Cosmetic additive and cosmetic containing same
A technology for cosmetics and additives, which is applied in the field of cosmetic additives containing polyols and cosmetics containing the additives for cosmetics, which can solve the problems of impaired dispersion, separation of cosmetics, and low heat resistance. Achieve excellent usability, suppress stickiness, and excellent heat resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
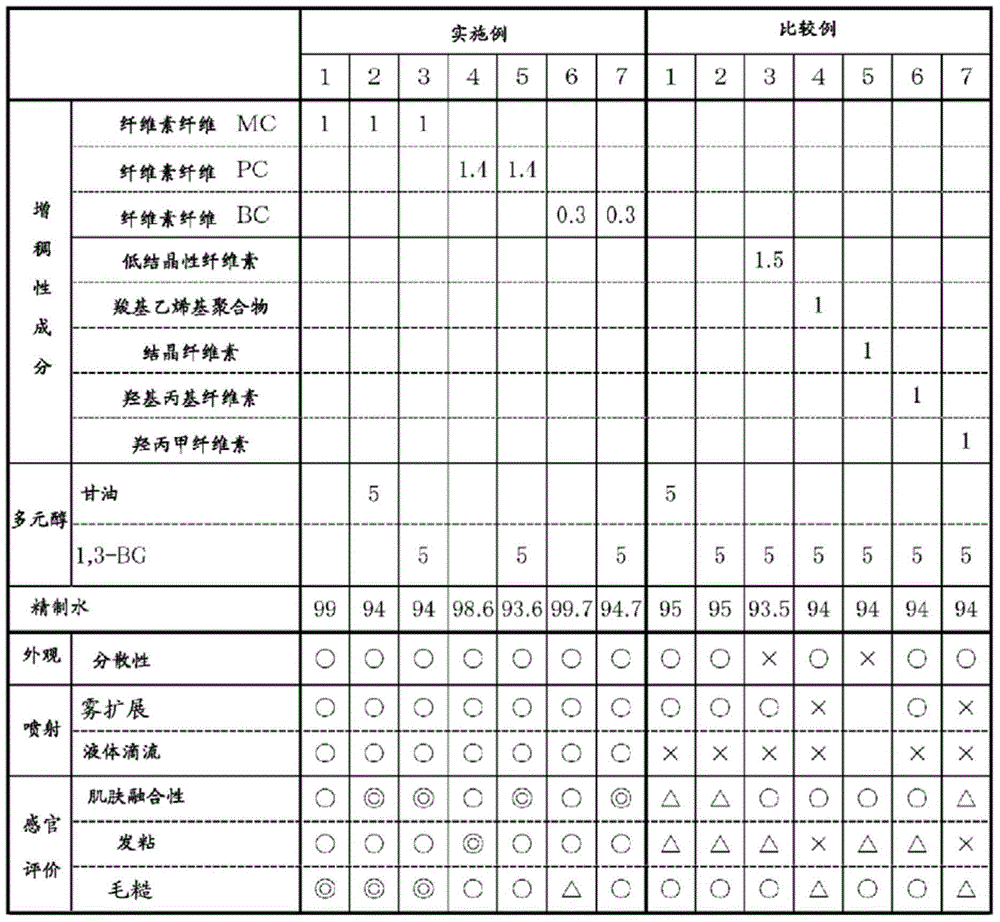
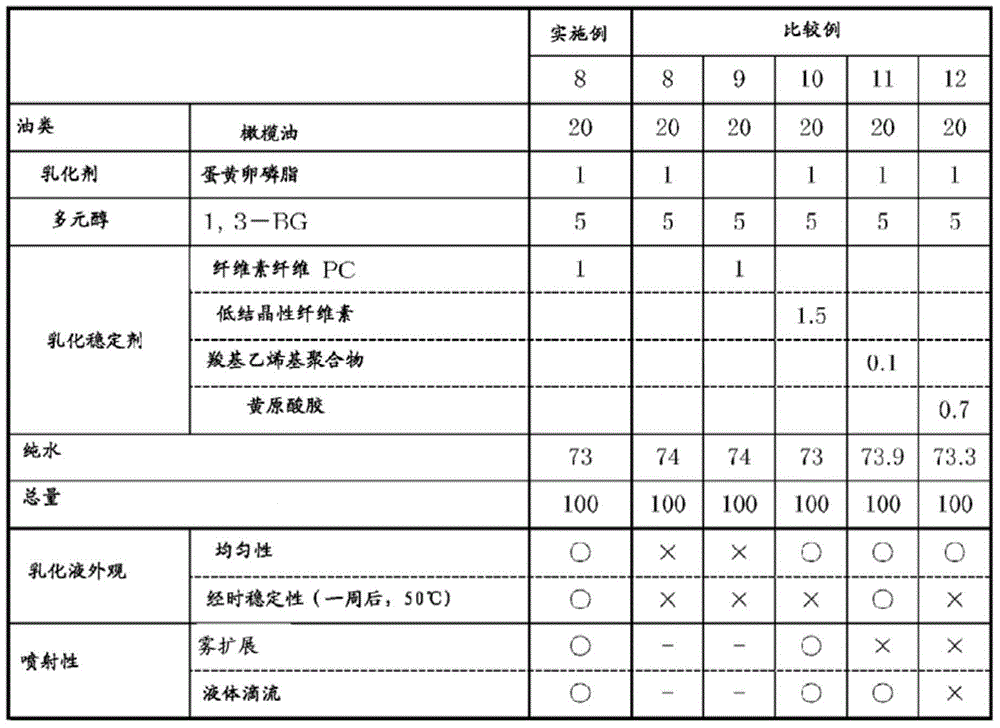
Examples
Embodiment
[0086] Hereinafter, the characteristics of the present invention will be described more specifically with reference to Examples and Comparative Examples. Materials, usage amounts, ratios, processing contents, and processing procedures shown in the following examples can be appropriately changed without departing from the gist of the present invention. Therefore, the scope of the present invention should not be limitedly interpreted by the specific examples shown below.
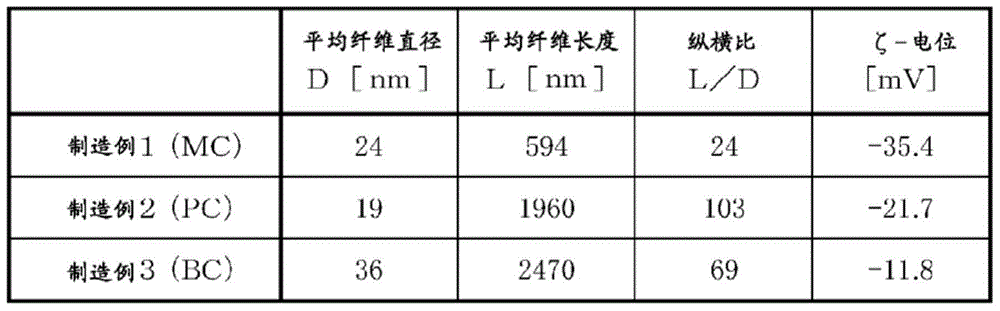
[0087] [Measurement of average fiber diameter D and average fiber length L]
[0088] The average fiber diameter D and the average fiber length L of the cellulose fibers obtained by the following production examples 1 to 3 were obtained from the TEM images and SEM images according to the procedure described in the third paragraph of the above page 7, and from these values Find the aspect ratio L / D.
[0089] [Measurement of ζ-potential]
[0090] The dispersion liquids of Production Examples 1 to 3 described b...
manufacture example 1
[0091] [Production Example 1: Production of Microcrystalline Cellulose-derived Cellulose Fiber]
