Anti-Mycoplasma bovis and Pasteurella fusion protein md‑UF1‑Md‑AP2
A fusion protein, md-uf1-md-ap2 technology, applied in the direction of DNA / RNA fragments, antibacterial drugs, peptide / protein components, etc., can solve the problems of difficult control and treatment, concurrent infection, and aggravated antibiotic residues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Example 1 Construction of a suppressive subtractive library after induction of housefly larvae by Salmonella and screening of the protein gene against Pasteurella multocida type A from bovine capsular serum
[0029] 1. The source of the induced strain
[0030] The inducer Salmonella chicken origin was isolated from poultry clinically suffering from salmonellosis, and the isolated bacteria were identified by S.S medium and molecular biology methods, and the results proved that it was Salmonella.
[0031] 2. Construction of a suppressive subtraction library after induction of housefly larvae by Salmonella gallinarum
[0032] Select 2 and 3 day-old houseflies ( Musca domestica L. ) larvae (the species is blowfly, the fly eggs were purchased from the Liaoyuan Ecological Breeding Factory in Jilin Province, and incubated by the Pharmacology and Toxicology Laboratory of Jilin Agricultural University). Dip the No. 2 insect needle into the Salmonella gallinarum solution (conc...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Example 2 Construction of a suppressive subtractive library after induction of housefly larvae by Mycoplasma pneumoniae and screening of anti-Mycoplasma bovis protein genes
[0036] 1. Isolation and identification of the induced strain Mycoplasma pneumoniae
[0037] The lung lesions of pigs suffering from pneumonia were collected, isolated and cultured according to the procedure of mycoplasma isolation and culture, colony morphology was observed, and the isolated bacteria were identified by molecular biology methods. The results showed that the colonies of isolated bacteria were observed under a 40 times ordinary optical microscope. The morphology has the typical characteristics of "fried egg", which preliminarily proves that the isolated bacteria are mycoplasma.
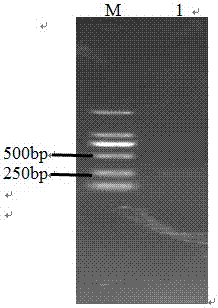
[0038]The Mycoplasma pneumoniae 16S rRNA full-length primer was used to identify it (see Table 1), and a fragment of about 1.5 kb was amplified, which was in line with the expected fragment size. After the ge...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Example 3 Fusion gene against Mycoplasma bovis, bovine capsular serum type A Pasteurella multocida Md -UF1- Md -Clone of AP2
[0046] 1. Use the kit (SV Total RNA Isolation) produced by Promega to extract the total RNA of three-day-old housefly larvae induced by Mycoplasma bovis and Salmonella gallinarum respectively, and use the kit produced by TaKaRa Oligotex TM -dT30 mRNA Purification Kit (From Total RNA) isolates and purifies mRNA;
[0047] 2. Reverse transcription to synthesize the first strand of cDNA
[0048] (1) Take two EP tubes and add the following reagents respectively, see Table 1:
[0049] Table 1 Reaction system
[0050]
[0051] (2) Mix by blowing and blowing, centrifuge briefly, incubate in a PCR machine at 72°C for 3 minutes, then at 42°C for 2 minutes, then centrifuge briefly, add the following reagents, see Table 2: Reaction System
[0052]
[0053] (4) Mix well, centrifuge briefly, and incubate in a PCR instrument at ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com