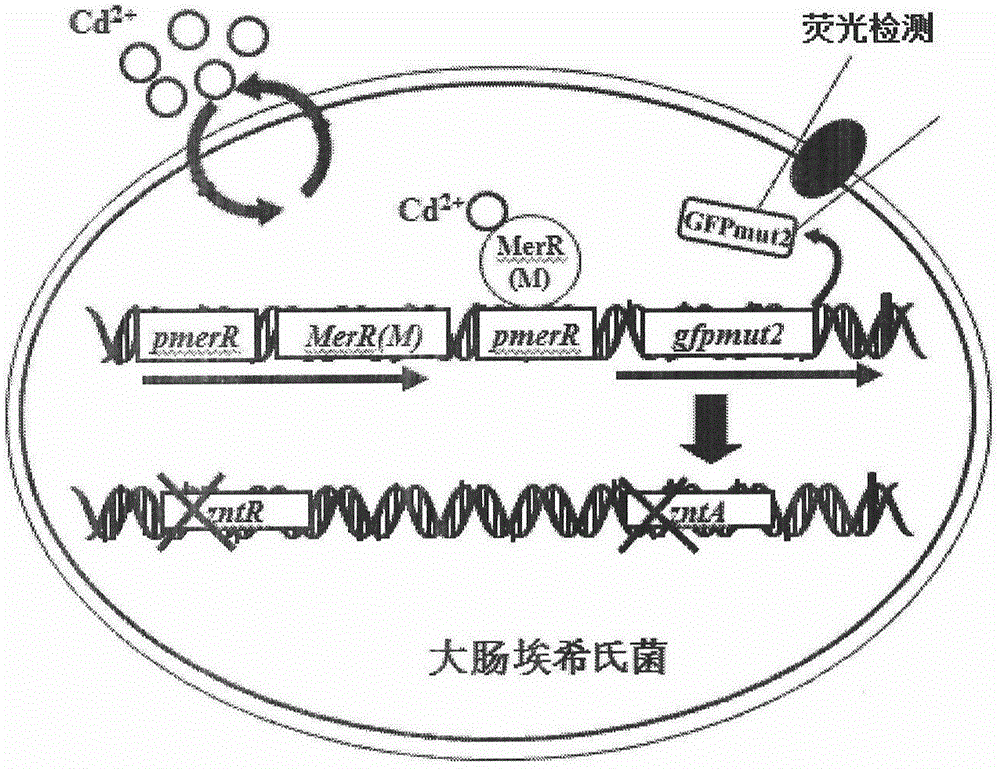
[0117] Embodiment 2. Construction of fusion reporter gene pmerR-MerR(M)-pmerR-gfpmut2
[0118] 1. Primer information and synthesis
[0119] According to the target gene pmerR and MerR(M) sequences published by GenBank and the known gfpmut2 gene sequence, use the Primer5.0 software to design primers, see Table 7, some primers introduce restriction sites at the 5' end or 3' end of the gene , design the primer Pmer-MerR-m-F for amplifying pmerR-MerR (M), the sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.20 and Pmer-MerR-m-R, the sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.21, amplify the pmerR-gfpmut2 gene The primer Pmer-GFPmut2-F sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.22 and the GFPmut2-R sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.23, and the final fusion fragment is connected to the identification primer M13F of the plasmid vector pMD19-T, and the sequence is shown in SEQ ID As shown in NO.24 and M13R, the sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.25. See Table 7 for specific information, and the primers were synthesized by Invitrog...
Embodiment 3
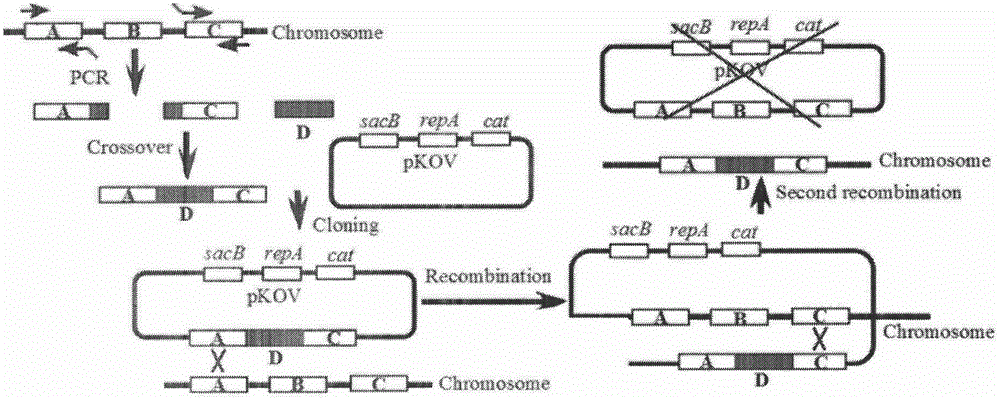
[0158] Example 3. Gene knock-in
[0159] 1. Primer information and synthesis
[0160] Use Primer5.0 software to design primers, see Table 14, design pmerR-MerR(M)-pmerR-gfpmut2 gene N-terminal and C-terminal inner primers, P 2 : zntR-cd-Ni, sequence as shown in SEQ ID N0.15 and P 5 : zntR-cd-gfpmut2-Ci, the sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.16 and the outer primer, P 1 : zntR-No, the sequence is shown in SEQ ID N0.14 and P 6 : zntR-Co, the sequence is as shown in SEQ ID N0.17, making P 2 : zntR-cd-Ni with P 3 : pmerR-MerR(M)-pmerR-gfpmut2-F, the sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.18, P 4 : pmerR-MerR(M)-pmerR-gfpmut2-R, the sequence is shown in SEQ ID N0.19, and P s : There is a complementary sequence between zmR-cd-gfpmut2-Ci, the gene knockout two outer primers are unchanged, P 3 with P 4 A pair of gene primers for amplifying pmerR-MerR(M)-pmerR-gfpmut2, P 7 : pkov-SalI, sequence as shown in SEQ ID N0.28 and P 8 : pkov-NotI, the sequence is as shown in SEQ ID No. 29, whic...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com