Method for separating iron, zinc and carbon in blast furnace sludge
A technology of blast furnace gas mud and gas mud, applied in the direction of process efficiency improvement, recycling technology, etc., can solve problems such as unconsidered zinc recovery, unknown effect, etc., achieve good magnetic separation effect, high comprehensive utilization rate of resources, energy The effect of low consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
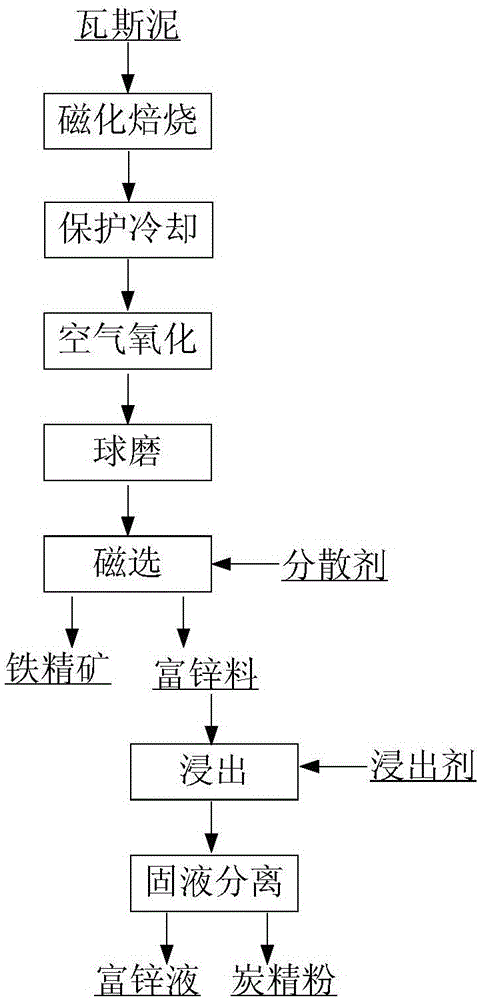
[0045] Example 1: In the laboratory, the gas mud was placed in a muffle furnace for 100 min at 600°C to convert iron oxide into magnetite; the obtained calcined sand was placed in an iron tank protected by nitrogen gas, and a thermoelectric Cool it to about 390°C, put it in the air and cool it to room temperature, so that the magnetite is transformed into pseudohematite; the obtained calcined sand has a finer particle size and lower hardness, and it is wet-milled in a ball mill for 7 minutes, and the particle size is less than 0.074mm. More than 85%; according to the mass fraction, add about 1% alcohol for magnetic separation, and the magnetic field strength is 0.1T, to obtain iron concentrate and zinc-rich material; Leach at ℃ for 4 hours, and filter to obtain zinc-enriched liquid and fine carbon powder. The obtained iron concentrate contains 43.6% iron, 6.7% zinc, 0.8% carbon, and an iron recovery rate of 75.6%; the zinc content of the zinc-enriched liquid is 72.6g / L, and th...
Embodiment 2
[0046]Example 2: Put the gas mud described in Table 1 in a muffle furnace for 80 minutes at 700°C, place the obtained calcined sand in an iron tank protected by nitrogen, and insert a thermocouple to cool it to about 400°C. Cool in the air to room temperature; then use a wet ball mill to grind the ore for 12 minutes, add about 0.5% water glass according to the mass fraction for magnetic separation, and the magnetic field strength is 0.2T to obtain iron concentrate and zinc-rich material; the obtained zinc-rich material is mixed with 15% ammonium chloride was leached at room temperature for 4 hours at a liquid-to-solid ratio of 3:1, and then filtered to obtain zinc-enriched liquid and fine carbon powder. The obtained iron concentrate contains 49.1% iron, 5.0% zinc, 0.6% carbon, and an iron recovery rate of 80.1%; the zinc content of the zinc-enriched liquid is 71.3g / L, and the zinc recovery rate is 72.2%; 5.9% iron, 2.8% zinc, 79.4% carbon recovery.
Embodiment 3
[0047] Example 3: Put the gas mud described in Table 1 in a muffle furnace and reduce it for 60 minutes at 800°C, place the obtained calcine in an iron tank with nitrogen protection, insert a thermocouple to cool to about 420°C, and place Cool in the air to room temperature; then use a wet ball mill to grind the ore for 15 minutes, add about 1% glycerin according to the mass fraction for magnetic separation, and the magnetic field strength is 0.3T to obtain iron concentrate and zinc-rich material; the obtained zinc-rich material is mixed with 15 % ammonia water was leached at 50°C for 4 hours at a liquid-solid ratio of 3:1, and filtered to obtain zinc-enriched liquid and fine carbon powder. The obtained iron concentrate contains 45.4% iron, 5.6% zinc, 0.6% carbon, and an iron recovery rate of 78.9%; the zinc content of the zinc-enriched liquid is 81.3g / L, and the zinc recovery rate is 78.5%; 6.1% iron, 1.4% zinc, 70.5% carbon recovery.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com