A method for recovering valuable metals from electronic waste
An electronic waste and valuable metal technology, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, can solve the problems of difficult to meet industrial production, low recovery rate of valuable metals, and lower overall yield, etc., and achieve low production costs and valuable metals. The effect of high recovery rate and high recovery rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
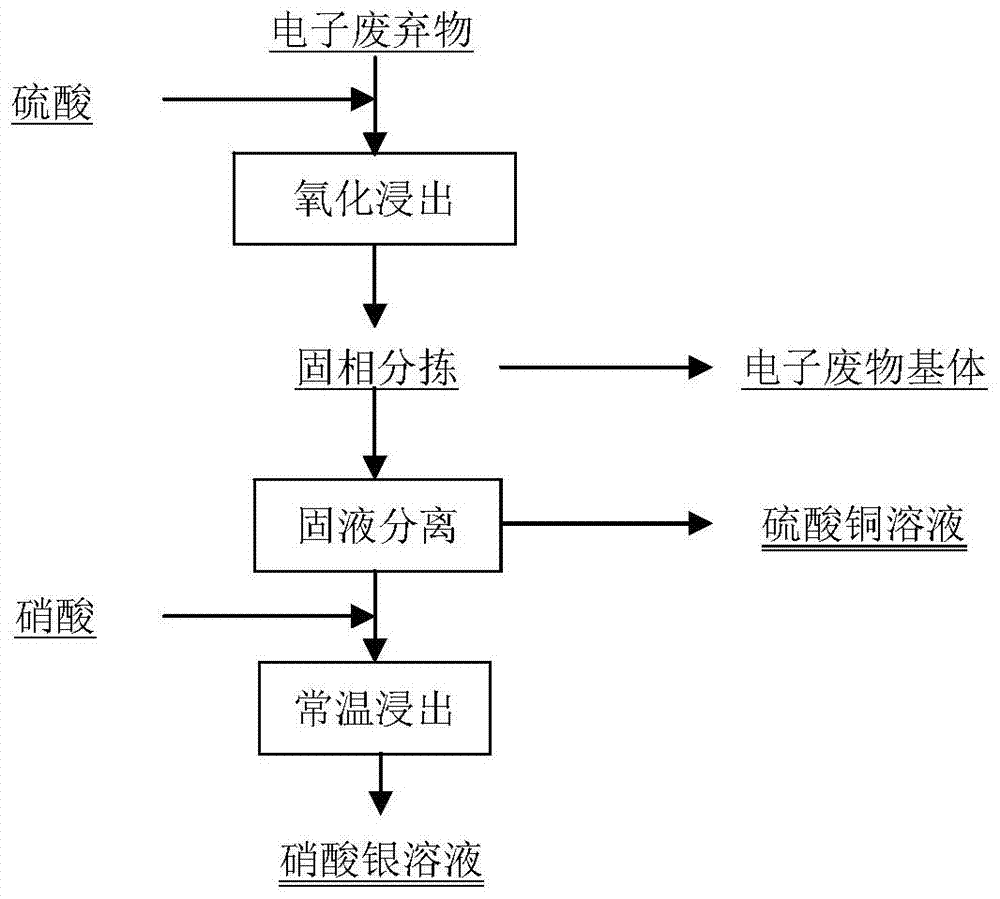
[0033] The method for recovering valuable metals from electronic waste in this embodiment, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0034] 1) Put 500g of copper-silver-containing electronic waste into a 2L container, prepare 500ml of sulfuric acid with a mass concentration of 40%, and add it to the container to ensure that the sulfuric acid is completely immersed in the electronic waste to obtain mixture A;
[0035] 2) After raising the temperature of the mixture A obtained in step 1) to 60°C, use an ozone generator to generate ozone and pass it in from the bottom of the mixed solution A for reaction, while stirring at 100rpm to ensure that the ozone is evenly dispersed in the system, and the amount of ozone introduced is 1L / h (that is, the amount of ozone per 1kg of electronic waste is 2L / h), and the reaction time is 4h; after the reaction, stop feeding ozone to obtain mixture B;
[0036] 3) Use a 10-mesh filter to separate the electronic waste matrix (organ...
Embodiment 2
[0039] The method for recovering valuable metals from electronic waste in this embodiment, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0040] 1) Put 500g of electronic waste into a 2L container, prepare 500ml of sulfuric acid with a mass concentration of 50%, and add it into the container to ensure that the sulfuric acid is completely submerged in the electronic waste to obtain mixture A;
[0041] 2) After raising the temperature of the mixture A obtained in step 1) to 50°C, use an ozone generator to generate ozone from the bottom of the mixture A for reaction, and stir at 200rpm to ensure that the ozone is evenly dispersed in the system, and the amount of ozone introduced is 1L / h (that is, the amount of ozone per 1kg of electronic waste is 2L / h), and the reaction time is 3h; after the reaction, stop feeding ozone to obtain mixture B;
[0042] 3) Use a 15-mesh filter to separate the electronic waste matrix (organic polymer material matrix) in the mixture B obtai...
Embodiment 3
[0045] The method for recovering valuable metals from electronic waste in this embodiment, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0046] 1) Put 500g of electronic waste into a 2L container, prepare 500ml of sulfuric acid with a mass concentration of 60%, and add it into the container to ensure that the sulfuric acid is completely immersed in the electronic waste to obtain mixture A;
[0047] 2) After raising the temperature of the mixture A obtained in step 1) to 40°C, use an ozone generator to generate ozone from the bottom of the mixture A for reaction, while stirring at 300rpm to ensure that the ozone is evenly dispersed in the system, and the amount of ozone introduced is 1L / h (that is, the amount of ozone per 1kg of electronic waste is 2L / h), and the reaction time is 2h; after the reaction, stop feeding ozone to obtain mixture B;
[0048] 3) Use a 20-mesh filter to separate the electronic waste matrix (organic polymer material matrix) in the mixture B ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com