Plant allelopathy inhibitor for controlling Gansu pedicularis
A plant allelopathic and inhibitor technology, applied in the direction of chemicals for biological control, plant growth regulators, plant growth regulators, etc., can solve the problems that have not yet been achieved, and achieve simple results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
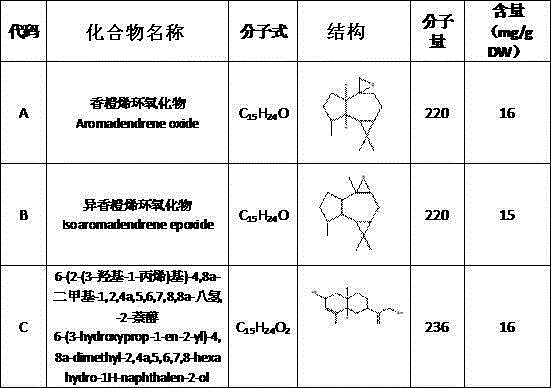
[0024] A phytoallelopathy inhibitor for the control of Artemisia gansuensis, including the epoxides of orangerene.
[0025] The orangerene epoxide is prepared by the following method, comprising the following steps:
[0026] (1) Obtaining the organic solvent extraction solution of allelochemical substances: Wash and crush the Artemisia arvensis donor material into 1-4mm, weigh 20g quantitatively, soak in 200ml of petroleum ether and ethyl acetate for 48 hours, every 12 hours Shake for 15 minutes, filter to obtain an organic solvent extract, and store at 4°C for future use. Obtain the extract for later use.
[0027] (2) Selection and packing of chromatographic column: adopt conventional method and dry column packing. Apply pressure to the bottom of the silica gel column to increase the flow rate of the eluent until the eluent flows out.
[0028] (3) Separation by column chromatography: mix the sample with silica gel, put 15ml of the solution to be tested into a round bottom ...
Embodiment 2
[0030] A phytoallelopathy inhibitor for the control of Artemisia gansuensis, including isoarrenene epoxides.
[0031] Isoarrenene epoxides are prepared by the following method, comprising the following steps:
[0032] (1) Obtaining the organic solvent extract of allelochemical substances: Wash and crush the Artemisia annua donor material into 1-4mm, weigh 20g quantitatively, soak in 200ml of petroleum ether and ethyl acetate for 48 hours, every 12 hours Shake for 15 minutes, filter to obtain an organic solvent extract, and store at 4°C for future use. Obtain the extract for later use.
[0033] (2) Selection and packing of chromatographic column: adopt conventional method and dry column packing. Apply pressure to the bottom of the silica gel column to increase the flow rate of the eluent until the eluent flows out.
[0034] (3) Separation by column chromatography: mix the sample with silica gel, put 15ml of the solution to be tested into a round bottom flask, add a small amo...
Embodiment 3
[0036] A plant allelopathic inhibitor for the control of Artemisia gansuensis, including 6-(2-(3-hydroxy-1-propenyl)yl)-4,8a-dimethyl-1,2,4a,5,6,7, 8,8a-Octahydro-2-naphthol.
[0037] 6-(2-(3-Hydroxy-1-propenyl)yl)-4,8a-dimethyl-1,2,4a,5,6,7,8,8a-octahydro-2-naphthol by following Method preparation comprises the following steps:
[0038] (1) Obtaining the organic solvent extraction solution of allelochemical substances: wash and grind Artemisia annua donor material into 1-4mm, weigh 20g quantitatively, soak in 200ml of petroleum ether and ethyl acetate for 48 hours, every 12 Shake for 15 minutes, filter to obtain an organic solvent extract, and store at 4°C for later use. Obtain the extract for later use.
[0039] (2) Selection and packing of chromatographic column: adopt conventional method and dry column packing. Apply pressure to the bottom of the silica gel column to increase the flow rate of the eluent until the eluent flows out.
[0040] (3) Separation by column chrom...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com