[0092] After adding 1,000 parts by mass of pure water to 15 parts by mass of commercially available microcrystalline cellulose (Funcel powder II for column chromatography manufactured by Funakoshi Co., Ltd.) to disperse it, use a high-pressure pulverizer (starburst system) manufactured by Suginomasin Co., Ltd., The pulverization treatment was performed 300 times at 200 MPa to obtain an aqueous dispersion (MC) of cellulose fibers derived from microcrystalline cellulose. The obtained dispersion liquid was measured in a Petri dish, dried at 110° C. for 5 hours, and the water was removed to measure the amount of residue and measure the concentration. As a result, the cellulose concentration (solid content concentration) in water was 1.2% by mass.
manufacture example 2
[0093] [Manufacture Example 2: Manufacture of pulp-derived cellulose fiber]
[0094] After adding 478.3 parts by mass of pure water to 21.7 parts by mass of commercially available kraft pulp (LBKP D-8 manufactured by International Paper Palpu Trading Co., Ltd., solid content 46% by mass) to disperse it, it was pulverized by high pressure using Suginomasin Co., Ltd. The device (starburst system) performed 280 pulverization treatments at 245 MPa to obtain an aqueous dispersion (PC) of pulp-derived cellulose fibers. The obtained dispersion liquid was measured in a Petri dish, dried at 110° C. for 5 hours, and the water was removed to measure the amount of residue and measure the concentration. As a result, the cellulose concentration (solid content concentration) in water was 1.5% by mass.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com